Abstract
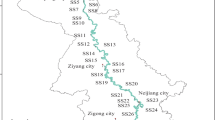
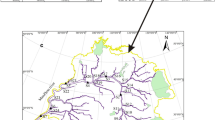
Selecting the Liuyanghe River watershed as an example, using monitoring data of water quality of nearly 10 years and the improved synthesis pollution index method to evaluate the water quality, the research studied the temporal and spatial characteristics of surface water quality of a typical basin in the red soil hilly region, and analyzed reasons for the surface water quality change. The results indicated the improved synthesis pollution index had a better serviceability than other methods, such as, Pollution Index method, Fuzzy Evaluation method, Grey-System method etc. As for the temporal characteristic, because of no-point source pollution, the water quality of Liuyanghe River watershed had become a more and more serious problem over a ten-year period. The spatial characteristic indicated that the pollution degree increased from upstream to downriver. Water quality upstream was better, and the content of the heavy metals was higher in the middle of the river, and the pollution of ammonia nitrogen intensified downriver. The result suggested the improved universal pollution index could be used in the assessment of the water environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao XZ, Zhang GS (1995) Formation and Countermeasures of the vulnerable Eco-environment of Red soil Hilly Region. Rural Eco-environ 11(4):45–48 (In Chinese)
Chang NB, Chen HW, Ning SK (2001) Identification of river water quality using the Fuzzy Synthetic Evaluation approach. J Environ Manage 63(3):293–305
Chaves P, Kojiri T (2007) Deriving reservoir operational strategies considering water quantity and quality objectives by stochastic fuzzy neural networks. Adv Water Resour 30(5):1329–1341
He LM, He ZL (2008) Water quality prediction of marine recreational beaches receiving watershed baseflow and stormwater runoff in southern California, USA. Water Res 42(10–11):2563–2573
Hirsch RM (1982) Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resour Res 18(1):107–121
Karmakar S, Mujumdar PP (2006) Grey fuzzy optimization model for water quality management of a river system. Adv Water Resour 29(7):1088–1105
Karmakar S, Mujumdar PP (2007) A two-phase grey fuzzy optimization approach for water quality management of a river system. Adv Water Resour 30(5):1218–1235
Liou YT, Lo SL (2005) A fuzzy index model for trophic status evaluation of reservoir waters. Water Res 39(7):1415–1423
Lu RK, Shi ZY (2000) Features and recover of degraded red soil. Soil 4:198–209 (In Chinese)
Lu RS, Lo SL (2002) Diagnosing reservoir water quality using self-organizing maps and fuzzy theory. Water Res 36(9):2265–2274
Luo HJ, Zhu JP, Jiang JH (2002) The suggestion of selecting pollution items on water quality evaluation. Environ Monit China 18(4):51–54 (In Chinese)
Ntengwe FW (2006) Pollutant loads and water quality in streams of heavily populated and industrialised towns. Phys Chem Earth 31(15–16):832–839
Nives SG (1999) Water quality evaluation by index in Dalama. Water Res 33(16):3423–3440
Pesce SF, Wunderlin DA (2000) Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Cordoba City on Suquia River. Water Res 34(11):2915–2926
Shetty GR, Malki H, Chellam S (2003) Predicting contaminant removal during municipal drinking water nanofiltration using artificial neural networks. J Memb Sci 212(1–2):99–112
Tian YP, Peng BZ, Xie TS (2001) Opinion on red desertification and types of desertified land in China. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 10(4):380–384 (In Chinese)
Xu ZX (2005a) Single factor water quality identification index for environmental quality assessment of surface water. J Tongji Univ (Nat Sci) 33(3):321–325 (In Chinese)
Xu ZX (2005b) Comprehensive water quality identification index for environmental quality assessment of surface water. J Tongji Univ (Nat Sci) 33(4):482–488 (In Chinese)
Xue QY, Liu JM (2004) Methods and analyses of water pollution comprehensive index assessment. Environ Eng 22(1):64–67 (In Chinese)
Zhang YW (2002) Water quality monitoring and assessment. Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, Zhengzhou (In Chinese)
Zhang XQ, Liang Q (2005) Application of fuzzy matter-element model based on coefficients of entropy in comprehensive evaluation of water quality. J Water Conserv 36(9):1057–1061 (In Chinese)
Zou ZH, Yuan Y, Sun JN (2006) Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment. J Environ Sci 18(5):1020–1023
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by the National 863 High Technologies Research Program of China (Grant No. 2007AA10Z222) and the Natural Science Foundation of China for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 50225926, Grant No. 50425927). Thanks very much for the help of revising the English writing of the paper provided by Dr. Raewyn Steel, and of comments and suggestions to improve a former draft of this manuscript by anonymous and kind reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Fang, Y., Zeng, G. et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of surface water quality by an improved universal pollution index in red soil hilly region of South China: a case study in Liuyanghe River watershed. Environ Geol 58, 101–107 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1497-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1497-4