Abstract
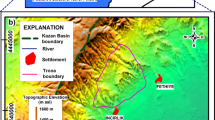
Lumped parameter modeling of environmental tracer (tritium, CFCs and tritiogenic helium-3) transport in the Kirkgoz karst springs (Antalya-Turkey) appears to be a useful tool for assessing the vulnerability to contamination. Based on tritium observations between 1963 and 2000, the springs revealed a mean residence time (MRT) of 120 years. This suggests an active transport volume of 71 billion cubic meters for the aquifer, a value that is coherent with the estimated void volume of karst aquifer based on the mass of associated travertine deposits. The CFC-11 and CFC-12 MRTs are in agreement with tritium-based MRT, after correcting for excess air effect. Excess crustal and mantle helium flux hindered the use of tritiogenic helium-3 as a potential tracer. The residence time distribution (RTD) indicates a groundwater transport system that is fed by recharges extending back to past several hundred years. This wide RTD suggests that any recent contamination that may have entered the system could progress slowly within the entire aquifer but would be unnoticed in the early period because of the dilution effect of uncontaminated past recharge waters. Once the contamination is recognized, it may last for many centuries ahead even if the contamination practice is stopped. Thus, control of contaminant release to aquifer and monitoring of contaminant level in Kirkgoz springs is an immediate task for the associated public health authorities.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cakir B (1998) Determination of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) based groundwater residence times in the karstic discharges of Western Taurids. MSc Thesis, Hacettepe University, Ankara [in Turkish]
Coskun N, Nazik M, Altug A (1985) Antalya-Kirkgoz springs and travertine plateau karst area investigation report. Geotechnical Services and Groundwater Division (DSI) open file report, Ankara [in Turkish]
Denizman C (1989) Hydrogeological investigation of the Kirkgoz springs and Antalya travertine plateau. MSc Thesis, Hacettepe University, Ankara [in Turkish]
DSI (2004) Hydrogeology and isotope hydrology of Antalya travertine plateau. DSI open file report, Ankara [in Turkish]
Ekmekci M (2005) Pesticide and nutrient contamination in the Kestel polje-Kirkgoz karst springs, Southern Turkey. Environ Geol 49:19–29
Ford DC, Williams PW (1989) Karst geomorphology and hydrology. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 601
Glover C, Robertson AHF (2003) Origin of tufa (cool-water carbonate) and related terraces in the Antalya area, SW Turkey. Geol J 38(3–4):329–358
Gonfianatini R, Fröhlich K, Araguas-Araguas L, Rozanski K (2003) Isotopes in groundwater hydrology. In: Kendall C, McDonnel JJ (eds) Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 203–246
Gunay G, Yayan TY (1979) Hydrogeology of the Antalya Kirkgoz Karst Springs. DSI open file report, Ankara [in Turkish]
Gunay G, Tezcan L, Ekmekci M, Atilla O (1995) Present state and future trends of karst ground water pollution in Antalya Travertine Plateau-Turkey. In: Karst groundwater protection, final report of COST Action 65-EUR16457 EN. Brussels, pp 305–324
GNIP data base (2007) International Atomic Energy Agency. http://www.iaea.org/inisnkm. Cited 5th February 2006
Kamenski IL, Tokarev IV, Tolstikhin IN (1991) 3H–3He dating: a case for mixing of young and old groundwaters. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 55:2895–2899
Karaguzel R, Scholz R, Ebel B (1999) Hydrogeological investigation of Antalya basin concerning the future domestic water needs of Antalya City (Turkey). Environ Geol 38/2:159–167
Kazemi GA, Lehr JH, Perrochet P (2006) Groundwater age. Wiley, New York, p 325
Kincaid TR (1999) Morphologic and fractal characterization of saturated karstic caves. PhD Thesis, University of Wyoming, Laramie, Wyoming
Korkmaz N (1990) The estimation of groundwater recharge from spring hydrographs. Hydrol Sci 35:209–217
Maloszewski P (1996) LP models for the interpretation of environmental tracer data. In: Manual on mathematical models in isotope hydrology, IAEA-TECDOC-910. Vienna, Austria, pp 9–58
Manual of Barometry (1963) WBAN volume. US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau, Washington, pp 850
Muhammetoglu A, Yalcin OB (2003) An integrated water pollution control project to protect groundwater of Antalya Plain from diffused sources. In: Proceedings of diffuse pollution conference, Dublin, chapter 7B groundwater, pp 39–45
Nativ R, Gunay G, Hotzl H, Reichert B, Solomon DK, Tezcan L (1999) Separation of groundwater-flow components in a karstified aquifer using environmental tracers. Appl Geochem 14:1001–1014
Niemi AJ (1990) Tracer responses and control of vessels with variable flow and volume. Isotopenpraxis 26:435–438
NOAA, ALE/GAGE data base (2007) National Oceanic and Atmospheric Agency. http://www.cdiac.esd.ornl.gov/ndps/alegage.html. Cited 5th February 2006
Ozyurt NN (2005) Investigation of the residence time distribution in the Aladag (Kayseri-Adana, Turkey) karstic aquifer. PhD Thesis, Hacettepe University, Ankara [in Turkish]
Ozyurt NN Bayari CS (2005a) LUMPED UNSTEADY: a Visual Basic® code of unsteady-state lumped-parameter models for mean residence time analyses of groundwater systems, Comput Geosci 31(3):329–341
Ozyurt NN, Bayari CS (2005b) Unsteady state lumped parameter modeling of 3H and CFCs transport: analyses of mean residence time in a mountainous karstic aquifer. Hydrol Process 19:3269–3284
Plummer LN, Busenberg E (1999) Chlorofluorocarbons. In: Cook P, Herczeg AL (eds) Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 441–478
Senel M (1997) Geological maps of Turkey 1/100,000 scale Isparta-K10 and K11 sheets. MTA Publications, Ankara [in Turkish]
Solomon DK, Cook PG (1999) 3H and 3He. In: Cook P, Herczeg AL (eds) Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 397–424
Tezcan L (1993) Mathematical modeling of karst aquifer systems using tritium isotope. PhD Thesis, Hacettepe University, Ankara [in Turkish]
Thorthwaite CW (1944) Report of the committee on transpiration and evaporation. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:687
UNDP (1983) Karst Waters of Southern Turkey, Technical Report, United Nations Development Programme, Report no. DP/UN/TUR-77–015/1, UNDP, New York, p 207
Yidirim M, Topkaya B (2006) Pollution potential of groundwater resources in Antalya city. Fresenius Environ Bull 15(9A):981–988
Yurtsever Y (1979) Environmental isotopes as a tool in hydrogeological investigations in southern karts regions of Turkey. In: Proceedings of the international seminar on Karst Hydrogeology, Antalya, Ankara, pp 269–293
Acknowledgment
D. Kip Solomon (University of Utah) and C. Serdar Bayari (Hacettepe University) are gratefully acknowledged for stimulating the author to study CFCs and noble gas isotopes in karst systems. This study is dedicated to the memories of Yucel Yurtsever and Ronit Nativ whose studies contributed a lot to the understanding of the hydrogeology of Kirkgoz springs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozyurt, N.N. Residence time distribution in the Kirkgoz karst springs (Antalya-Turkey) as a tool for contamination vulnerability assessment. Environ Geol 53, 1571–1583 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0811-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0811-x