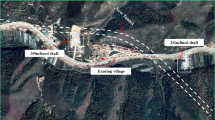
Abstract
Ground vibrations generated by commercial explosives in tunnel construction may cause structural damage in urban areas. Therefore, suppressing the vibration effects and mitigating the possible hazard after blasting is important. We present a new method of controlled blasting that is environmentally friendly, and easy to utilize for tunnel construction. Small charges in this method are detonated sequentially to produce minimum side effects. The efficiency of the charges may be increased based on the previously monitored shots. This method is utilized in a tunnel construction in Istanbul with five experimental shots. In these experiments, the duration and also the quantity of explosives were carefully controlled. We were able to obtain better results with short durations (480 ms) instead of long durations (9,000 ms) although the vibration levels defined as peak particle velocity (PPV) became bigger while the quantity of the explosive charge increased from 3.088 to 9.264 kg.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonym (1986) Vibration of buildings–effects on structures. DIN Standards, pp 4150–4153
Anonym (1987) Explosives and rock blasting. Atlas Powder Company, Dallas
Barton N, Lien L, Lunde J (1974) Analysis of rock mass quality and support practice in tunneling and a guide for estimating support requirements. Internal Report of Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Oslo, Norway, pp 6–9
Bhandari S (1997) Engineering rock blasting operations. AA Balkema, Rotterdam
Blair DP (1990). Some problems associated with standard charge weight vibration scaling laws. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international symposium on fragmentation by blasting, Brisbane, pp 149–158
Duvall WI, Fogelson DE (1962) Review criteria for estimating damage to residences from blasting vibration. US Bureau of Mines Report of Investigation 5968
Edwards AT, Northwood TD (1960) Experimental studies of the effects of blasting on structures. Engineering 210:538–546
Ghosh A (1983) A new analytical predictor of ground vibrations induced by blasting. M.Sc. Thesis of the University of Arizona
Guha R (1984) Ground vibrations from surface mine blasting-an investigation. M.Tech.Thesis of Mining Engineering Department of Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad
Harrison PJ, HudsonFREig JA (2000) Engineering rock mechanics. Pergamon, part 1–2
Kahriman A, Ozer U, Aksoy M, Karadogan A, Tuncer G (2006) Environmental impacts of bench blasting at Hisarcik Boron open pit mine in Turkey. Environ Geol 50(7):1015–1023
Khandelwal M, Singh TN (2005) Prediction of blast induced ground vibrations and frequency in opencast mine: a neural network approach. J Sound Vib (in press)
Konya CJ, Walter EJ (1990) Surface blast design. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Kuzmenko AA, Vorobey VD, Denisyuk II, Dauetas AA (1993) Seismic effects of blasting in rock. Balkema, Rotterdam
Langefors U, Kihlstrom B, Westerberg H (1958) Ground vibration in blasting. Water power
Lizotte YC (1996) Controlled blasting at the CANMET experimental mine. Mining Engineers, pp 74–78
Martin CAT, Faroni K, Gelormino T (2000) Fifteen years of blast vibration control and improved public relations for two trap rock quarries. In: Proceedings of the 26th annual conference on explosion and blasting techniques, ISEE, vol. 1, California, pp 187–196
Nicholls HR, Johnson CF, Duvall WI (1971) Blasting vibration effects on structures. US Bureau of Mines Report of Investigation 656
Olofsson SO (2002) Blasters’ manual. APPLEX AB, Ärla
Pal Roy P, Chakraborty AK (2000) In: Holmberg R (ed) Explosives and blasting technique. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 71–78
Persson PA, Holmberg R, Lee J (1994) Rock blasting and explosives engineering. CRC, USA
Rosental FM, Morlock GL (1987) Blasting guidance manual. US Office of surface mining reclamation and enforcement
Singh PK, Singh RB, Singh DP (1998) A study on the effect of total charge versus charge per delay on ground vibration due to blasting. FOSMIN’98, India, pp 128–133
Singh RB, Pal Roy P (1993) Blasting in ground excavations and mines. AA Balkema, Rotterdam
Singh PK, Vogt W (1998) Ground vibration: prediction for safe and efficient blasting. Erzmetall 51(10):677–684
Singh PK, Vogt W, Singh RB, Singh MM, Singh DP (1997) Response of surface structures to rock blasting. Mineral Resource Engineering Imperial College Press, 6(4):185–194
Siskind DE, Stagg MS, Kopp JW, Dowding CH (1980) Structure response and damage produced by ground vibration from surface mine blasting. US Bureau of Mines Report of Investigation 8507
Venkatesh HS (2005) Influence of total charge in a blast on the intensity of ground vibrations-field experiment and computer simulation. Fragblast 9(3):127–138
Zhang J (2000) In: Holmberg R (ed) Explosives and blasting technique. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 335–341
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges the support of the Alke Atac Musterek Ortakligi Company and would like to thank the field supervisor and workers for the efforts to complete the experiments in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzu, C. The mitigation of the vibration effects caused by tunnel blasts in urban areas: a case study in Istanbul. Environ Geol 54, 1075–1080 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0875-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0875-7