Abstract
Purpose
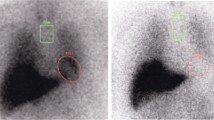
Molecular imaging with 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) has been used in Parkinson’s disease (PD), but there is no consensual index to discriminate between normal and PD patients in the Caucasian population. The purpose of this study was to determine diagnostic cutoff points in the quantification of MIBG cardiac uptake in our population of PD patients. We have also calculated the reproducibility over a range of interpretation expertise.
Methods
The study included 14 PD patients and 14 normal age- and sex-matched controls. Heart to mediastinum ratios (H/M) were calculated at 15 min (H/M15m) and 4 h (H/M4h) post-injection by three observers with different interpretation expertise, one of whom drew the regions of interest at three different times. The intraobserver and interobserver reliability was calculated (interclass correlation coefficient and coefficient of variability). Diagnosis was estimated by maximizing the Youden index for H/M and washout ratios. Discrimination ability was assessed by the area under the curve (AUC). Sensitivity and specificity were reported, using our thresholds.
Results
The parameter with the best diagnostic accuracy was the H/M4h ratio, with a major AUC (0.976 area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve). The threshold was 1.43 with a 95% confidence interval of 1.37–1.50. Using this threshold, the sensitivity and specificity were 93 and 100%. The interobserver and intraobserver variabilities measuring this ratio were 3.2 and 3.1%, respectively.
Conclusion
The diagnostic cutoff point for 123I-MIBG myocardial scintigraphy in a Caucasian population with PD was 1.43 for the H/M4h index, with a good sensitivity and specificity. The technique is easy to use, with a good reproducibility over a range of interpretation expertise.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wieland DM, Wu JL, Brown LE, Mangner TJ, Swanson DP, Beierwaltes WH. Radiolabeled adrenergic neuron-blocking agents: adrenomedullary imaging with [131I]iodobenzylguanidine. J Nucl Med 1980;21:349–53.
Glowniak JV, Turner FE, Gray LL, Palac RT, Lagunas-Solar MC, Woodward WR. Iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging of the heart in idiopathic congestive cardiomyopathy and cardiac transplants. J Nucl Med 1989;30:1182–91.
Merlet P, Valette H, Dubois-Randé JL, Moyse D, Duboc D, Dove P, et al. Prognostic value of cardiac metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging in patients with heart failure. J Nucl Med 1992;33:471–7.
Hattori N, Schwaiger M. Metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy of the heart: what have we learnt clinically? Eur J Nucl Med 2000;27:1–6.
Merlet P, Benvenuti C, Moyse D, Pouillart F, Dubois-Randé JL, Duval AM, et al. Prognostic value of MIBG imaging in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Nucl Med 1999;40:917–23.
Momose M, Kobayashi H, Iguchi N, Matsuda N, Sakomura Y, Kasanuki H, et al. Comparison of parameters of 123I-MIBG scintigraphy for predicting prognosis in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Nucl Med Commun 1999;20:529–35.
Cohen-Solal A, Esanu Y, Logeart D, Pessione F, Dubois C, Dreyfus G, et al. Cardiac metaiodobenzylguanidine uptake in patients with moderate chronic heart failure: relationship with peak oxygen uptake and prognosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 1999;33:759–66.
Wakabayashi T, Nakata T, Hashimoto A, Yuda S, Tsuchihashi K, Travin MI, et al. Assessment of underlying etiology and cardiac sympathetic innervation to identify patients at high risk of cardiac death. J Nucl Med 2001;42:1757–67.
Yamada T, Shimonagata T, Fukunami M, Kumagai K, Ogita H, Hirata A, et al. Comparison of the prognostic value of cardiac iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging and heart rate variability in patients with chronic heart failure: a prospective study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41:231–8.
Verberne HJ, Brewster LM, Somsen GA, van Eck-Smit BLF. Prognostic value of myocardial 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) parameters in patients with heart failure: a systematic review. Eur Heart J 2008;29:1147–59.
Jacobson AF, Senior R, Cerqueira MD, Wong ND, Thomas GS, Lopez VA, et al. Myocardial iodine-123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine imaging and cardiac events in heart failure. Results of the prospective ADMIRE-HF (AdreView Myocardial Imaging for Risk Evaluation in Heart Failure) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:2212–21.
Jacobson AF, Lombard J, Banerjee G, Camici PG. 123I-mIBG scintigraphy to predict risk for adverse cardiac outcomes in heart failure patients: design of two prospective multicenter international trials. J Nucl Cardiol 2009;16:113–21.
Boogers MJ, Borleffs CJ, Henneman MM, van Bommel RJ, van Ramshorst J, Boersma E, et al. Cardiac sympathetic denervation assessed with 123-iodine metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging predicts ventricular arrhythmias in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:2769–77.
Tamaki S, Yamada T, Okuyama Y, Morita T, Sanada S, Tsukamoto Y, et al. Cardiac iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging predicts sudden cardiac death independently of left ventricular ejection fraction in patients with chronic heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction: results from a comparative study with signal-averaged electrocardiogram, heart rate variability, and QT dispersion. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:426–35.
Estorch M, Camacho V, Paredes P, Rivera E, Rodríguez-Revuelto A, Flotats A, et al. Cardiac (123)I-metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging allows early identification of dementia with Lewy bodies during life. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:1636–41.
Ishibashi K, Saito Y, Murayama S, Kanemaru K, Oda K, Ishiwata K, et al. Validation of cardiac (123)I-MIBG scintigraphy in patients with Parkinson’s disease who were diagnosed with dopamine PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:3–11.
Agostini D, Carrió I, Verberne HJ. How to use myocardial 123I-MIBG in chronic heart failure. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2009;36:555–9.
Flotats A, Carrió I, Agostini D, Le Guludec D, Marcassa C, Schäfers M, et al. Proposal for standardization of (123)I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) cardiac sympathetic imaging by the EANM Cardiovascular Committee and the European Council of Nuclear Cardiology. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:1802–12.
Nakajima K, Yoshita M, Matsuo S, Taki J, Kinuya S. Iodine-123-MIBG sympathetic imaging in Lewy-body diseases and related movement disorders. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;52:378–88.
Rinne JO, Ruottinen H, Bergman J, Haaparanta M, Sonninen P, Solin O. Usefulness of a dopamine transporter PET ligand [(18)F]beta-CFT in assessing disability in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;67:737–41.
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1992;55:181–4.
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 1967;17:427–42.
Solanki KK, Bomanji J, Moyes J, Mather SJ, Trainer PJ, Britton KE. A pharmacological guide to medicines which interfere with the biodistribution of radiolabelled meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG). Nucl Med Commun 1992;13:513–21.
Huguet F, Fagret D, Caillet M, Piriou A, Besnard JC, Guilloteau D. Interaction of metaiodobenzylguanidine with cardioactive drugs: an in vitro study. Eur J Nucl Med 1996;23:546–9.
Bombardieri E, Atktolun C, Baum RP, Bishof-Delaloye A, Buscombe J, Chatal JF, et al. 131I/123I-Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scintigraphy: procedure guidelines for tumour imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:BP132–9.
Verberne HJ, Habraken JBA, van Eck-Smit BLF, Agostini D, Jacobson AF. Variations in 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) late heart mediastinal ratios in chronic heart failure: a need for standardisation and validation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:547–53.
Verberne HJ, Feenstra C, de Jong WM, Somsen GA, Van Eck-Smit BL, Busemann Sokole E. Influence of collimator choice and simulated clinical conditions on 123I-MIBG heart/mediastinum ratios: a phantom study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:1100–7.
Somsen GA, Verberne HJ, Fleury E, Righetti AR. Normal values and within-subject variability of cardiac I-123 MIBG scintigraphy in healthy individuals: implications for clinical studies. J Nucl Cardiol 2004;11:126–33.
Estorch M, Carrió I, Berná L, López-Pousa J, Torres G. Myocardial iodine-labeled metaiodobenzylguanidine 123 uptake relates to age. J Nucl Cardiol 1995;2(2 Pt 1):126–32.
van der Veen L, Scholte A, Stokkel M. Mathematical methods to determine quantitative parameters of myocardial 123I-MIBG studies: a review of the literature. Nucl Med Commun 2010;31(7):617–28. Review.
Sawada H, Oeda T, Yamamoto K, Kitagawa N, Mizuta E, Hosokawa R, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of cardiac metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy in Parkinson disease. Eur J Neurol 2009;16(2):174–82.
Estorch M, Camacho V, Fuertes J, Rodríguez-Revuelto A, Hernández MA, Flotats A, et al. Demencia con Cuerpos de Lewy y enfermedad de Alzheimer: diagnóstico diferencial mediante estudio de inervación simpática cardiaca con MIBG. Rev Esp Med Nucl 2006;25:229–35.
Escamilla-Sevilla F, Pérez-Navarro MJ, Muñoz-Pasadas M, Ortega-Léon T, Gallego-Peinado M, Cabello-García D, et al. Diagnostic value of cardiac 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (123I-MIBG) scintigraphy in Lewy body disorders. Neurologia 2009;24:170–6.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (FISS PI070426 and RECAVA) and by Agència de Gestió d'Ajuts Universitaris i de Recerca (AGAUR 2009 SGR 1049).
The authors wish to thank nuclear medicine technicians Manel Tantull and Josep L. Carrasco for their skilful help in the realization of these studies.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muxí, Á., Paredes, P., Navales, I. et al. Diagnostic cutoff points for 123I-MIBG myocardial scintigraphy in a Caucasian population with Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38, 1139–1146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1754-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1754-8