Abstract
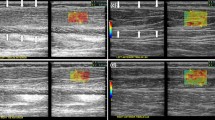
Congenital muscle dystrophy includes a range of genetic disorders characterized by muscle weakness and contractures. We report the magnetic resonance (MR), ultrasound (US) and real-time sonoelastography (RTE) imaging findings of the thigh muscles of a 15-year-old boy with Bethlem myopathy diagnosed with clinical, electromyographic and histopathological criteria. Ultrasound and MR showed hyperechoic appearance and high signal intensity on T1- and T2-weighted sequences respectively at the periphery of the vastus lateralis and the long head of the biceps femoris muscles, and at a central area within the rectus femoris muscles. RTE was employed to examine the elastic properties of the muscle. The elastograms were presented as colour-coded maps superimposed on the B-mode images and revealed that the elastographic pattern correlated with the MR and US pattern of involvement. The abnormal muscle areas were stiffer (blue) than the normal-appearing areas (green), a finding that probably correlates with the presence of dystrophic collagen at the affected areas. This report suggests that RTE could be used as an additional imaging tool to evaluate the pattern of muscle changes in congenital myopathy. Further studies are needed to investigate the specificity and clinical value of RTE in the diagnosis and monitoring of neuromuscular disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lampe AK, Bushby KMD. Collagen VI related muscle disorders. J Med Genet. 2005;42:673–85.
Reed UC, Ferreira LG, Liu EC, Resende MB, Carvalho MS, Marie SK, et al. Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and Bethlem myopathy: clinical and genetic heterogeneity. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2005;63:785–90.
Meola G, Sansone V, Rotondo G, et al. Computerized tomography and magnetic resonance muscle imaging in Miyoshi’s myopathy. Muscle Nerve. 1996;11:1476–80.
Mercuri E, Cini C, Counsell S, Allsop J, Zolkipli Z, Jungbluth H, et al. Muscle MRI findings in a three-generation family affected by Bethlem myopathy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2002;6:309–14.
Mercuri E, Counsell S, Allsop J, et al. Selective muscle involvement on magnetic resonance imaging in autosomal dominant Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Neuropediatrics. 2002;33:10–4.
Mercuri E, Cini C, Pichiecchio A, Allsop J, Counsell S, Zolkipli Z, et al. Muscle magnetic resonance imaging in patients with congenital muscular dystrophy and Ullrich phenotype. Neuromuscul Disord. 2003;13:554–8.
Mercuri E, Bushby K, Ricci E, Birchall D, Pane M, Kinali M, et al. Muscle MRI findings in patients with limb girdle muscular dystrophy with calpain 3 deficiency (LGMD2A) and early contractures. Neuromuscul Disord. 2005;15:164–71.
Mercuri E, Lampe A, Allsop J, Knight R, Pane M, Kinali M, et al. Muscle MRI in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and Bethlem myopathy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2005;15:303–10.
Bönnemann CG, Brockmann K, Hanefeld F. Muscle ultrasound in Bethlem myopathy. Neuropediatrics. 2003;34:335–6.
De Zordo T, Fink C, Feuchtner GM, Smekal V, Reindl M, Klauser AS. Real-time sonoelastography findings in healthy Achilles tendons. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193:W134–8.
De Zordo T, Lill SR, Fink C, Feuchtner GM, Jaschke W, Bellmann-Weiler R, et al. Real-time sonoelastography of lateral epicondylitis: comparison of findings between patients and healthy volunteers. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193:180–5.
Drakonaki EE, Allen GM, Wilson DJ. Real-time ultrasound elastography of the normal Achilles tendon: reproducibility and pattern description. Clin Radiol 2009;64:1196–202.
Ariji Y, Katsumata A, Hiraiwa Y, Izumi M, Iida Y, Goto M, et al. Use of sonographic elastography of the masseter muscles for optimizing massage pressure: a preliminary study. J Oral Rehabil. 2009;36:627–35.
Hete B, Shung KK. A study of the relationship between mechanical and ultrasonic properties of dystrophic and normal skeletal muscle. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1995;21:343–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drakonaki, E.E., Allen, G.M. Magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound and real-time ultrasound elastography of the thigh muscles in congenital muscle dystrophy. Skeletal Radiol 39, 391–396 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-009-0861-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-009-0861-0