Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of radioiodine (131I), alone or in combination with lithium, on thyroid volume and the prevention of radioiodine-induced thyrotoxicosis. This is the first clinical trial including only patients with multinodular goitre, normal TSH values and negative anti-thyroid auto-antibodies at baseline.
Methods
Eighty consecutive patients were randomised to receive 131I plus lithium (group I+L) or 131I alone (group I). Thyroid ultrasonography and biochemical analyses were performed at baseline and at 1, 3, 6, 12 and 24 months after treatment.
Results
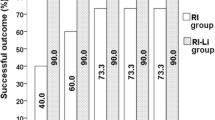
At 1–4 weeks after treatment, 131I-induced hyperthyroidism was observed in 58.8% of patients and was prevented by lithium administration. A low incidence of hypothyroidism (19%) was recorded at 24 months, whereas up to 44% of patients developed anti-thyroid antibodies. A significant reduction in thyroid volume was observed after 131I, with a mean decrease of 47.2% (median 48.2%) at 24 months, without differences between the groups. Moreover, it was shown that the decrease in thyroid volume after 131I was also due to the significant shrinkage of thyroid nodules.
Conclusion
This demonstrates that adjunctive lithium is able to reduce radioiodine-induced hyperthyroidism. Therefore, such treatment appears to be safe in older patients and those with underlying cardiovascular disease. In the present large series, 131I therapy was demonstrated to be highly effective in reducing thyroid and nodular volume even in patients treated with low 131I doses (2.5 MBq/ml of thyroid tissue), further supporting the view that radioiodine therapy represents a real alternative to surgery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berghout A, Wiersinga WM, Drexhage HA, Smiths NJ, Touber JL. Comparison of placebo with l-thyroxine alone or with carbimazole for treatment of sporadic non-toxic goiter. Lancet 1990;336:193–7.
Wiersinga WM. Determinants of outcome in sporadic nontoxic goiter. Thyroidology 1992;4:41–3.
Sawin CT, Geller A, Wolf PA, Belanger AJ, Baker E, Bacharach P, et al. Low serum thyrotropin concentrations as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation in older persons. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1249–52.
Faber J, Galloe AM. Changes in bone mass during prolonged subclinical hyperthyroidism due to l-thyroxine treatment: a meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol 1994;130:350–6.
Kay TWH, D’Endem MC, Andrews JT, Martin FIR. Treatment of non-toxic multinodular goiter with radioactive iodine. Am J Med 1988;84:19–22.
Hegedus L, Hansen BM, Knudsen N, Hansen JM. Reduction of size of thyroid with radioactive iodine in multinodular non-toxic goiter. Br Med J 1988;297:661–2.
Verelst J, Bonnyns M, Glinoer D. Radioiodine therapy in voluminous multinodular non-toxic goiter. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1990;122:417–21.
Nygaard B, Hegedus L, Gervil M, Hjalgrim H, Soe-Jensen P, Hansen JM. Radioiodine treatment of multinodular non-toxic goiter. Br Med J 1993;307:828–32.
Huysman DA, Hermus AR, Corstens FH, Barentsz JO, Kloppenborg PW. Large, compressive goiters treated with radioiodine. Ann Intern Med 1994;121:757–62.
Le Moli R, Wesche MFT, Tiel-van Buul MMC, Wiersinga WM. Determinants of longterm outcome of radioiodine therapy of sporadic non-toxic goiter. Clin Endocrinol 1999;50:783–9.
Wesche MFT, Tiel-v Buul MMC, Lips P, Smits NJ, Wiersinga WM. A randomized trial comparing levothyroxine with radioactive iodine in the treatment of sporadic non-toxic goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:998–1005.
Nygaard B, Knudsen JH, Hegedus L, Scient AV, Hansen JE. Thyrotropin receptor antibodies and Graves’ disease, a side-effect of 131I treatment in patients with nontoxic goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997;82:2926–30.
de Klerk JM, van Isselt JW, van Dijk A, Hakman ME, Pameijer FA, Koppeschaar HP, et al. Iodine-131 therapy in sporadic nontoxic goiter. J Nucl Med 1997;38:372–6.
Nieuwlaat WA, Huysmans DA, van den Bosch HC, Sweep CGF, Ross HA, Corstens FH, et al. Pretreatment with a single, low dose of recombinant human thyrotropin allows dose reduction of radioiodine therapy in patients with nodular goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:3121–9.
Silva MN, Rubio IG, Romao R, Gebrin EM, Buchpiguel C, Tomimori E, et al. Administration of a single dose of recombinant human thyrotrophin enhances the efficacy of radioiodine treatment of large compressive multinodular goiters. Clin Endocrinol 2004;60:300–8.
Nieuwlaat WA, Hermus AR, Sivro-Prndelj F, Corstens FH, Huysmans DA. Pretreatment with recombinant human TSH changes the regional distribution of radioiodine on thyroid scintigrams of nodular goiters. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:5330–6.
Wolff J, Berens SC, Jones AB. Inhibition of thyrotropin-stimulated adenyl cyclase activity of beef thyroid membranes by low concentration of lithium ion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1970;39:77–82.
Bogazzi F, Bartalena L, Campomori A, Brogioni S, Traino C, De Martino F, et al. Treatment with lithium prevents serum thyroid hormone increase after thionamide withdrawal and radioiodine therapy in patients with Graves’ disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:4490–5.
Pons F, Carrio I, Estorch M, Ginjaume M, Pons J, Milian R. Lithium as an adjuvant of iodine-131 uptake when treating patients with well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Clin Nucl Med 1987;12:644–7.
Koong SS, Reynolds JC, Movius EG, Keenan AM, Ain KB, Lakshmanan MC, et al. Lithium as a potential adjuvant to 131I therapy of metastatic, well differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:912–6.
Rago T, Chiovato L, Aghini-Lombardi F, Grasso L, Pinchera A, Vitti P. Non-palpable thyroid nodules in a borderline iodine-sufficient area: detection by ultrasonography and follow-up. J Endocrinol Invest 2001;24:770–6.
Wesche MF, Tiel-v Buul MM, Smits NJ, Wiersinga WM. Reduction in goiter size by 131I therapy in patients with non-toxic multinodular goiter. Eur J Endocrinol 1995;132:86–7.
Nygaard B, Faber J, Hegedus L, Hansen JM. 131I treatment of nodular non-toxic goiter. Eur J Endocrinol 1996;134:15–20.
Huysman D, Hermus A, Edelbroek M, Barentsz J, Corstens F, Kloppenborg P. Radioiodine for non-toxic multinodular goiter. Thyroid 1997;7:235–9.
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ. Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research. 3rd ed. USA: W.H. Freeman and Company; 1995. p. 151.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vannucchi, G., Chiti, A., Mannavola, D. et al. Radioiodine treatment of non-toxic multinodular goitre: effects of combination with lithium. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32, 1081–1088 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-1818-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-1818-8