Abstract
Purpose
Renal function is monitored during chemotherapy because chemotherapeutic drugs are excreted by the kidneys and are potentially nephrotoxic. Doses are adjusted according to the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), i.e. the more reduced the GFR, the lower the treatment dose. Plasma clearance of 51Cr-EDTA is a reliable indicator of GFR before and during treatment with potentially nephrotoxic drugs, but its measurement is costly. GFR can also be estimated using an algorithm that converts plasma creatinine concentration to GFR, e.g. the MDRD equation. The aim of this investigation was to evaluate the reliability of estimated GFR (eGFR) in detecting changes in GFR as assessed by the MDRD equation in cancer patients treated with nephrotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs.
Methods
We included all patients from the Department of Oncology undergoing chemotherapy who were referred to the Department of Nuclear Medicine for measurement of GFR by the 51Cr-EDTA plasma clearance technique at least four times during the study period of 12 months. The eGFR was calculated from plasma creatinine concentration and the MDRD formula. GFR was determined by the 51Cr-EDTA plasma clearance method.
Results
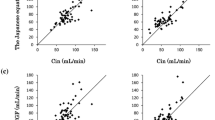
In 48 patients with a mean age of 47 years, GFR decreased from 86 to 73 ml/min/1.73 m2 (mean values, p < 0.002) from the first to the last measurement, whereas plasma creatinine concentration and eGFR remained unchanged. In 13 patients (27 %) the finding of a decreased GFR led to adjustment of the dose of the chemotherapy drug. Eight of the 13 patients with decreased GFR also had a reduced eGFR but five patients had a normal eGFR. These five patients would have been treated with the nephrotoxic drug at a dose that was too high.
Conclusion
Neither creatinine plasma concentration nor eGFR (MDRD) can be recommended as a replacement for measurement of GFR with the 51Cr-EDTA plasma clearance method in patients treated with nephrotoxic cytostatic drugs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekhart C, de Jonge ME, Huitema AD, Schellens JH, Rodenhuis S, Beijnen JH. Flat dosing of carboplatin is justified in adult patients with normal renal function. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6502–8.
Springate JE. Ifosfamide metabolite chloroacetaldehyde causes renal dysfunction in vivo. J Appl Toxicol. 1997;17:75–9.
Zaki EL, Springate JE, Taub M. Comparative toxicity of ifosfamide metabolites and protective effect of mesna and amifostine in cultured renal tubule cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2003;17:397–402.
Lichtman SM, Wildiers H, Launay-Vacher V, Steer C, Chatelut E, Aapro M. International Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) recommendations for the adjustment of dosing in elderly cancer patients with renal insufficiency. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43:14–34.
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Med Sci. 2007;334:115–24.
Taguchi T, Nazneen A, Abid MR, Razzaque MS. Cisplatin-associated nephrotoxicity and pathological events. Contrib Nephrol. 2005;148:107–21.
Brøchner-Mortensen J, Rødbro P. Comparison between total and renal plasma clearance of [51Cr]EDTA. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976;36:247–9.
Kampmann J, Siersbaek Nielsen K, Kristensen M, Hansen JM. Rapid evaluation of creatinine clearance. Acta Med Scand. 1974;196:517–20.
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16:31–41.
Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, Stevens LA, Zhang YL, Hendriksen S, et al. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145:247–54.
Hudson JQ, Nyman HA. Use of estimated glomerular filtration rate for drug dosing in the chronic kidney disease patient. Curr Opin Hypertens. 2011;20:482–91.
Froissart M, Rossert J, Jacquot C, Paillard M, Houillier P. Predictive performance of the modification of diet in renal disease and Cockcroft-Gault equations for estimating renal function. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:763–73.
Stevens LA, Nolin TD, Richardson MM, Feldman HI, Lewis JB, Rodby R, et al. Comparison of drug dosing recommendations based on measured GFR and kidney function estimating equations. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54:33–42.
Groth S, Aasted M. 51Cr-EDTA clearance determined by one plasma sample. Clin Physiol. 1981;1:417–25.
DuBois D, DuBois EF. Clinical calorimetry. X. A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. Arch Intern Med. 1916;17:863–71.
Brøchner-Mortensen J, Jensen S, Rødbro P. Delimitation of plasma creatinine concentration values for assessment of relative renal function in adult patients. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1977;11:257–62.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartlev, L.B., Boeje, C.R., Bluhme, H. et al. Monitoring renal function during chemotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39, 1478–1482 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-012-2158-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-012-2158-0