Abstract
Purpose
Radiolabeled cyclic RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) peptides have great potential for the early tumor detection and noninvasive monitoring of tumor metastasis and therapeutic response. 18F-labeled RGD analogs ([18F]-AH111585 and [18F]Galacto-RGD) have been investigated in clinical trials for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of integrin expression in cancer patients. To develop new RGD radiotracers with higher tumor accumulation, improved in vivo kinetics, easy availability and low cost, we developed two new RGD peptides and labeled them with generator-eluted 68Ga (t1/2 = 68 min) for PET imaging of integrin αvβ3 expression in tumor xenograft models.
Materials and methods
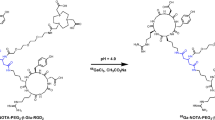
The two new cyclic RGD dimers, E[PEG4-c(RGDfK)]2 (P4-RGD2, PEG4 = 15-amino-4,7,10,13-tetraoxapentadecanoic acid) and E[Gly3-c(RGDfK)]2 (G3-RGD2, G3 = Gly-Gly-Gly) were designed, synthesized and conjugated with 1,4,7-triazacyclononanetriacetic acid (NOTA) for 68Ga labeling. The microPET imaging and biodistribution of the 68Ga labeled RGD tracers were investigated in integrin αvβ3-positive tumor xenografts.
Results
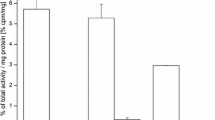
The new RGD dimers with the Gly3 and PEG4 linkers showed higher integrin αvβ3 binding affinity than no-linker RGD dimer (RGD2). NOTA-G3-RGD2 and NOTA-P4-RGD2 could be labeled with 68Ga within 30 min with higher purity (>98%) and specific activity (8.88–11.84 MBq/nmol). Both 68Ga-NOTA-P4-RGD2 and 68Ga-NOTA-G3-RGD2 exhibited significantly higher tumor uptake and tumor-to-normal tissue ratios than 68Ga-NOTA-RGD2.
Conclusion
Because of their high affinity, high specificity and excellent pharmacokinetic properties, further investigation of the two novel RGD dimers for clinical PET imaging of integrin αvβ3 expression in cancer patients is warranted.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1995;1:27–31.
Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol 2002;29:15–8.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000;407:249–57.
Sharma RA, Harris AL, Dalgleish AG, Steward WP, O’Byrne KJ. Angiogenesis as a biomarker and target in cancer chemoprevention. Lancet Oncol 2001;2:726–32.
Folkman J. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel hospital, Boston. Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1757–63.
Eliceiri BP, Cheresh DA. The role of alphav integrins during angiogenesis: insights into potential mechanisms of action and clinical development. J Clin Invest 1999;103:1227–30.
Cai W, Chen X. Multimodality molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis. J Nucl Med 2008;49(Suppl 2):113S–28S.
Cai W, Niu G, Chen X. Imaging of integrins as biomarkers for tumor angiogenesis. Curr Pharm Des 2008;14:2943–73.
Hsu AR, Chen X. Advances in anatomic, functional, and molecular imaging of angiogenesis. J Nucl Med 2008;49:511–4.
Cai W, Rao J, Gambhir SS, Chen X. How molecular imaging is speeding up antiangiogenic drug development. Mol Cancer Ther 2006;5:2624–33.
Chen X. Multimodality imaging of tumor integrin αvβ3 expression. Mini Rev Med Chem 2006;6:227–34.
Liu S. Radiolabeled multimeric cyclic RGD peptides as integrin αvβ3 targeted radiotracers for tumor imaging. Mol Pharm 2006;3:472–87.
Cai W, Zhang X, Wu Y, Chen XA. Thiol-reactive 18F-labeling agent, N-[2-(4-18F-fluorobenzamido)ethyl]maleimide, and synthesis of RGD peptide-based tracer for PET imaging of αvβ3 integrin expression. J Nucl Med 2006;47:1172–80.
Chen X, Park R, Shahinian AH, Tohme M, Khankaldyyan V, Bozorgzadeh MH, et al. 18F-labeled RGD peptide: initial evaluation for imaging brain tumor angiogenesis. Nucl Med Biol 2004;31:179–89.
Li ZB, Chen K, Chen X. 68Ga-labeled multimeric RGD peptides for microPET imaging of integrin αvβ3 expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:1100–8.
Wu Y, Zhang X, Xiong Z, Cheng Z, Fisher DR, Liu S, et al. microPET imaging of glioma integrin αvβ3 expression using 64Cu-labeled tetrameric RGD peptide. J Nucl Med 2005;46:1707–18.
Wu Z, Li ZB, Chen K, Cai W, He L, Chin FT, et al. MicroPET of tumor integrin αvβ3 expression using 18F-labeled PEGylated tetrameric RGD peptide (18F-FPRGD4). J Nucl Med 2007;48:1536–44.
Zhang X, Xiong Z, Wu Y, Cai W, Tseng JR, Gambhir SS, et al. Quantitative PET imaging of tumor integrin αvβ3 expression with 18F-FRGD2. J Nucl Med 2006;47:113–21.
Haubner R, Weber WA, Beer AJ, Vabuliene E, Reim D, Sarbia M, et al. Noninvasive visualization of the activated αvβ3 integrin in cancer patients by positron emission tomography and [18F]Galacto-RGD. PLoS Med 2005;2:e70.
Liu S, Hsieh WY, Jiang Y, Kim YS, Sreerama SG, Chen X, et al. Evaluation of a 99mTc-labeled cyclic RGD tetramer for noninvasive imaging integrin αvβ3-positive breast cancer. Bioconjug Chem 2007;18:438–46.
Beer AJ, Grosu AL, Carlsen J, Kolk A, Sarbia M, Stangier I, et al. [18F]galacto-RGD positron emission tomography for imaging of αvβ3 expression on the neovasculature in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:6610–6.
Kenny LM, Coombes RC, Oulie I, Contractor KB, Miller M, Spinks TJ, et al. Phase I trial of the positron-emitting Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide radioligand 18F-AH111585 in breast cancer patients. J Nucl Med 2008;49:879–86.
Beer AJ, Haubner R, Sarbia M, Goebel M, Luderschmidt S, Grosu AL, et al. Positron emission tomography using [18F]Galacto-RGD identifies the level of integrin αvβ3 expression in man. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:3942–9.
Al-Nahhas A, Win Z, Szyszko T, Singh A, Khan S, Rubello D. What can gallium-68 PET add to receptor and molecular imaging? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:1897–901.
Fani M, Andre JP, Maecke HR. 68Ga-PET: a powerful generator-based alternative to cyclotron-based PET radiopharmaceuticals. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2008;3:67–77.
Maecke HR, Andre JP. 68Ga-PET radiopharmacy: a generator-based alternative to 18F-radiopharmacy. In: Schubiger PA, Lehmann L, Friebe M, editors. PET chemistry: the driving force in molecular imaging. Ernst Schering Research Foundation Workshop. Berlin: Springer; 2007. p. 215–42.
Shi J, Kim Y-S, Zhai S, Liu Z, Chen X, Liu S. Improving tumor uptake and pharmacokinetics of 64Cu-labeled cyclic RGD peptide dimers with Gly3 and PEG4 Linkers. Bioconjug Chem. in press.
Shi J, Wang L, Kim Y-S, Zhai S, Liu Z, Chen X, et al. Improving tumor uptake and excretion kinetics of 99mTc-labeled cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic (RGD) dimers with triglycine linkers. J Med Chem 2008;51:7980–90.
Cai W, Wu Y, Chen K, Cao Q, Tice DA, Chen X. In vitro and in vivo characterization of 64Cu-labeled Abegrin, a humanized monoclonal antibody against integrin αvβ3. Cancer Res 2006;66:9673–81.
Li ZB, Cai W, Cao Q, Chen K, Wu Z, He L, et al. 64Cu-labeled tetrameric and octameric RGD peptides for small-animal PET of tumor αvβ3 integrin expression. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1162–71.
Dijkgraaf I, Kruijtzer JA, Liu S, Soede AC, Oyen WJ, Corstens FH, et al. Improved targeting of the αvβ3 integrin by multimerisation of RGD peptides. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:267–73.
Janssen M, Oyen WJ, Massuger LF, Frielink C, Dijkgraaf I, Edwards DS, et al. Comparison of a monomeric and dimeric radiolabeled RGD-peptide for tumor targeting. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2002;17:641–6.
Chen X, Tohme M, Park R, Hou Y, Bading JR, Conti PS. Micro-PET imaging of αvβ3-integrin expression with 18F-labeled dimeric RGD peptide. Mol Imaging 2004;3:96–104.
Janssen ML, Oyen WJ, Dijkgraaf I, Massuger LF, Frielink C, Edwards DS, et al. Tumor targeting with radiolabeled αvβ3 integrin binding peptides in a nude mouse model. Cancer Res 2002;62:6146–51.
Jia B, Liu Z, Shi J, Yu Z, Yang Z, Zhao H, et al. Linker effects on biological properties of 111In-labeled DTPA conjugates of a cyclic RGDfK dimer. Bioconjug Chem 2008;19:201–10.
Chen X, Liu S, Hou Y, Tohme M, Park R, Bading JR, et al. MicroPET imaging of breast cancer alphav-integrin expression with 64Cu-labeled dimeric RGD peptides. Mol Imaging Biol 2004;6:350–9.
Beer AJ, Niemeyer M, Carlsen J, Sarbia M, Nahrig J, Watzlowik P, et al. Patterns of αvβ3 expression in primary and metastatic human breast cancer as shown by 18F-Galacto-RGD PET. J Nucl Med 2008;49:255–9.
Wu Z, Li ZB, Cai W, He L, Chin FT, Li F, et al. 18F-labeled mini-PEG spacered RGD dimer (18F-FPRGD2): synthesis and microPET imaging of alphavbeta3 integrin expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:1823–31.
Glaser M, Morrison M, Solbakken M, Arukwe J, Karlsen H, Wiggen U, et al. Radiosynthesis and biodistribution of cyclic RGD peptides conjugated with novel [18F]fluorinated aldehyde-containing prosthetic groups. Bioconjug Chem 2008;19:951–7.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by the National Cancer Institute (NCI R01 CA119053, R21CA121842, P50 CA114747 and U54 CA119367). We thank Dr. Kai Chen for excellent technical support. Z. Liu would like to thank Dr. Zibo Li for training in the use of the 68Ge/68Ga generator and also acknowledges the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for partial financial support during his visit to Stanford University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table S1
Biodistribution of 68Ga labeled RGD dimers in U87MG tumor xenografts at 1 h p.i (n = 4, Mean±SD) (DOC 33.5 KB)
Supplementary Table S2
Tumor-to-nontumor (T/NT) Ratios (n = 4, Means±SD) (DOC 30.0 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Niu, G., Shi, J. et al. 68Ga-labeled cyclic RGD dimers with Gly3 and PEG4 linkers: promising agents for tumor integrin αvβ3 PET imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36, 947–957 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-1045-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-1045-1