Abstract
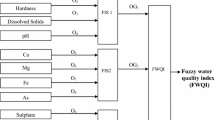
A method based on concept of fuzzy set theory has been used for decision-making for the assessment of physico-chemical quality of groundwater for drinking purposes. Conventional methods for water quality assessment do not consider the uncertainties involved either in measurement of water quality parameters or in the limits provided by the regulatory bodies. Fuzzy synthetic evaluation model gives the certainty levels for the quality class of the water based on the prescribed limit of various regulatory bodies and opinion of the experts from the field of drinking water quality. In this paper, application of fuzzy rule based optimization model is illustrated with twenty groundwater samples from Sohna town of Gurgaon district of Southern Haryana, India. These samples were analysed for 15 different physico-chemical parameters, out of them nine important parameters were used for the quality assessment using fuzzy synthetic evaluation approach. From this study, it has been concluded that all the water samples are in acceptable category whose certainty level ranges from 44 to 100%. Water from these sources can be used for the drinking purposes if alternate water source is not available without any health concern on the basis of physico-chemical characteristics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (1989) Standard method for examination of water and waste water, 17th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Bureau of Indian Standards (1991) Indian Standard specification for drinking water. BIS Publication No. IS: 10501, New Delhi
Chang N, Chen HW, King SK (2001) Identification of river water quality using the fuzzy synthetic evaluation approach. J Environ Manage 63:293–305
Dahiya S, Datta D, Kushwaha HS (2005) A fuzzy synthetic evaluation approach for assessment of physico-chemical quality of groundwater for drinking purposes. Environ Geochem 8(1&2):158–165
Dahiya S, Singh B, Gaur S, Garg VK, Kushwaha HS (2007) Analysis of groundwater quality using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. J Hazard Mater (in press). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.119
Dahiya S, Kaur A, Jain N (2000) Prevalence of fluorosis among school children of district Bhiwani, Haryana—A case study. Indian J Environ Health 42(4):192–195
Duque WO, Huguet NF, Domingo JL, Schuhmacher M (2006) Assessing water quality in rivers with fuzzy inference systems: A case study, Environ Int 32(6):733–742
Fisher B (2003) Fuzzy environmental decision-making: application to air pollution, Atmos Environ 37:1865–1877
Garg VK, Dahiya S, Chaudhary A, Deepshikha (1998) Fluoride distribution in underground waters of Jind district, Haryana, India. Ecol Environ Conserv 4(172):19–23
Klir GJ, Yuan B (1995) Fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic, theory and applications. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Mamdani EH (1976) Advances in the linguistic synthesis of fuzzy controllers. Int J Man Mach Stud 8(6):669–678
Mckone TE, Deshpande AW (2005) Can fuzzy logic bring complex environmental problems into focus? Environ Sci Technol 39:42A–47A
Mujumdar PP, Sashikumar K (2002) A fuzzy risk approach for seasonal water quality management of river water. Water Resour Res 38(1):1004
Sii HI, Sherrard JH, Wilson TE (1993) A water quality index based on fuzzy sets theory. Proceedings of the 1993 Joint ASCE-CSCE National Conference on Environmental Engineering, July 12–14, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, pp 253–259
World Health Organisation (1984) Guidelines for drinking water quality (Volume II) Recommendation, Geneva
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8:338–353
Acknowledgement
Authors are thankful to University Grants Commission, Government of India, New Delhi for financial support by funding this Project to Dr. V. K. Garg under Sanction number F.3/99/2001(SR-II).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, B., Dahiya, S., Jain, S. et al. Use of fuzzy synthetic evaluation for assessment of groundwater quality for drinking usage: a case study of Southern Haryana, India. Environ Geol 54, 249–255 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0812-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0812-9