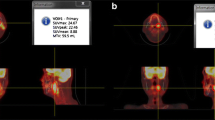
Abstract
Purpose
The question as to whether the regional textural features extracted from PET images predict prognosis in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) remains open. In this study, we investigated the prognostic impact of regional heterogeneity in patients with T3/T4 OPSCC.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the records of 88 patients with T3 or T4 OPSCC who had completed primary therapy. Progression-free survival (PFS) and disease-specific survival (DSS) were the main outcome measures. In an exploratory analysis, a standardized uptake value of 2.5 (SUV 2.5) was taken as the cut-off value for the detection of tumour boundaries. A fixed threshold at 42 % of the maximum SUV (SUVmax 42 %) and an adaptive threshold method were then used for validation. Regional textural features were extracted from pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT images using the grey-level run length encoding method and grey-level size zone matrix. The prognostic significance of PET textural features was examined using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and Cox regression analysis.
Results
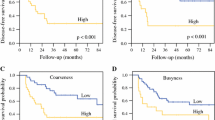
Zone-size nonuniformity (ZSNU) was identified as an independent predictor of PFS and DSS. Its prognostic impact was confirmed using both the SUVmax 42 % and the adaptive threshold segmentation methods. Based on (1) total lesion glycolysis, (2) uniformity (a local scale texture parameter), and (3) ZSNU, we devised a prognostic stratification system that allowed the identification of four distinct risk groups. The model combining the three prognostic parameters showed a higher predictive value than each variable alone.
Conclusion
ZSNU is an independent predictor of outcome in patients with advanced T-stage OPSCC, and may improve their prognostic stratification.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Applebaum KM, Furniss CS, Zeka A, Posner MR, Smith JF, Bryan J, et al. Lack of association of alcohol and tobacco with HPV16-associated head and neck cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:1801–10.
Bouvard V, Baan RSK, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, et al. A review of human carcinogens - Part B: biological agents. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:321–2.
Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, Weber R, Rosenthal DI, Nguyen-Tân PF, et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:24–35.
Fakhry C, Westra WH, Li S, Cmelak A, Ridge JA, Pinto H, et al. Improved survival of patients with human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in a prospective clinical trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:261–9.
Sedaghat AR, Zhang Z, Begum S, Palermo R, Best S, Ulmer KM, et al. Prognostic significance of human papillomavirus in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Laryngoscope. 2009;119:1542–9.
Wu Y, Posner MR, Schumaker LM, Nikitakis N, Goloubeva O, Tan M, et al. Novel biomarker panel predicts prognosis in human papillomavirus-negative oropharyngeal cancer: an analysis of the TAX 324 trial. Cancer. 2011;118:1811–7.
Granata R, Miceli R, Orlandi E, Perrone F, Cortelazzi B, Franceschini M, et al. Tumor stage, human papillomavirus and smoking status affect the survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer: an Italian validation study. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:1832–7.
Cheng NM, Chang JT, Huang CG, Tsan DL, Ng SH, Wang HM, et al. Prognostic value of pretreatment (18)F-FDG PET/CT and human papillomavirus type 16 testing in locally advanced oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:1673–84.
Dibble EH, Alvarez AC, Truong MT, Mercier G, Cook EF, Subramaniam RM. 18F-FDG metabolic tumor volume and total glycolytic activity of oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer: adding value to clinical staging. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:709–15.
Lim R, Eaton A, Lee NY, Setton J, Ohri N, Rao S, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycolysis predict outcome in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:1506–13.
Tixier F, Le Rest CC, Hatt M, Albarghach N, Pradier O, Metges JP, et al. Intratumor heterogeneity characterized by textural features on baseline 18F-FDG PET images predicts response to concomitant radiochemotherapy in esophageal cancer. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:369–78.
Cheng NM, Fang YH, Chang JT, Huang CG, Tsan DL, Ng SH, et al. Textural features of pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT images: prognostic significance in patients with advanced T-stage oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:1703–9.
Cook GJ, Yip C, Siddique M, Goh V, Chicklore S, Roy A, et al. Are pretreatment 18F-FDG PET tumor textural features in non-small cell lung cancer associated with response and survival after chemoradiotherapy? J Nucl Med. 2013;54:19–26.
Hatt M, Tixier F, Cheze Le Rest C, Pradier O, Visvikis D. Robustness of intratumour 18F-FDG PET uptake heterogeneity quantification for therapy response prediction in oesophageal carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:1662–71.
Yang F, Thomas MA, Dehdashti F, Grigsby PW. Temporal analysis of intratumoral metabolic heterogeneity characterized by textural features in cervical cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:716–27.
O’Sullivan B, Shah J. New TNM staging criteria for head and neck tumors. Semin Surg Oncol. 2003;21:30–42.
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–16.
Huang SL, Chao A, Hsueh S, Chao FY, Huang CC, Yang JE, et al. Comparison between the hybrid capture II test and an SPF1/GP6+ PCR-based assay for detection of human papillomavirus DNA in cervical swab samples. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:1733–9.
Lin CY, Chen HC, Lin RW, You SL, You CM, Chuang LC, et al. Quality assurance of genotyping array for detection and typing of human papillomavirus. J Virol Methods. 2007;140:1–9.
Luo CW, Roan CH, Liu CJ. Human papillomaviruses in oral squamous cell carcinoma and pre-cancerous lesions detected by PCR-based gene-chip array. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;36:153–8.
Al-Swiahb JN, Huang CC, Fang FM, Chuang HC, Huang HY, Luo SD, et al. Prognostic impact of p16, p53, epidermal growth factor receptor, and human papillomavirus in oropharyngeal cancer in a betel nut-chewing area. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;136:502–8.
Hatt M, Cheze-le Rest C, van Baardwijk A, Lambin P, Pradier O, Visvikis D. Impact of tumor size and tracer uptake heterogeneity in (18)F-FDG PET and CT non-small cell lung cancer tumor delineation. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:1690–7.
La TH, Filion EJ, Turnbull BB, Chu JN, Lee P, Nguyen K, et al. Metabolic tumor volume predicts for recurrence and death in head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:1335–41.
Tang C, Murphy JD, Khong B, La TH, Kong C, Fischbein NJ, et al. Validation that metabolic tumor volume predicts outcome in head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:1514–20.
Chang KP, Tsang NM, Liao CT, Hsu CL, Chung MJ, Lo CW, et al. Prognostic significance of 18F-FDG PET parameters and plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:21–8.
Tan S, Kligerman S, Chen W, Lu M, Kim G, Feigenberg S, et al. Spatial-temporal [18F]FDG-PET features for predicting pathologic response of esophageal cancer to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85:1375–82.
Nestle U, Kremp S, Schaefer-Schuler A, Sebastian-Welsch C, Hellwig D, Rübe C, et al. Comparison of different methods for delineation of 18F-FDG PET-positive tissue for target volume definition in radiotherapy of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1342–8.
Larson SM, Erdi Y, Akhurst T, Mazumdar M, Macapinlac HA, Finn RD, et al. Tumor treatment response based on visual and quantitative changes in global tumor glycolysis using PET-FDG imaging. The visual response score and the change in total lesion glycolysis. Clin Positron Imaging. 1999;2:159–71.
Loh HH, Leu JG, Luo RC. The analysis of natural textures using run length features. IEEE Trans Ind Electron. 1988;35:323–8.
Thibault G, Fertil B, Navarro C, Pereira S, Cau P, Levy N, et al. Texture indexes and gray level size zone matrix: application to cell nuclei classification. In: Krasnoproshin V, Ablameyko S, Sadykhov R, editors. Pattern Recognition and Information Processing: Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference, 19–21 May 2009, Minsk, Belarus. Minsk: Belarusian State University; 2009. p. 140–5.
Tixier F, Hatt M, Le Rest CC, Le Pogam A, Corcos L, Visvikis D. Reproducibility of tumor uptake heterogeneity characterization through textural feature analysis in 18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:693–700.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Gerlinger M, Swanton C. How darwinian models inform therapeutic failure initiated by clonal heterogeneity in cancer medicine. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:1139–43.
Orlhac F, Soussan M, Maisonobe JA, Garcia CA, Vanderlinden B, Buvat I. Tumor texture analysis in 18F-FDG PET: relationships between texture parameters, histogram indices, standardized uptake values, metabolic volumes, and total lesion glycolysis. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:414–22.
Zhang H, Tan S, Chen W, Kligerman S, Kim G, D’Souza WD, et al. Modeling pathologic response of esophageal cancer to chemoradiation therapy using spatial-temporal 18F-FDG PET features, clinical parameters, and demographics. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88:195–203.
Schinagl DA, Span PN, van den Hoogen FJ, Merkx MA, Slootweg PJ, Oyen WJ, et al. Pathology-based validation of FDG PET segmentation tools for volume assessment of lymph node metastases from head and neck cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:1828–35.
Arens AI, Troost EG, Hoeben BA, Grootjans W, Lee JA, Grégoire V, et al. Semiautomatic methods for segmentation of the proliferative tumour volume on sequential FLT PET/CT images in head and neck carcinomas and their relation to clinical outcome. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:915–24.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Financial support
This study was supported by the grant NMRPG102-2221-E-182-074-MY2 from the National Science Council, Taiwan. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ching-Han Hsu and Tzu-Chen Yen contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
(DOC 95 kb)
Supplementary Figure 1
(TIFF 99 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
(TIFF 33 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
(TIFF 813 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, NM., Fang, YH.D., Lee, Ly. et al. Zone-size nonuniformity of 18F-FDG PET regional textural features predicts survival in patients with oropharyngeal cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42, 419–428 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2933-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2933-1