Abstract
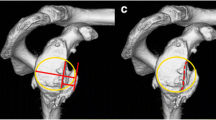
Glenoid labral tears exceeding 180° are an uncommon entity in which characteristic clinical and MR imaging features can lead to a more accurate preoperative diagnosis. We provide a description of glenoid labral tears that exceed 180°, and their characteristic magnetic resonance imaging features. In the young, heavily muscled male athlete, the identification of multiple sites of labral pathology and isolated, extensive posterior labral injuries are features that should raise suspicion for labral tears that exceed 180°.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan PA, Helms CA, Dussault R, Anderson MW, Major NM. Musculoskeletal MRI. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 2001:107–209.
Garneau RA, Renfrew DL, Moore TE, El-Khoury GY, Nepola JV, Lemke JH. Glenoid labrum: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiology 1991;179:519–522.
Legan JM, Burkhard TK, Goff WB, et al. Tears of the glenoid labrum: MR imaging of 88 arthroscopically confirmed cases. Radiology 1991;179:241–246.
Mohana-Borges AVR, Chung CB, Resnick D. Superior labral anteroposterior tear: Classification and diagnosis on MRI and MR arthrography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003;181:1449–1462.
Tirman PF, Feller JF, Janzen DL, et al. Association of glenoid labral cysts with labral tears and glenohumeral instability: radiologic findings and clinical significance. Radiology 1994;190:653–658.
Perthes G. Operation bei habitueller schulterluxation. Deutsche Z Chir 1906;85:199–227.
Palmer WE, Brown JH, Rosenthal DI. Labral-ligamentous complex of the shoulder: evaluation with MR arthrography. Radiology 1994;190:645–661.
Cordasco FA, Steinman S, Flatlow EL, Bigliani LU. Arthroscopic treatment of glenoid labral tears. Am J Sports Med 1993;21(3):425–431.
Howell SM, Galinat BJ. The glenoid-labral socket: a constrained articular surface. Clin Orthop 1989;243:122–124.
Turkel SJ, Ithaca MW, Marshall JL, Girgis FG. Stabilizing mechanisms preventing anterior dislocation of the glenohumeral joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1981;63:1208–1217.
Altchek DW, Warren RF, Wickiewicz TL, Ortiz G. Arthroscopic labral debridement: a three year follow-up study. Am J Sports Med 1992;20:702.
Snyder ST, Rames RD, Wolbert E. Labral lesions. In: McGinty JB, ed. Operative arthroscopy. New York: Raven Press; 1991:491–500.
Payne LZ, Jokl P. The results of arthroscopic debridement of glenoid labral tears based on tear location. Arthroscopy 1993;9(5):560–565.
Acknowledgement
Acknowledgement is given to Dr. Laurence Higgins, MD, in the Duke University Department of Orthopedics for his contributions on the surgical implications of extensive labral tears
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Report presented at ARRS 2002, Atlanta, GA
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindauer, K.R., Major, N.M., Rougier-Chapman, D.P. et al. MR imaging appearance of 180–360° labral tears of the shoulder. Skeletal Radiol 34, 74–79 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-004-0879-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-004-0879-2