Abstract
Purpose
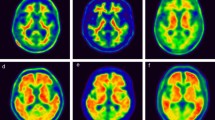
Positron emission tomography (PET) with 11C-labelled Pittsburgh compound B ([11C]PIB) enables the quantitation of β-amyloid accumulation in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Voxel-based image analysis techniques conducted in a standard brain space provide an objective, rapid and fully automated method to analyze [11C]PIB PET data. The purpose of this study was to evaluate both region- and voxel-level reproducibility of automated and simplified [11C]PIB quantitation when using only 30 min of imaging data.
Methods
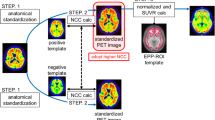
Six AD patients and four healthy controls were scanned twice with an average interval of 6 weeks. To evaluate the feasibility of short scanning (convenient for AD patients), [11C]PIB uptake was quantitated using 30 min of imaging data (60 to 90 min after tracer injection) for region-to-cerebellum ratio calculations. To evaluate the reproducibility, a test-retest design was used to derive absolute variability (VAR) estimates and intraclass correlation coefficients at both region-of-interest (ROI) and voxel level.
Results
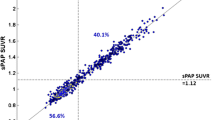
The reproducibility both at the region level (VAR 0.9–5.5%) and at the voxel level (VAR 4.2–6.4%) was good to excellent. Based on the variability estimates obtained, power calculations indicated that 90% power to obtain statistically significant difference can be achieved using a sample size of five subjects per group when a 15% change from baseline (increase or decrease) in [11C]PIB accumulation in the frontal cortex is anticipated in one group compared to no change in another group.
Conclusion
Our results showed that an automated analysis method based on an efficient scanning protocol provides reproducible results for [11C]PIB uptake and appears suitable for PET studies aiming at the quantitation of amyloid accumulation in the brain of AD patients for the evaluation of progression and treatment effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klunk WE, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt DP. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer's disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann Neurol 2004;55:306–19. doi:10.1002/ana.20009.
Kemppainen NM, Aalto S, Wilson IA, Någren K, Helin S, Brück A, et al. Voxel-based analysis of PET amyloid ligand [11C]PIB uptake in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2006;67:1575–80. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000240117.55680.0a.
Edison P, Archer HA, Hinz R, Hammers A, Pavese N, Tai YF, et al. Amyloid, hypometabolism, and cognition in Alzheimer disease: an [11C]PIB and [18F]FDG PET study. Neurology 2007;68:501–8. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000244749.20056.d4.
Rowe CC, Ng S, Ackermann U, Gong SJ, Pike K, Savage G, et al. Imaging beta-amyloid burden in aging and dementia. Neurology 2007;68:1718–25. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000261919.22630.ea.
Mikhno A, Devanand D, Pelton G, Cuasay K, Gunn R, Upton N, et al. Voxel-based analysis of 11C-PIB scans for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease. J Nucl Med 2008;49:1262–9. doi:10.2967/jnumed.107.049932.
Yaqub M, Tolboom N, Boellaard R, Berckel BNM, van Tilburg EW, Luurtsema G, et al. Simplified parametric methods for [11C]PIB studies. Neuroimage 2008;42:76–86. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.04.251.
Lopresti BJ, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Hoge JA, Ziolko SK, Lu X, et al. Simplified quantification of Pittsburgh Compound B amyloid imaging PET studies: a comparative analysis. J Nucl Med 2005;46:1959–72.
Price JC, Klunk WE, Lopresti BJ, Lu X, Hoge JA, Ziolko SK, et al. Kinetic modeling of amyloid binding in humans using PET imaging and Pittsburgh Compound-B. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2005;25:1528–47. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600146.
Kemppainen NM, Aalto S, Wilson IA, Någren K, Helin S, Brück A, et al. PET amyloid ligand [11C]PIB uptake is increased in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2007;68:1603–6. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000260969.94695.56.
Friston KJ, Worsley KJ, Poline JB, Frith CD, Franckowiak RSJ. Statistical parametric maps in functional brain imaging. A general approach. Hum Brain Mapp 1995;2:189–210. doi:10.1002/hbm.460020402.
Meyer JH, Gunn RN, Myers R, Grasby PM. Assessment of spatial normalization of PET ligand images using ligand-specific templates. Neuroimage 1999;9:545–53. doi:10.1006/nimg.1999.0431.
Ziolko SK, Weissfield LA, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Hoge JA, Lopresti BJ, et al. Evaluation of voxel-based methods for the statistical analysis of PIB PET amyloid imaging studies in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage 2006;33:94–102. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.063.
Brück A, Aalto S, Nurmi E, Bergman J, Rinne JO. Cortical 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa uptake and frontal cognitive functions in early Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2005;26:891–8. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.07.014.
Kemppainen J, Aalto S, Fujimoto T, Kalliokoski KK, Långsjö J, Oikonen V, et al. High intensity exercise decreases global brain glucose uptake in humans. J Physiol 2005;568:323–32. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.091355.
Salmi E, Aalto S, Hirvonen J, Långsjö JW, Maksimov AT, Oikonen V, et al. Measurement of GABAA receptor binding in vivo with [11C]flumazenil: a test-retest study in healthy subjects. Neuroimage 2008;41:260–9. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.02.035.
Engler H, Forsberg A, Almkvist O, Blomquist G, Larsson E, Savitcheva I, et al. Two-year follow-up of amyloid deposition in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Brain 2006;129:2856–66. doi:10.1093/brain/awl178.
Razifar P, Ringheim A, Engler H, Hall H, Långström B. Masked-volume-wise PCA and "reference Logan" illustrate similar regional differences in kinetic behavior in human brain PET study using [11C]-PIB. BMC Neurol 2009;9:2. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-9-2.
Hooper PK, Meikle SR, Eberl S, Fulham MJ. Validation of postinjection transmission measurements for attenuation correction in neurological FDG-PET studies. J Nucl Med 1996;37:128–36.
Blomquist G, Engler H, Nordberg A, Ringheim A, Wall A, Forsberg A, et al. Unidirectional influx and net accumulation of PIB. Open Neuroimaging J 2008;2:114–25. doi:10.2174/1874440000802010114.
Acknowledgments
The assistance of the personnel of Turku PET Centre and CRST is gratefully acknowledged. This study was financially supported by grants from the Academy of Finland (project # 205954), the Sigrid Jusélius Foundation and Turku University Hospital (EVO).
Conflicts of Interest
Marita Kailajärvi works currently for Turku Imanet, GE Healthcare. The other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aalto, S., Scheinin, N.M., Kemppainen, N.M. et al. Reproducibility of automated simplified voxel-based analysis of PET amyloid ligand [11C]PIB uptake using 30-min scanning data. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36, 1651–1660 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1174-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1174-1