Abstract
Purpose
Serotonin1A (5-HT1A) receptors exist in high- and low-affinity states, and agonist ligands bind preferentially to the high-affinity state of the receptor and provide a measure of functional 5-HT1A receptors. Although the antagonist tracers are established PET ligands in clinical studies, a successful 5-HT1A receptor agonist radiotracer in living brain has not been reported. [11C]MPT, our first-generation agonist radiotracer, shows in vivo specificity in baboons; however, its utility is limited owing to slow washout and immeasurable plasma free fraction. Hence we performed structure-activity relationship studies of MPT to optimize a radiotracer that will permit valid quantification of 5-HT1A receptor binding. We now report the synthesis and evaluation of [11C]MMP as an agonist PET tracer for 5-HT1A receptors in baboons.
Methods
In vitro binding assays were performed in bovine hippocampal membranes and membranes of CHO cells expressing 5-HT1A receptors. [11C] labeling of MMP was performed by reacting desmethyl-MMP with [11C]CH3OTf. In vivo studies were performed in baboons, and blocking studies were conducted by pretreatment with 5-HT1A receptor ligands WAY-100635 and (±)-8-OH-DPAT.
Results
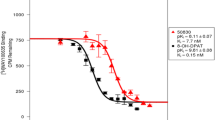
MMP is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist (K i 0.15 nM). Radiosynthesis of [11C]MMP was achieved in 30 ± 5% (n = 15) yield at EOS with a specific activity of 2,600 ± 500 Ci/mmol (n = 12). PET studies in baboons demonstrated specific binding of [11C]MMP to 5-HT1A receptor-enriched brain regions, as confirmed by blockade with WAY-100635 and (±)-8-OH-DPAT.
Conclusion
We identified [11C]MMP as an optimal agonist PET tracer that shows quantifiable, specific binding in vivo to 5-HT1A receptors in baboons.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herrick DK. Constitutively active serotonin receptors. Method Princip Med Chem 2005;24:223–41.
Hensler JG. Regulation of 5-HT1A receptor functions in brain following agonist or antidepressant administration. Life Sci 2003;72:1665–82.
Neumeister A, Bain E, Nugent AC, Carson RE, Bonne O, Luckenbaugh DA, et al. Reduced serotonin type 1A receptor binding in panic disorder. J Neurosci 2004;24:589–91.
Arango V, Underwood MD, Boldrini M, Tamir H, Kassir SA, Hsiung S-C, et al. Serotonin1A receptors, serotonin transporter binding and serotonin transporter mRNA expression in the brainstem of depressed suicide victims. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001;25:892–903.
Arango V, Huang YY, Underwood MD, Mann JJ. Genetics of the serotonergic system in suicidal behavior. J Psychiatric Res 2003;37:375–86.
Sullivan GM, Oquendo MA, Simpson N, Van Heertum RL, Mann JJ, Parsey RV. Brain serotonin1A receptor binding in depression is related to psychic and somatic anxiety. Biol Psychiatry 2005;58:947–54.
Merlet I, Ostrowsky K, Costes N, Ryvlin P, Isnard J, Faillenot I, et al. 5-HT1A receptor binding and intracerebral activity in temporal lobe epilepsy: an [18F]MPPF-PET study. Brain 2004;127:900–13.
Tiihonen J, Keski-Rahkonen A, Lopponen M, Muhonen M, Kajander J, Allonen T, et al. Brain serotonin 1A receptor binding in bulimia nervosa. Biol Psychiatry 2004;55:871–3.
Kepe V, Barrio JR, Huang S-C, Ercoli L, Siddarth P, Shoghi-Jadid K, et al. Serotonin1A receptors in the living brain of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006;103:702–7.
Kuenzel HE, Steiger A, Held K, Antonijevic IA, Frieboes R-M, Murck H. Changes in sleep electroencephalogram and nocturnal hormone secretion after administration of the antidyskinetic agent sarizotan in healthy young male volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2005;180:327–32.
Lai MKP, Tsang SWY, Francis PT, Esiri MM, Keene J, Hope T, et al. Reduced serotonin 5-HT1A receptor binding in the temporal cortex correlates with aggressive behavior in Alzheimer disease. Brain Res 2003;974:82–7.
Lopez RML, Ayala D, Benhamu B, Morcillo MJ, Viso A. Arylpiperazine derivatives acting at 5-HT1A receptors. Curr Med Chem 2002;9:443–69.
Meltzer HY, Li Z, Kaneda Y, Ichikawa J. Serotonin receptors: their key role in drugs to treat schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2003;27:1159–72.
Burnet PWJ, Eastwood SL, Harrison PJ. [3H]WAY-100635 for 5-HT1A receptor autoradiography in human brain: a comparison with [3H]8-OH-DPAT and demonstration of increased binding in the frontal cortex in schizophrenia. Neurochem Internat 1997;30:565–74.
Hall H, Lundkvist C, Halldin C, Farde L, Pike VW, McCarron JA, et al. Autoradiographic localization of 5-HT1A receptors in the post-mortem human brain using [3H]WAY-100635 and [11C]WAY-100635. Brain Res 1997;745:96–108.
Arango V, Underwood MD, Gubbi AV, Mann JJ. Localized alterations in pre- and postsynaptic serotonin binding sites in the ventrolateral prefrontal cortex of suicide victims. Brain Res 1995;688:121–33.
Parsey RV, Oquendo MA, Ogden RT, Olvet DM, Simpson N, Huang Y, et al. Altered serotonin 1A binding in major depression: a [carbonyl-C-11]WAY100635 positron emission tomography study. Biol Psychiatry 2006;59:106–13.
Parsey RV, Oquendo MA, Simpson NR, Ogden RT, Van Heertum RL, Arango V, et al. Effects of sex, age, and aggressive traits in man on brain serotonin 5-HT1A receptor binding potential measured by PET using [C-11]WAY-100635. Brain Res 2002;954:173–82.
Clawges HM, Depree KM, Parker EM, Graber SG. Human 5-HT1 receptor subtypes exhibit distinct G protein coupling behaviors in membranes from Sf9 cells. Biochemistry 1997;36:12930–8.
Watson J, Collin L, Ho M, Riley G, Scott C, Selkirk JV, et al. 5-HT1A receptor agonist-antagonist binding affinity difference as a measure of intrinsic activity in recombinant and native tissue systems. Br J Pharmacol 2000;130:1108–14.
Gozlan H, Thibault S, Laporte AM, Lima L, Hamon M. The selective 5-HT1A antagonist radioligand [3H]WAY 100635 labels both G-protein-coupled and free 5-HT1A receptors in rat brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol 1995;288:173–86.
Mongeau R, Welner SA, Quirion R, Suranyi-Cadotte BE. Further evidence for differential affinity states of the serotonin1A receptor in rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1992;590:229–38.
Bailer UF, Frank GK, Henry SE, Price JC, Meltzer CC, Weissfeld L, et al. Altered brain serotonin 5-HT1A receptor binding after recovery from anorexia nervosa measured by positron emission tomography and [carbonyl-11C]WAY-100635. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005;62:1032–41.
Cleare AJ, Messa C, Rabiner EA, Grasby PM. Brain 5-HT1A receptor binding in chronic fatigue syndrome measured using positron emission tomography and [11C]WAY-100635. Biol Psychiatry 2005;57:239–46.
Kegeles LS, Mann JJ. In vivo imaging of neurotransmitter systems using radiolabeled receptor ligands. Neuropsychopharmacology 1997;17:293–307.
Cumming P, Gillings NM, Jensen SB, Bjarkam C, Gjedde A. Kinetics of the uptake and distribution of the dopamine D2,3 agonist (R)-N-[1-11C]n-propylnorapomorphine in brain of healthy and MPTP-treated Gottingen miniature pigs. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:547–53.
Cumming P, Wong DF, Gillings N, Hilton J, Scheffel U, Gjedde A. Specific binding of [11C]raclopride and N-[3H]propyl-norapomorphine to dopamine receptors in living mouse striatum: occupancy by endogenous dopamine and guanosine triphosphate-free G protein. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2002;22:596–604.
Narendran R, Hwang DR, Slifstein M, Talbot PS, Erritzoe D, Huang Y, et al. In vivo vulnerability to competition by endogenous dopamine: comparison of the D2 receptor agonist radiotracer (-)-N-[11C]propyl-norapomorphine ([11C]NPA) with the D2 receptor antagonist radiotracer [11C]-raclopride. Synapse 2004;52:188–208.
Hirsch SR, Kissling W, Bauml J, Power A, O’Connor R. A 28-week comparison of ziprasidone and haloperidol in outpatients with stable schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 2002;63:516–23.
Passchier J, van Waarde A. Visualization of serotonin-1A (5-HT1A) receptors in the central nervous system. Eur J Nucl Med 2001;28:113–29.
Gozlan H, Ponchant M, Daval G, Verge D, Menard F, Vanhove A, et al. 125I-Bolton-Hunter-8-methoxy-2-[N-propyl-N-propylamino]tetralin as a new selective radioligand of 5-HT1A sites in the rat brain. In vitro binding and autoradiographic studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1988;244:751–9.
Ponchant M, Beaucourt JP, Vanhove A, Daval G, Verge D, Hamon M, et al. [125I-BH-8-MeO-N-PAT, a new ligand for the study of 5-HT1A receptors in the central nervous system]. C R Acad Sci III 1988;306:147–52.
Zhuang ZP, Kung MP, Kung HF. Synthesis of (R,S)-trans-8-hydroxy-2-[N-n-propyl-N-(3′-iodo-2′-propenyl)amino]tetral in (trans-8-OH-PIPAT): a new 5-HT1A receptor ligand. J Med Chem 1993;36:3161–5.
Halldin C, Wikstrom H, Swahn CG, Sedvall G, Stjernlof P, Farde L. Preparation of [propyl-11C]OSU 191, a highly potent and selective 5-HT1A agonist for PET [abstract]. J Label Compd Radiopharm 1994;35:S675–7.
Suehiro M, Underwood M, Arango V, Wang TS, Kassir S, Bakalian M, et al. In vivo biodistribution of a radiotracer for imaging serotonin-1A receptor sites with PET: [11C]LY274601. Life Sci 1998;63:1533–42.
Mathis CA, Huang Y, Simpson NR. Synthesis and evaluation of 5-HT1A agonists as radioligands: failure of G protein-coupled receptor agonists as in vivo imaging agents. J Label Compd Radiopharm 1997;40:563–4.
Thorell JO, Hedberg MH, Johansson AM, Hacksell U, Stone-Elander S, Eriksson L, et al. (R)-[N-11C-methyl]-11-hydroxy-10-methylaporphine as a ligand for 5-HT1A receptors: synthesis and evaluation of its biodistribution in monkey with PET. J Label Compd Radiopharm 1995;44:S179.
Barf TA, Visser GM, van Waarde A, Korte SM, Postema F, Leyssen D, et al. Synthesis and biodistribution of [C-11]Org-13502, a high-affinity serotonin (5-HT1A) receptor ligand. J Nucl Med 1995;36:163.
Fujio M, Nagata S, Kawamura K, Sugiyama N, Tanaka H, Uno K, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of 11C-labeled (S)-N-{[1-(2-phenylethyl) pyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl}-3-methylthiobenzamide as a PET 5-HT1A receptor ligand. Nucl Med Biol 2002;29:657–63.
Hwang DR, Ngo K, Savenkova L, Huang Y, Guo NN, Zhu Z, et al. 1-[2[(4-[F-18]fluorobenzamido-1-ethyl]4-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphth-1-yl)-piperidine (FBP). J Label Compd Radiopharm 2001;44:S179.
Vandecapelle M, Dumont F, De Vos F, Strijckmans K, Leysen D, Audenaert K, et al. Synthesis and preliminary in vivo evaluation of 4-[18F]fluoro-N-{2-[4-(6-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl}benzamide, a potential PET radioligand for the 5-HT1A receptor. J Label Compd Radiopharm 2004;47:531–42.
Vandecapelle M, De Vos F, Vermeirsch H, De Ley G, Audenaert K, Leysen D, et al. In vivo evaluation of 4-[123I]iodo-N-[2[4-(6-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridinyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]benzamide, a potential SPECT radioligand for the 5-HT1A receptor. Nucl Med Biol 2001;28:639–43.
Zimmer L, Fournet G, Benoit J, Guillaumet G, Le Bars D. Carbon-11 labelling of 8{{3-[4-(2-[11C]methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-2-hydroxypropyl}oxy}thiochroman, a presynaptic 5-HT1A receptor agonist, and its in vivo evaluation in anaesthetised rat and in awake cat. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:541–6.
Lu S-Y, Hong J, Musachio JL, Chin FT, Vermeulen ES, Wikstrom HV, et al. Alternative methods for labeling the 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 1-[2-(4-fluorobenzoylamino)ethyl]-4-(7-methoxynaphthyl)piperazine (S14506), with carbon-11 or fluorine-18. J Label Compd Radiopharm 2005;48:971–81.
Kumar JSD, Majo VJ, Hsiung S-C, Millak MS, Liu K-P, Tamir H, et al. Synthesis and in vivo validation of [O-Methyl-11C]-2-[4-[4-(7-methoxy-1-naphthalenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl]-4-methyl-2H-[1,2,4]triazine-3,5-dione: a novel 5-HT1A receptor agonist positron emission tomography ligand. J Med Chem 2006;49:125–34.
Mann JJ, Kumar JSD. Radiolabeled compounds and uses thereof. WO 2006083424, 2006;55.
Prabhakaran J, Parsey RV, Hsiung S-C, Majo VJ, Millak MS, Tamir H, et al. Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of [O-methyl-11C]2-{4-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-butyl}-4-methyl-2H-[1,2,4]- triazine-3,5-dione as an agonist PET ligand for 5-HT1A receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006;16:2101–4.
Kumar JSD, Prabhakaran J, Arango V, Parsey RV, Underwood MD, Simpson NR, et al. Synthesis of [O-methyl-11C]1-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid piperidin-1-ylamide: a potential PET ligand for CB1 receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2004;14:2393–6.
Wilson AA, Jin L, Garcia A, DaSilva JN, Houle S. An admonition when measuring the lipophilicity of radiotracers using counting techniques. Appl Radiat Isot 2001;54:203–8.
Hoyer D, Engel G, Kalkman, HO. Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 recognition sites in rat and pig brain membranes: radioligand binding studies with [3H]-5HT, [3H]-8-OH-DPAT, [125I]iodocyanopindolol, [3H]-mesulergine and [3H]-ketanserin. Eur J Pharmacol 1985;118:13–23.
Newman-Tancredi A, Cussac D, Marini L, Millan MJ. Antibody capture assay reveals bell-shaped concentration-response isotherms for h5-HT1A receptor-mediated Gai3 activation: conformational selection by high-efficacy agonists, and relationship to trafficking of receptor signaling. Mol Pharmacol 2002;62:590–601.
Woods RP, Grafton ST, Holmes CJ, Cherry SR, Mazziotta JC. Automated image registration: I. General methods and intrasubject, intramodality validation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998;22:139–52.
Gandelman MS, Baldwin RM, Zoghbi SS, Zea-Ponce Y, Innis RB. Evaluation of ultrafiltration for the free-fraction determination of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) radiotracers beta-CIT, IBF, and iomazenil. J Pharm Sci 1994;83:1014–9.
Langer O, Halldin C, Chou Y, Sandell J, Swahn C, Nagren K, et al. Carbon-11 pb-12: an attempt to visualize the dopamine d4 receptor in the primate brain with positron emission tomography. Nucl Med Biol 2000;27:707–14.
Zhang MR, Haradahira T, Maeda J, Okauchi T, Kawabe K, Noguchi J, et al. Syntheses and pharmacological evaluation of two potent antagonists for dopamine D4 receptors: [11C]YM-50001 and N-[2-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)-piperizin-1-yl]ethyl]-3-[11C]methoxybenzamide. Nucl Med Biol 2002;29:233–41.
Stowe RL, Barnes NM. Selective labelling of 5-HT7 receptor recognition sites in rat brain using [3H]5-carboxamidotryptamine. Neuropharmacology 1998;37:1611–9.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by research grants from the National Institute of Health (P50 MH62185, R21 MH077161 and K08 MH76258-01A1). The authors thank Dr. Bryan Roth and the NIMH-PDSP program for the competitive receptor-transporter binding assays. Ms. Agata Bukowska assisted in the radiolabeling studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, J.S.D., Prabhakaran, J., Majo, V.J. et al. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of a novel 5-HT1A receptor agonist radioligand [O-methyl-11C]2-(4-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-4-methyl-1,2,4-triazine-3,5(2H,4H)dione in nonhuman primates. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34, 1050–1060 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0324-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0324-y