Abstract
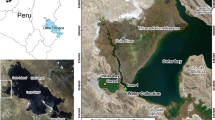
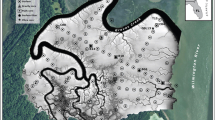
Macrotidal salt marshes play an important role in sedimentary processes in estuaries and can act as a sink for fine sediments and contaminants. This study examines sedimentation rates and the history of heavy metal accumulation in the Allen Creek salt marsh in the Bay of Fundy, Canada. Pb-210 and Cs-137 measurements and accelerated mass spectrometer (AMS) dating indicate a sedimentation rate of about 1.1 cm/year, which is consistent with independent observations. Elevated normalized concentrations of As in the upper section of the deposit may reflect an increase in organic matter content while a consistent decrease in Mn toward the surface of the section may be due to a decrease in natural supply. A peak in metal concentrations in the early to mid twentieth century is attributed to inputs from local foundries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos CL (1984) An overview of the sedimentological research in the Bay of Fundy. In: Gordon DC Jr, Dadswell MJ (eds) Update on the marine environmental consequences of tidal power development in the upper reaches of the Bay of Fundy, Canadian technical report of fisheries and aquatic sciences, 1256, pp 31–44
Appleby BG, Oldfield F (1978) The calculation of lead-210 dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. Catena 5:1–8
Barra R, Cisternas M, Suarez C, Araneda A, Pinones O, Popp P (2004) PCBs and HCHs in a salt-marsh sediment record from South-Central Chile: use of tsunami signatures and 137Cs fallout as temporal markers. Chemosphere 55:965–972
Chen Z, Kostaschuk RM, Yang M (2001) Cases and solutions: heavy metals on tidal flats in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ Geol 40:742–749
Chmura GL, Coffey A, Crago R (2001) Variation in surface sediment deposition on salt marshes in the Bay of Fundy. J Coast Res 17:221–227
Davidson-Arnott Robin GD, Proosdij DV, Ollerhead J, Schostak L (2002) Hydrodynamics and sediment at ion in salt marshes: examples from a macrotidal marsh, Bay of Fundy. Geomorphology 48:209–231
Dellwig O, Hinrichs J, Hild A, Brumsack HJ (2000) Changing sedimentation in tidal flat sediments of the southern North Sea from the Holocene to the present: a geochemical approach. J Sea Res 44:195–208
Dowdle PR, Laverman AM, Oremland RS (1996) Bacterial dissimilatory reduction of arsenic(V) to arsenic(III) in anoxic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1664–1669
Hung GA, Chmura GL (2005) Spatial variability of heavy metals in salt marsh sediments of the Bay of Fundy. In: Percy JA, Evans AJ, Wells PG, Rolston SJ (eds) The changing Bay of Fundy: beyond 400 years, proceedings of the 6th Bay of Fundy workshop, Environment Canada––Atlantic region occasional report no. 23:68–75
Kim G, Hussain N, Church TM, Carey WL (1997) The fallout isotope 207Bi in a Delaware salt Marsh: a comparison with 210Pb and 137Cs as a geochronological tool. Sci Total Environ 196:31–41
Ollerhead J, Davidson-Arnott RGD, Scott A (2007). Cycles of salt marsh extension and contraction, Cumberland Basin, Bay of Fundy, Canada. In: Sanjaume E (ed) Geomorphologia littoral y Quaternari: Homenatge al Professor VM Rossello I Verger (in press)
Palanques A, Sanchez-Cabeza JA, Masque P, Leon L (1998) Historical record of heavy metals in a highly contaminated Mediterranean deposit: the Besos Prodelta. Mar Chem 61:209–217
Parker WR, Aube JG (2002) Metal levels in sediment samples collected under salman aquaculture net pens in the Bay of Fundy, New Brunswick. Surveillance Report EPS-5-AR-02–01, Environment Canada, Environmental Protection Branch-Atlantic Region, Dartmouth, NS
Roman CT, Peck JA, Allen JR, King JW, Appleby PG (1997) Accretion of a New England (USA) salt marsh in response to inlet migration, storms, and sea-level rise. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 45:717–727
Spencer KL (2002) Spatial variability of metals in the inter-tidal sediments of the Medway Estuary, Kent, UK. Mar Pollut Bull 44:933–944
Summerby-Murray R (2002) Interpreting deindustrialised landscapes of Atlantic Canada: memory and industrial heritage in Sackville, New Brunswick. Can Geogr 46:48–62
Tam NF, Wong YS (2000) Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environ Pollut 110:195–205
Valius H (1999) Anthropogenically derived heavy metals in recent sediments of the Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 38:945–962
van Proosdij D, Ollerhead J, Davidson-Arnott RGD, Schostak LE (1999) Allen Creek marsh, Bay of Fundy: a macro-tidal coastal salt marsh. Can Geogr 43:316–322
van Proosdij D, Ollerhead J, Davidson-Arnott RGD (2006) Seasonal and annual variations in the volumetric sediment balance of a macro-tidal salt marsh. Mar Geol 225:103–127
World Bank Group (1998) Pollution prevention and abatement handbook, pp 312–315
Yeats PA, Dalziel JA (2005) Recent heavy metal measurements in the Bay of Fundy. In: Percy JA, Evans AJ, Wells PG, Rolston SJ (eds) The changing Bay of Fundy: beyond 400 years, proceedings of the 6th Bay of Fundy workshop, Environment Canada––Atlantic region occasional report no. 23, pp 56–61
Yang M, Kostaschuk R, Chen Z (2004) Historical changes in heavy metals in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ Geol 46:857–864
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. W. G. Zhang for radioisotope measurements and Dr. J. Ollerhead for field assistance and comments on an early draft of this paper. AMS dates were provided by the Geological Survey of Japan. Financial support was provided by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and East China Normal University. The manuscript greatly benefited from comments by an anonymous reviewer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostaschuk, R., Chen, Z., Saito, Y. et al. Sedimentation rates and heavy metals in a macrotidal salt marsh: Bay of Fundy, Canada. Environ Geol 55, 1291–1298 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1077-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1077-z