Abstract
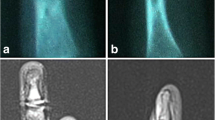
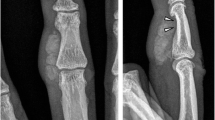
We are reporting an unusual case of isolated intraosseous tophus in medial hallux sesamoid presenting as tumor-like lesion in a teenage patient without prior history of gouty attack and underlying systemic disorders. The lesion manifested isointensity to surrounding muscles with internal low signal on spin echo (SE) T1-weighted images, and heterogeneous low signal intensity on fast spin echo (FSE) T2-weighted images. Computed tomography (CT) scan disclosed expansion and diffusely increased attenuation of the medial hallux sesamoid with focal cortical erosion and extraosseous extension of high attenuation content. The subsequent resection and pathology revealed intraosseous tophus deposition, which is particularly rare at this site and at this age. Imaging studies revealed some characteristic imaging features which can retrospectively be attributed to gouty tophus. When an expansile osteolytic lesion manifesting low signal intensity on T2-weighted image and internal calcifications on CT scan is encountered, the possibility of intraosseous tophus should be included in the list of differential diagnoses, even in a teenage patient without prior history of gout.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clement KH Chen, LR Yeh, HB Pan, et al. Intraarticular gouty tophi of the knee: CT and MR imaging in 12 patients. Skeletal Radio 1999; 28:75–80.
Anthony S. Fauci, Eugene Braunwald, Kurt J. Isselbacher, et al. Harrison's principles of internal medicine, 15th edn. United States of America: International Edition, 2001:2268–2271.
Clement KH Chen, CB. Chung, LR Yeh, et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome caused by tophaceous gout: CT and MR imaging features in 20 patients. AJR 2000; 175:655–659.
Yu JS, Chung C, Recht M, Dailiana T, Jurdi R. MR imaging of tophaceous gout (abstract). AJR 1997; 168:523–527.
Bonaldi VM, Duong H, Starr MR, Sarazin L, Richardson J. Tophaceous gout of the lumbar spine mimicking an epidural abscess: MR features. AJNR 1996; 17:1949–1952.
Duprez TP, Malghem J, Vande Berg BC, Noel HM, Munting EA, Maldague BE. Gout in the cervical spine: MR pattern mimicking diskovertebral infection. AJNR 1996; 17:151–153.
Miller LJ, Pruett SW, Losada R, Fruauff A, Sagerman P. Tophaceous gout of the lumbar spine: MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1996; 20:1004–1005.
Seidl G, Ullrich R, Trattnig S, et al. MR imaging in gout [in German]. Radiologe 1996; 36:632–636.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SZ., Yeh, L., Chou, YJ. et al. Isolated intraosseous gout in hallux sesamoid mimicking a bone tumor in a teenaged patient. Skeletal Radiol 32, 647–650 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-003-0692-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-003-0692-3