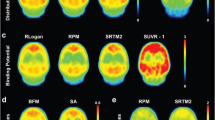
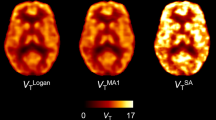
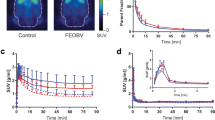
Abstract
Purpose
[11C]Flumazenil (FMZ) is a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist that binds reversibly to central-type gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA-A) sites. A validated approach for analysis of [11C]FMZ is the invasive one-tissue (1T) compartmental model. However, it would be advantageous to analyse FMZ binding with whole-brain pixel-based methods that do not require a-priori hypotheses regarding preselected regions. Therefore, in this study we compared invasive and noninvasive data-driven methods (Logan graphical analysis, LGA; multilinear reference tissue model, MRTM2; spectral analysis, SA; basis pursuit denoising, BPD) with the 1T model.
Methods
We focused on two aspects: (1) replacing the arterial input function analyses with a reference tissue method using the pons as the reference tissue, and (2) shortening the scan protocol from 90 min to 60 min. Dynamic PET scans were conducted in seven healthy volunteers with arterial blood sampling. Distribution volume ratios (DVRs) were selected as the common outcome measure.
Results
The SA, LGA with and without arterial input, and MRTM2 agreed best with the 1T model DVR values. The invasive and noninvasive BPD were slightly less well correlated. The full protocol of a 90-min emission data performed better than the 60-min protocol, but the 60-min protocol still delivered useful data, as assessed by the coefficient of variation, and the correlation and bias analyses.
Conclusion
This study showed that the SA, LGA and MRTM2 are valid methods for the quantification of benzodiazepine receptor binding with [11C]FMZ using an invasive or noninvasive protocol, and therefore have the potential to reduce the invasiveness of the procedure.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koeppe RA, Holthoff VA, Frey KA, Kilbourn MR, Kuhl DE. Compartmental analysis of [11C]flumazenil kinetics for the estimation of ligand transport rate and receptor distribution using positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1991;11:735–44.
Holthoff VA, Koeppe RA, Frey KA, Paradise AH, Kuhl DE. Differentiation of radioligand delivery and binding in the brain: validation of a two-compartment model for [11C]flumazenil. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1991;11:745–52.
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wolf AP, Dewey SL, Schlyer DJ, et al. Graphical analysis of reversible radioligand binding from time-activity measurements applied to [N-11C-methyl]-(-)-cocaine PET studies in human subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1990;10:740–7.
Cunningham VJ, Jones T. Spectral analysis of dynamic PET studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1993;13:15–23.
Ihara M, Tomimoto H, Ishizu K, Mukai T, Yoshida H, Sawamoto N, et al. Decrease in cortical benzodiazepine receptors in symptomatic patients with leukoaraiosis: a positron emission tomography study. Stroke 2004;35:942–7.
Koepp MJ, Labbe C, Richardson MP, Brooks DJ, Van Paesschen W, Cunningham VJ, et al. Regional hippocampal [11C]flumazenil PET in temporal lobe epilepsy with unilateral and bilateral hippocampal sclerosis. Brain 1997;120(Pt 10):1865–76.
Hammers A, Koepp MJ, Richardson MP, Labbé C, Brooks DJ, Cunningham VJ, et al. Central benzodiazepine receptors in malformations of cortical development: a quantitative study. Brain 2001;124:1555–65.
Lammertsma AA, Bench CJ, Hume SP, Osman S, Gunn K, Brooks DJ, et al. Comparison of methods for analysis of clinical [11C]raclopride studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1996;16:42–52.
Lammertsma AA, Hume SP. Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. Neuroimage 1996;4:153–8.
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Ding YS, Alexoff DL. Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1996;16:834–40.
Gunn RN, Gunn SR, Turkheimer FE, Aston JA, Cunningham VJ. Positron emission tomography compartmental models: a basis pursuit strategy for kinetic modeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2002;22:1425–39.
Klumpers UM, Veltman DJ, Boellaard R, Comans EF, Zuketto C, Yaqub M, et al. Comparison of plasma input and reference tissue models for analysing [(11)C]flumazenil studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2008;28:579–87.
Millet P, Graf C, Buck A, Walder B, Ibanez V. Evaluation of the reference tissue models for PET and SPECT benzodiazepine binding parameters. Neuroimage 2002;17:928–42.
Delforge J, Pappata S, Millet P, Samson Y, Bendriem B, Jobert A, et al. Quantification of benzodiazepine receptors in human brain using PET, [11C]flumazenil, and a single-experiment protocol. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1995;15:284–300.
Ichise M, Toyama H, Fornazzari L, Ballinger JR, Kirsh JC. Iodine-123-IBZM dopamine D2 receptor and technetium-99m-HMPAO brain perfusion SPECT in the evaluation of patients with and subjects at risk for Huntington’s disease. J Nucl Med 1993;34:1274–81.
Maziere M, Hantraye P, Prenant C, Sastre J, Comar D. Synthesis of ethyl 8-fluoro-5,6-dihydro-5-[11C]methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo [1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate (RO 15.1788-11C): a specific radioligand for the in vivo study of central benzodiazepine receptors by positron emission tomography. Int J Appl Radiat Isot 1984;35:973–6.
Barre L, Debruyne D, Abadie P, Moulin M, Baron JC. A comparison of methods for the separation of [11C]Ro 15-1788 (flumazenil) from its metabolites in the blood of rabbits, baboons and humans. Int J Radiat Appl Instrum 1991;42:435–9.
Meyer JH, Gunn RN, Myers R, Grasby PM. Assessment of spatial normalization of PET ligand images using ligand-specific templates. Neuroimage 1999;9:545–53.
Mintun MA, Raichle ME, Kilbourn MR, Wooten GF, Welch MJ. A quantitative model for the in vivo assessment of drug binding sites with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 1984;15:217–27.
Yaqub M, Boellaard R, Kropholler MA, Lammertsma AA. Optimization algorithms and weighting factors for analysis of dynamic PET studies. Phys Med Biol 2006;51:4217–32.
Millet P, Graf C, Buck A, Walder B, Westera G, Broggini C, et al. Similarity and robustness of PET and SPECT binding parameters for benzodiazepine receptors. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2000;20:1587–603.
Endres CJ, Bencherif B, Hilton J, Madar I, Frost JJ. Quantification of brain mu-opioid receptors with [11C]carfentanil: reference-tissue methods. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:177–86.
Abadie P, Baron JC, Bisserbe JC, Boulenger JP, Rioux P, Travère JM, et al. Central benzodiazepine receptors in human brain: estimation of regional Bmax and KD values with positron emission tomography. Eur J Pharmacol 1992;213:107–15.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the work of our colleagues Brigitte Dzewas and Choletta Kruschke for their excellent technical assistance in data acquisition. We would also like to thank Vin Cunningham and Roger Gunn for provision of software for spectral analysis and basis pursuit and for helpful discussion. This work was supported by the Kommission für Klinische Forschung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miederer, I., Ziegler, S.I., Liedtke, C. et al. Kinetic modelling of [11C]flumazenil using data-driven methods. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36, 659–670 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-0990-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-0990-z