Abstract
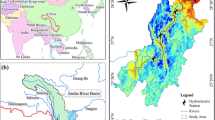
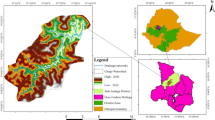
This research selected water soil erosion indicators (land cover, vegetation cover, slope) to assess the risk of soil erosion, ARCMAP GIS ver.9.0 environments and ERDAS ver.9.0 were used to manage and process satellite images and thematic tabular data. Landsat TM images in 2003 were used to produce land/cover maps of the study area based on visual interpreting method and derived vegetation cover maps, and the relief map at the scale of 1:50,000 to calculate the slope gradient maps. The area of water soil erosion was classified into six grades by an integration of slope gradients, land cover types, and vegetation cover fraction. All the data were integrated into a cross-tabular format to carry out the grid-based analysis of soil erosion risk. Results showed that the upper basin of Miyun Reservoir, in general, is exposed to a moderate risk of soil erosion, there is 715,848 ha of land suffered from water soil erosion in 2003, occupied 46.62% of total area, and most of the soil erosion area is on the slight and moderate risk, occupied 45.60 and 47.58% of soil erosion area, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton V (2006) Satellite remote sensing for water erosion assessment: a review. Catena 65:2–18
Awasthi KD, Sitaula BK, Singh BR, Bajacharaya RM (2002) Land-use change in two Nepalese watersheds: GIS and geomorphometric analysis. Land Degrad Dev 13:495–513
Beijing Municipal Commission of Population and Family Planning (2005) New status and characteristics of population development of Beijing. http://www.bjfc.gov.cn/Article/Detail.asp?UNID=8524
Boggs G, Devonport C, Evans K, Puig P (2001) GIS-based rapid assessment of erosion risk in a small catchment in the wet/dry tropics of Australia. Land Degrad Dev 12:417–434
Chen WH, Liu LY, Zhang C, Pan YC, Wang JH, Wang JD (2005) The fast method of soil erosion investigation based on remote sensing. Res Soil Water Conserv 12:8–10
Chinese Soil Taxonomy Research Group, Institute of Soil Science, Academia Sinica and Cooperative Research Group on Chinese Soil Taxonomy (1995) Chinese soil taxonomy (Revised Proposal). China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing
Fan JR, Zhang JH, Zhong XH, Liu SZ, Tao HP (2004) Monitoring of soil erosion and assessment for contribution of sediments to rivers in a typical watershed of the upper Yangtze river basin. Land Degrad Dev 15:411–421
Gao JR (1999) Construction and countermeasures of water protection forest in Miyun reservoir watershed of Beijing City. Bull Soil Water Conserv 19:1–6
Gu ZW, Zhan ZJ, Gao JT, Yao TQ, Chen B (2006) Seismomagnetic research in Beijing and its adjacent area, China. Phys Chem Earth 31:258–267
Lal R (2001) Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad Dev 12:519–539
Li ZG, Luo ZD (2006) On method for evaluating soil erosion severity in county scale—index of soil erosion severity and its application. Bull Soil Water Conserv 26:41–51
Liu JY (1996) Macro-scale survey and dynamic study of natural resources and environment of China by remote sensing. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing, pp 113–124
Ma XW, Yang QK, Liu BY (2002) Assessment of China potential soil and water loss based on GIS. J Soil Water Conserv 16:49–54
Qiao YL, Qiao Y (2002) Fast soil erosion investigation and dynamic analysis in the loess plateau of China by using information composite technique. Adv Space Res 29:85–88
Renard KG, Kertesz A, Markus B, Richter G (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE). Agricultural handbook No. 537. United States Department of Agriculture, Washington, p 665
Siakeu J, Oguchi T (2000) Soil erosion analysis and modeling: a review. Trans Jpn Geomorphol Union 21:413–429
The Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China (1997) National professional standards for classification and gradation of soil erosion, SL 190-1996
Wang XD, Zhong XH, Fan JR (2005) Spatial on the distribution of soil erosion sensitivity on the Tibet Plateau. Pedosphere 15:465–472
Yang DZ, Xu XD, Liu XD, Xu Q, Ding GA, Cheng XH, Chen HL, Zhou HG, Wang ZF, Wang WY (2005) Complex sources of air-soil-water pollution processes in the Miyun reservoir region. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 48((Supp. II)):230–245
Yang QK, Li R, Cao MM (2006) Advances of quantitative assessment on regional soil erosion. Adv Earth Sci 21:848–855
Yu XX, Niu JZ, Xu JL (2004) Effects of closing mountain for forest restoration in the watershed of Miyun reservoir Beijing. For Stud China 6:28–35
Yuan JP (1999) Preliminary study on grade scale of soil erosion intensity. Bull Soil Water Conserv 19:54–57
Zhao XL, Zhang ZX, Liu B, Wang CY (2002) Method of monitoring soil erosion dynamic based on remote sensing and GIS. Bull Soil Water Conserv 22:29–32
Zhou WF, Wu BF (2005) Soil erosion estimation of the upriver areas of Miyun Reservoir located on the Chaobai River using remote sensing and GIS. Trans CSAE 21:46–50
Zhuang DF, Liu JY, Liu ML (1999) Research activities on land use/land cover in the past ten years in China using space technology. Chin Geogr Sci 9:330–334
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KZCX1-YW-08-03) and The Monitoring Program of Water and Soil Conservation in Miyun Reservoir Supported by Haihe River Water Conservancy Commission, The Ministry of Water Resources, People’s Republic of China (Grant No. HX020014). Special thanks to the anonymous referees for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y.C., Zhou, Y.M., Wu, B.F. et al. Risk assessment of water soil erosion in upper basin of Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China. Environ Geol 57, 937–942 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1376-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1376-z