Abstract
Objective
Objectives were to study the MRI appearance of the repaired distal biceps tendon (DBT), anatomically reinserted, and to search for a correlation between tendon measurements and functional results.
Materials and methods
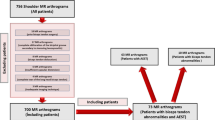
Twenty-five patients (mean age, 49 ± 4.9 years old) who benefited from 3-T MRI follow-up of the elbow after surgical reinsertion of the DBT were retrospectively included and compared to a control group (n = 25; mean age, 48 ± 10 years old). MRI was performed during the month of clinical follow-up and on average 22 months after surgery. Delayed complications (secondary avulsion, new rupture), intratendinous osteoma, tendinous signal on T1-weighted (T1w) and fat-suppressed proton density-weighted (FS-PDw) images as well as DBT measurements were recorded. The maximum isometric elbow flexion strength (MEFS) and range of motion of the elbow were assessed.
Results
Repaired DBT demonstrated a heterogeneous but normally fibrillar structure. Its low T1w signal was less pronounced than that of normal tendons, and the FS-PDW image signal was similar to that of T1w images. MRI detected seven osteomas (Se = 53 % vs. plain radiography), one textiloma and one secondary avulsion. Repaired DBT measurements were significantly correlated with MEFS (dominant arm R2: 0.38; nondominant arm R2: 0.54); this correlation involved the insertion surface (Δ = −75.7 mm2, p = 0.046), transverse diameter (Δ = −2.6 mm, p = 0.018), anteroposterior diameter at the level of the radial head (Δ = −3.9 mm, p = 0.001) and DBT cross-sectional area (Δ = −50.2 mm2, p = 0.003).
Conclusion
The quality of functional outcome after anatomical elbow rehabilitation of DBT correlates with the extent of tendinous hypertrophy during the healing process.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Safran MR, Graham SM. Distal biceps tendon ruptures: incidence, demographics, and the effect of smoking. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 2002(404):275-283
Morrey BF. Injury of the flexors of the elbow: biceps tendon injury. The elbow and its disorders. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2008:518-535.
Mazzocca AD, Spang JT, Arciero RA. Distal biceps rupture. Orthop Clin N Am. 2008;39(2):237–49. vii.
Vidal AF, Drakos MC, Allen AA. Biceps tendon and triceps tendon injuries. Clin Sports Med. 2004;23(4):707–22.
Schneider A, Bennett JM, O’Connor DP, Mehlhoff T, Bennett JB, Savvidou C. Bilateral ruptures of the distal biceps brachii tendon Spontaneous distal biceps tendon ruptures: are they related to statin administration. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb Surg. 2009;18(5):804–7.
Savvidou C, Moreno R. Spontaneous distal biceps tendon ruptures: are they related to statin administration? Hand surgery: An international journal devoted to hand and upper limb surgery and related research. J Asia Pac Fed Soc Surg Hand. 2012;17(2):167–71.
Rineer CA, Ruch DS. Elbow tendinopathy and tendon ruptures: epicondylitis, biceps and triceps ruptures. J Hand Surg. 2009;34(3):566–76.
Bernstein AD, Breslow MJ, Jazrawi LM. Distal biceps tendon ruptures: a historical perspective and current concepts. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2001;30(3):193–200.
Chillemi C, Marinelli M, De Cupis V. Rupture of the distal biceps brachii tendon: Conservative treatment versus anatomic reinsertion—clinical and radiological evaluation after 2 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;8:705–8.
Baker BE, Bierwagen D. Rupture of the distal tendon of the biceps brachii. Operative versus non-operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67(3):414–7.
Geaney LE, Mazzocca AD. Biceps brachii tendon ruptures: a review of diagnosis and treatment of proximal and distal biceps tendon ruptures. Physician Sports Med. 2010;38(2):117–25.
Catonne Y, Delattre O, Pascal-Mousselard H, d’Istria FC, Busson J, Rouvillain JL. Rupture of the distal tendon of the biceps brachialis: apropos of 43 cases. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1995;81(2):163–72.
Boyd HB, Anderson LD. A method for reinsertion of the distal biceps brachii tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1961;43(7):1041–3.
Lintner S, Fischer T. Repair of the distal biceps tendon using suture anchors and an anterior approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;322:116–9.
Barnes SJ, Coleman SG, Gilpin D. Repair of avulsed insertion of biceps. A new technique in four cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75(6):938–9.
Bain GI, Prem H, Heptinstall RJ, Verhellen R, Paix D. Repair of distal biceps tendon rupture: A new technique using the Endobutton. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb Surg. 2000;9(2):120–6.
Morrey BF, Askew LJ, An KN, Dobyns JH. Rupture of the distal tendon of the biceps brachii. A biomechanical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67(3):418–21.
Bell RH, Wiley WB, Noble JS, Kuczynski DJ. Repair of distal biceps brachii tendon ruptures. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb Surg. 2000;9(3):223–6.
Nesterenko S, Domire ZJ, Morrey BF, Sanchez-Sotelo J. Elbow strength and endurance in patients with a ruptured distal biceps tendon. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb Surg. 2010;19(2):184–9.
Balabaud L, Ruiz C, Nonnenmacher J, Seynaeve P, Kehr P, Rapp E. Repair of distal biceps tendon ruptures using a suture anchor and an anterior approach Repair of distal biceps tendon ruptures in athletes. J Hand Surg (Edinb Scotl). 2004;29(2):178–82.
Cain RA, Nydick JA, Stein MI, Williams BD, Polikandriotis JA, Hess AV. Complications following distal biceps repair. J Hand Surg. 2012;37(10):2112–7.
Schmidt CC, Diaz VA, Weir DM, Latona CR, Miller MC. Repaired distal biceps magnetic resonance imaging anatomy compared with outcome. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb Surg. 2012;21(12):1623–31.
Marnitz T, Spiegel D, Hug K, Huper M, Gerhardt C, Steffen IG. MR imaging findings in flexed abducted supinated (FABS) position and clinical presentation following refixation of distal biceps tendon rupture using bioabsorbable suture anchors. RoFo: Fortschr auf dem Geb Rontgenstrahlen und Nuklearmedizin. 2012;184(5):432–6.
Ramnath RR. 3T MR imaging of the musculoskeletal system (Part I): Considerations, coils, and challenges. Mag Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2006;14(1):27–40.
Brasseur JL. The biceps tendons: From the top and from the bottom. J Ultrasound. 2012;15(1):29–38.
Soucie JM, Wang C, Forsyth A, Funk S, Denny M, Roach KE. Range of motion measurements: Reference values and a database for comparison studies. Haemophilia. Off J World Fed Hemophilia. 2011;17(3):500–7.
Sotje G, Besch L. Distal rupture of the biceps tendon—a magnetic resonance tomography follow-up. Aktuelle Traumatol. 1993;23(2):105–7.
Roger B, Saillant G. Imagerie par résonance magnétique du tendon patellaire opéré Getroa Opus XXX: Sauramps Medical; 2003:389-394.
Maffulli N, Thorpe AP, Smith EW. Magnetic resonance imaging after operative repair of Achilles tendon rupture. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2001;11(3):156.
Khan KM, Cook JL, Bonar F, Harcourt P, Astrom M. istopathology of common tendinopathies. Update and implications for clinical management. Sports Med (Auckland NZ). 1999;27(6):393–408.
Fantino O, Besse J, Moyen B, Tran Minh V. Imagerie du tendon calcanéen opéré: Echographie et IRM. Getroa Opus XXX: Sauramps Medical; 2003. p. 395–408.
Greenberg JA, Fernandez JJ, Wang T, Turner C. EndoButton-assisted repair of distal biceps tendon ruptures. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb Surg. 2003;12(5):484–90.
Klonz A, Loitz D, Wohler P, Reilmann H. Rupture of the distal biceps brachii tendon: isokinetic power analysis and complications after anatomic reinsertion compared with fixation to the brachialis muscle. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb Surg. 2003;12(6):607–11.
Behounek J, Hrubina M, Skotak M, Krumpl O, Zahalka M, Dvorak J. Evaluation of surgical repair of distal biceps tendon ruptures. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cechoslovaca. 2009;76(1):47–53.
Freeman CR, McCormick KR, Mahoney D, Baratz M, Lubahn JD, Nesterenko S. Nonoperative treatment of distal biceps tendon ruptures compared with a historical control group. Elbow strength and endurance in patients with a ruptured distal biceps tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(10):2329–34.
Morrey BF, Chao EY, Hui FC. Biomechanical study of the elbow following excision of the radial head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61(1):63–8.
Askew LJ, An KN, Morrey BF, Chao EY, Morrey BF, Chao EY. Isometric elbow strength in normal individuals. Biomechanical study of the elbow following excision of the radial head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;61(222):261–6.
Wittstein J, Queen R, Abbey A, Moorman CT. 3rd. Isokinetic testing of biceps strength and endurance in dominant versus nondominant upper extremities. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb eons. 2010;19(6):874–7.
Sotereanos DG, Pierce TD, Varitimidis SE. A simplified method for repair of distal biceps tendon ruptures. J Should Elb Surg Am Should Elb Surg. 2000;9(3):227–33.
Leighton MM, Bush-Joseph CA, Bach Jr BR, Wittstein J, Queen R, Abbey A. Distal biceps brachii repair. Results in dominant and nondominant extremities Isokinetic testing of biceps strength and endurance in dominant versus nondominant upper extremities. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;19(317):114–21.
D’Alessandro DF, Shields Jr CL, Tibone JE, Chandler RW, Wittstein J, Queen R. Repair of distal biceps tendon ruptures in athletes Isokinetic testing of biceps strength and endurance in dominant versus nondominant upper extremities. Am J Sports Med. 1993;21(1):114–9.
Hetsroni I, Pilz-Burstein R, Nyska M, Back Z, Barchilon V, Mann G. Avulsion of the distal biceps brachii tendon in middle-aged population: is surgical repair advisable? A comparative study of 22 patients treated with either nonoperative management or early anatomical repair. Injury. 2008;39(7):753–60.
Silva J, Eskander MS, Lareau C, DeAngelis NA. Treatment of distal biceps tendon ruptures using a single-incision technique and a Bio-Tenodesis screw. edics. 2010;33(7):477.
Frazier MS, Boardman MJ, Westland M, Imbriglia JE. Surgical treatment of partial distal biceps tendon ruptures. J Hand ery. 2010;35(7):1111–4.
Berlet GC, Johnson JA, Milne AD, Patterson SD, King GJ. Distal biceps brachii tendon repair. An in vitro biomechanical study of tendon reattachment. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26(3):428–32.
Author disclosure statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alemann, G., Dietsch, E., Gallinet, D. et al. Repair of distal biceps brachii tendon assessed with 3-T magnetic resonance imaging and correlation with functional outcome. Skeletal Radiol 44, 629–639 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-014-2079-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-014-2079-z