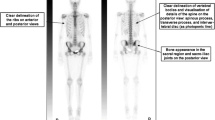
Abstract
Purpose
This study was designed to assess the additional value of SPECT/CT of the trunk used in conjunction with conventional nuclear imaging and its effects on patient management in a large patient series.
Methods
In 353 patients, whole-body scintigraphy (WBS), SPECT, and SPECT/CT were prospectively performed for staging and restaging. SPECT/CT of the trunk was performed in all patients. In the 308 evaluable patients (211 with breast cancer, 97 with prostate cancer), clinical follow-up was used as the gold standard. Bone metastases were confirmed in 72 patients and excluded in 236. Multistep analyses per lesion and per patient were performed. Clinical relevance was expressed in terms of downstaging and upstaging rates on a per-patient basis.
Results
In the total patient group, sensitivities, specificities, and negative and positive predictive values on a per-patient basis were 93 %, 78 %, 95 % and 59 % for WBS, 94 %, 71 %, 97 % and 53 % for SPECT, and 97 %, 94 %, 97 % and 88 % for SPECT/CT, respectively. In all subgroups, specificity and positive predictive value were significantly (p < 0.01) better with SPECT/CT. Downstaging of metastatic disease in the total, breast cancer and prostate cancer groups using SPECT/CT was possible in 32.1 %, 33.8 % and 29.5 % of patients, respectively. Upstaging in previously negative patients by additional SPECT/CT was observed in three breast cancer patients (2.1 %). Further diagnostic imaging procedures for unclear scintigraphic findings were necessary in only 2.5 % of patients. SPECT/CT improved diagnostic accuracy for defining the extent of multifocal metastatic disease in 34.6 % of these patients.
Conclusions
SPECT/CT significantly improved the specificity and positive predictive value of bone scintigraphy in cancer patients. In breast cancer patients, we found a slight increase in sensitivity. SPECT/CT had a significant effect on clinical management because of correct downstaging and upstaging, better definition of the extent of metastases, and a reduction in further diagnostic procedures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horger M, Eschmann SM, Pfannenberg C, Vonthein R, Besenfelder H, Claussen CD, et al. Evaluation of combined transmission and emission tomography for classification of skeletal lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(3):655–61.
Nomayr A, Romer W, Strobel D, Bautz W, Kuwert T. Anatomical accuracy of hybrid SPECT/spiral CT in the lower spine. Nucl Med Commun. 2006;27(6):521–8.
Willowson K, Bailey DL, Baldock C. Quantitative SPECT reconstruction using CT-derived corrections. Phys Med Biol. 2008;53(12):3099–112.
Reinartz P, Schaffeldt J, Sabri O, Zimny M, Nowak B, Ostwald E, et al. Benign versus malignant osseous lesions in the lumbar vertebrae: differentiation by means of bone SPET. Eur J Nucl Med. 2000;27(6):721–6.
Romer W, Nomayr A, Uder M, Bautz W, Kuwert T. SPECT-guided CT for evaluating foci of increased bone metabolism classified as indeterminate on SPECT in cancer patients. J Nucl Med. 2006;47(7):1102–6.
Utsunomiya D, Shiraishi S, Imuta M, Tomiguchi S, Kawanaka K, Morishita S, et al. Added value of SPECT/CT fusion in assessing suspected bone metastasis: comparison with scintigraphy alone and nonfused scintigraphy and CT. Radiology. 2006;238(1):264–71.
Strobel K, Burger C, Seifert B, Husarik DB, Soyka JD, Hany TF. Characterization of focal bone lesions in the axial skeleton: performance of planar bone scintigraphy compared with SPECT and SPECT fused with CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(5):W467–474.
Helyar V, Mohan HK, Barwick T, Livieratos L, Gnanasegaran G, Clarke SE, et al. The added value of multislice SPECT/CT in patients with equivocal bony metastasis from carcinoma of the prostate. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37(4):706–13.
Zhao Z, Li L, Li F, Zhao L. Single photon emission computed tomography/spiral computed tomography fusion imaging for the diagnosis of bone metastasis in patients with known cancer. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(2):147–53.
Sharma P, Kumar R, Singh H, Bal C, Julka PK, Thulkar S, et al. Indeterminate lesions on planar bone scintigraphy in lung cancer patients: SPECT, CT or SPECT-CT? Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41(7):843–50.
Palmedo H, Bucerius J, Joe A, Strunk H, Hortling N, Meyka S, et al. Integrated PET/CT in differentiated thyroid cancer: diagnostic accuracy and impact on patient management. J Nucl Med. 2006;47(4):616–24.
Silvestri GA, Gould MK, Margolis ML, Tanoue LT, McCrory D, Toloza E, et al. Noninvasive staging of non-small cell lung cancer: ACCP evidenced-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest. 2007;132(3 Suppl):178S–201S.
Abuzallouf S, Dayes I, Lukka H. Baseline staging of newly diagnosed prostate cancer: a summary of the literature. J Urol. 2004;171(6 Pt 1):2122–7.
Houssami N, Costelloe CM. Imaging bone metastases in breast cancer: evidence on comparative test accuracy. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(4):834–43.
Schirrmeister H, Guhlmann A, Kotzerke J, Santjohanser C, Kühn T, Kreienberg R, et al. Early detection and accurate description of extent of metastatic bone disease in breast cancer with fluoride ion and positron emission tomography. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(8):2381–9.
Schirrmeister H, Glatting G, Hetzel J, Nüssle K, Arslandemir C, Buck AK, et al. Prospective evaluation of the clinical value of planar bone scans, SPECT, and (18)F-labeled NaF PET in newly diagnosed lung cancer. J Nucl Med. 2001;42(12):1800–4.
Even-Sapir E, Metser U, Mishani E, Lievshitz G, Lerman H, Leibovitch I. The detection of bone metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer: 99mTc-MDP planar bone scintigraphy, single- and multi-field-of-view SPECT, 18F-fluoride PET, and 18F-fluoride PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 2006;47(2):287–97.
Bubendorf L, Schopfer A, Wagner U, Sauter G, Moch H, Willi N, et al. Metastatic patterns of prostate cancer: an autopsy study of 1,589 patients. Hum Pathol. 2000;31(5):578–83.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palmedo, H., Marx, C., Ebert, A. et al. Whole-body SPECT/CT for bone scintigraphy: diagnostic value and effect on patient management in oncological patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41, 59–67 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2532-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2532-6