Abstract
Purpose
Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (IPEH) is a soft tissue, tumor-like, benign, reactive, vascular proliferation that, although not rare, is uncommonly imaged. We report the imaging findings of intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia in 13 patients, highlighting characteristic imaging features.
Materials and methods
We retrospectively reviewed 13 patients with IPEH who had corresponding MR and/or ultrasound imaging. MR imaging studies were evaluated for lesion location, shape, size, signal intensity, signal heterogeneity, and enhancement. Ultrasound studies were assessed for lesion shape, size, echogenicity, heterogeneity, and vascularity. Demographic data, including patient age, gender, and clinical history were also reviewed.
Results
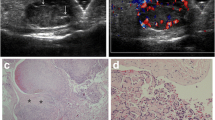
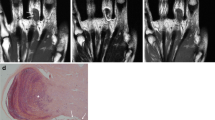
Most patients (11 of 13) presented with an enlarging mass. The age range was 10–72 years (mean 46) with ten females and three males. Eleven of the 13 lesions were primary IPEH without an associated preexisting vascular lesion. Ten of 13 lesions were in the superficial soft tissues, all of which were primary IPEH. Two of the three lesions in the deep tissues were secondary IPEH, arising within a preexisting vascular lesion. Lesions were small (mean 1.4 cm) and had a rounded shape. All of the primary lesions demonstrated high T2 signal peripherally and variable T2 signal centrally, with most demonstrating superficial location (91 %), peripheral enhancement (89 %) and associated dominant vessel (73 %). The five lesions evaluated by ultrasound were all hypoechoic with either scattered or peripheral vascularity on Doppler.
Conclusions
Primary papillary endothelial hyperplasia is commonly seen in the superficial soft tissues when captured on imaging and has a characteristic imaging appearance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss SW, Goldblum JR. Enzinger & Weiss’s soft tissue tumors. Philadelphia: Mosby; 2008. p. 633–79.
Masson P. Hemangioendotheliome vegetant intra-vasculaire. Bull Soc Anat Paris. 1926;93:517–23.
Clearkin KP, Enzinger FM. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976;100(8):441–4.
Hashimoto H, Daimaru Y, Enjoji M. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. a clinicopathologic study of 91 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983;5(6):539–46.
Sartore L, Voltan A, Tomat V, Bassetto F, Salmaso R. Masson’s disease in hand surgery: a clinicopathologic study of four cases. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2011;36(8):694–7.
Kitagawa Y, Tamai K, Kim Y, Hayashi M, Makino A, Takai S. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia of the digit: MRI features with histological correlation. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2013;38(3):306–12.
Lee SJ, Choo HJ, Park JS, Park YM, Eun CK, Hong SH, et al. Imaging findings of intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia presenting in extremities: correlation with pathological findings. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(8):783–9.
Elder DE, Elenitsas R, Bernett L, Johnson J, Murphy GF, Xu X. Lever’s histopathology of the skin. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008.
Kuo T, Sayers CP, Rosai J. Masson’s “vegetant intravascular hemangioendothelioma:” a lesion often mistaken for angiosarcoma: study of seventeen cases located in the skin and soft tissues. Cancer. 1976;38(3):1227–36.
Kauffman SL, Stout AP. Malignant hemangioendothelioma in infants and children. Cancer. 1961;14:1186–96.
Clifford PD, Temple HT, Jorda M, Marecos E. Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson’s tumor) presenting as a triceps mass. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33(7):421–5.
Pins MR, Rosenthal DI, Springfield DS, Rosenberg AE. Florid extravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson’s pseudoangiosarcoma) presenting as a soft-tissue sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1993;117(3):259–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have no disclosures and have not received any grants or assistance. This investigational protocol was conducted with the approval of the Institutional Review Board and in accordance with the requirements of a retrospective review as well as HIPAA; informed consent was not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Craig, K.A., Escobar, E., Inwards, C.Y. et al. Imaging characteristics of intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. Skeletal Radiol 45, 1467–1472 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-016-2445-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-016-2445-0