Abstract
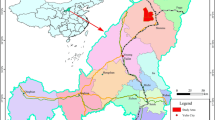
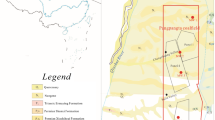
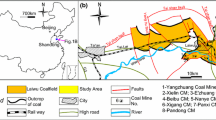
Aquifers overlying coal seams are common water sources in coalmines. The unexpected inflow of water can flood mines and threatens the mine safety. Mine flooding caused by the overlying aquifers has occurred more frequently in recent years in China. Proposed in this paper is a new method that involves three basic maps and two predictions to tackle this geo-hazard. This new approach is based on the water abundance in the overlying aquifer and risk analysis of the roof collapse. It couples groundwater flow models with rock mechanics analysis. The method was successfully applied to prediction of the water intrusion from the overlying aquifer at Jinggezhuang Coalmine in Kailuan, China. The areas with high risk of water intrusion were delineated. Visual Modflow (version 2.61) was used to simulate the inflows at two active working faces. The developed approach can predict the total inflow for a working face and the transient inflow as the working face advances.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao H, Lin Z (1985) Regional characteristics of mine-hydrogeological conditions of coal deposits in China. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 12(2):14–17
Jinggezhuang Mine (1989) Geological report of mining stage in Jinggezhuang Mine, Internal Unpublished Report. Jinggezhuang, Kailuan, China
Shen G, Li B (1992) Theory and practice of specific mining in coal mine. Publishing House of Coal Industry, Beijing, p 210
Waterloo (1993) Visual MODFLOW, User’s Manual—The Most Completely Fully integrated Modeling Environment for MODFLOW, MODPATH and MT3D, Waterloo Hydrogeologic, Inc
Wu Q, Jin Y (1995) Decision system of preventing and remedying mine water in Northern China Coalfield. Publishing House of Coal Industry, Beijing, p 128
Wu Q, Wang M, Wu X (2004) Investigations of retarded groundwater bursting along fault zones in seam floor in coal mines. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci 41:557–572
Xue Y (1989) Principle of groundwater dynamics. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, p 380
Zhao Q (1992) Manual of coal mine safety. Publishing House of Coal Industry, Beijing, p 58
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by China National Natural Science Foundation (grant number 40572149) and the Key Projects of Ministry of Education of P.R. China (grant number 2004-295).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Zhou, W. Prediction of inflow from overlying aquifers into coalmines: a case study in Jinggezhuang Coalmine, Kailuan, China. Environ Geol 55, 775–780 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1030-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1030-1