Abstract
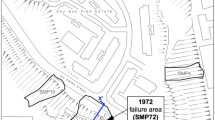
Because of terrain, geological structure, river down-incising and human activities, the upriver Minjiang Valley in Sichuan Province, Southwest China, constitutes a disaster area prone to frequent landslides. During the roadway rebuilding periods, the Xiaozongqu landslide reactivated on the G213 Roadway in Maoxian District of Sichuan Province. From the September to November in 2002, the landslide sped up, reaching a maximum movement rate of 32 mm/d. The rapid slide seriously threatened the road. To stabilize the landslide and eliminate the damage of landslide to the road, remedying its damage and monitoring further developments are crucial. Based on its kinematic behaviour, remediation was implemented in two phases from November 2002 to October 2003. Systematic monitoring has been carried out since 18 June 2003 to determine kinematic variations of the landslide during the post-remediation period and to assess the effects of remediation and the potential of the landslide for further destructive influences on the roadway.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogaard TA, Antoine P, Desvarreux P, Girayd A, Van Asch TWJ (2000) The slope movements within the Mondorès graben (Dròme, France); the interaction between geology, hydrology and typology. Eng Geol 55:297–312
Chai HJ, Huang RQ, Liu HC (1997) Analysis and evaluation on landslide for its risk degree of damming a river (in Chinese with English abstract). Chin J Geol Haz Con 8(4):1–7
Chai HJ, Liu HC (2002) Study on landslide damming of river in upper of Minjiang River (in Chinese with English abstract). J Mount Sci 20(5):616–620
Chang XJ, Ding J, Wei LW, Wang DW, Mao Y, Yan Y (2007) Distribution of the geological hazards in the upper reaches of the Minjiang River, Sichuan (in Chinese with English abstract). Sedi Geol Tethyan Geol 27(1):103–108
Chen SF, Wilson CJL (1996) Emplacement of the Longmen Shan Thrust-Nappe Belt along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. J Str Geol 18(4):413–430
Fang LG, Sun ZB, Wang Q (2007) The analysis of mechanism and stability of slope reinforced with the pre-forced cable and anti-slipping pile (in Chinese with English abstract). Highway Eng 32(4):152–155
Gui SQ (2005) Design method for using stabilizing piles with pre-stressed anchored cables in landslide remediation works (in Chinese with English abstract). Earth Sci-J China Univ Geosci 30(2):7–15
Jiang LW, Wang ST, Liu HC, Li YS, Wang YS (2002) Research on hypergene Geological hazards in the upstream of Min River (in Chinese with English abstract). J Geol Haz Environ Preserv 13(1):13–17
Kwong AKL, Wang M, Lee CF, Law KT (2004) A review of landslide problems and mitigation measures in Chongqing and Hong Kong: similarities and differences. Eng Geol 76:27–39
Leynes RD, Pioquinto WPC, Caranto JA (2005) Landslide hazard assessment and mitigation measures in Philippine geothermal fields. Geoth 34:209–221
Martens J (2007) Investigation and geogrid reinforced repair of the foxridge drive landslide, Mission, Kansas. Environ Eng Geosci 13(3):255–264
Qiao JP (1994) Study on the regularities governing the density distribution of collapses and landslides on the upper Minjiang River basin (in Chinese with English abstract). Resour Environ in the Yangtze Valley 3(4):365–370
Uribe-Etxebarria G, Morales T, Uriarte JA, Ibarra V (2005) Rock cut stability assessment in mountainous regions. Environ Geol 48:1002–1013
Varnes DJ (1978) Slope movements and types and processes. In: Eckel EB (ed) Landslides and engineering practice, highway res. Board Special Rep 29:20–48
Wang LS, Yang LZ, Li TB, Wei H (2000) Evolution mechanism of Jiaochang earthquake landslide on Ming River and its controlling (in Chinese with English abstract). J Geol Haz Environ Preserv 11(3):195–199
Wang QC (2005) Summary report of remediation design of the Xiaozongqu landslide on Chengdu-Jiuzhaigou Ring Route in Maoxian District, Sichuan Province (in Chinese), pp 5–11
Wei ZA, Li SH, Wang JG, Wan L (2006) A dynamic comprehensive method for landslide control. Eng Geol 84:1–11
Xie MW, Esaki T, Cai MF (2004) A time-space based approach for mapping rainfall-induced shallow landslide hazard. Environ Geol 46(6–7):840–850
Yan EC, Liu HC, Zhang ZY (1998) A study on the distribution regularity of landslide in the Minjiang River between Maowen and Wenchuan County (in Chinese with English abstract). Mount Res 18(2):109–113
Yu T, He CR (2000) Research on the regional stability along the structural belt in Longman Mountains (in Chinese with English abstract). J Seismol Res 23(4):378–383
Zhou PG (2004) Indicator system and techniques of landslide monitoring (in Chinese with English abstract). J Geomech 10(1):19–26
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge support from the Sichuan Provincial Highway Administration Bureau for the landslide monitoring project and also sincerely thank Prof. Daniel Kister for valuable suggestions during the writing of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Wang, Q. Remediation and analysis of kinematic behaviour of a roadway landslide in the upper Minjiang River, Southwest China. Environ Geol 58, 1521–1532 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1653-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1653-x