Abstract
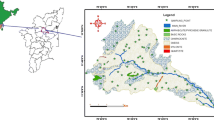
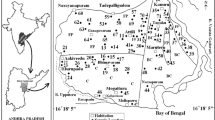
Systematic hydrogeochemical survey has been carried out for understanding the sources of dissolved ions in the groundwaters of the area occupied by Sarada river basin, Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Khondalites, charnockites and granite gneisses and calc-granulites of Precambrians and alluvial deposits of Quaternaries underlie the study area. Groundwaters are both fresh and brackish; the latter waters being a dominant. Most groundwaters are characterized by Na+:HCO −3 facies due to chemical weathering of the rocks. Enrichment of Na+, K+, Cl−, SO 2−4 , NO −3 and F− in some groundwater samples is caused by seawater intrusion, locally accompanied by ion-exchange, and anthropogenic activities, resulting in an increase of brackish in the groundwaters. Based on the results of this hydrogeochemical study, suitable management measures are recommended to solve the water quality problems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammineedu E, Venkateswara Rao V, Prakasa Rao BS (2002) Significance of rain gauge network in assessment of water resources of Sarada River basin. J Appl Hydrol XV:67–76
APHS (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Appelo CAJ (1994) Some calculations on multicomponent transport with cation exchange in aquifers. Ground Water 32:968–975
Appelo CAJ, Willemsen A (1987) Geochemical calculations and observations on salt-water intrusions, I, a combined geochemical/mixing cell model. J Hydrol 94:313–330
Appelo CAJ, Willemsen A, Beckman HE, Griffioen J (1990) Geochemical calculations and observations on salt-water intrusions, II, validation of a geochemical model with column experiments. J Hydrol 120:225–250
Appelo CAJ, Hendriks JH, Veldhuizen MV (1993) Flushing factors and a sharp front solution for solute transport with multicomponent ion exchange. J Hydrol 146:89–113
Back W (1966) Hydrochemical facies and groundwater flow pattern in northern part of Atlantic Coastal Plain. US Geological Survey Professional Paper 498A
BIS (1991) Drinking water specifications. Bureau of Ifndian Standards, IS 10500, India
CGWB (2001) Hydrogeological framework and development prospects in Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh. Technical Report of Central Ground Water Board, Hyderabad, Southern Region, India
Davis SN, Dewiest JM (1966) Hydrogeology. Wiley, New York
Drever JI (1988) The Geochemistry of natural waters. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Faure G (1998) Principles and applications of geochemistry. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Fetter CW (1990) Applied hydrogeology. CBS Publishers and Distributors, New Delhi, India
Hem JD (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. US Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 2254, Scientific Publishers, India
John Devadas D, Subba Rao N, Srinivasa Rao KV, Thirupathi Rao B, Subrahmanyam A (2006a) Drainage characteristics of the Sarada river basin, Andhra Pradesh for watershed management. J Ind Acad Geosci (In press)
John Devadas D, Subba Rao N, Thirupathi Rao B, Srinivasa Rao KV, Subrahmanyam A (2006b) Hydrogeomorphological studies for the location of groundwater potential zones in the Sarada river basin. Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh. Gond Geol Mag 21:59–64
Karanth KR (1991) Impact of human activities on hydrogeological environment. J Geol Soc India 38:195–206
Langelier WF, Ludwig HF (1942) Graphic method for indicating the mineral character of natural water. J Am Water Works Assoc 34:335–352
Pawar NJ, Shaikh IJ (1995) Nitrate pollution of groundwaters from basaltic aquifers–Deccan trap hydrologic province, India. Environ Geol 25:197–204
Prudhviraj KN, Vaidyanadhan R (1981) Geomorphology and evaluation of the Sarada river basin, Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Ann Natl Assoc Geogr I:24–35
Richard LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. US Department of Agriculture Hand book 60
Sawyer CN, McCarty PL (1967) Chemistry for sanitary engineers. McGraw-Hill, New York
Singh RP, Chauhan BS, Swaroop D, Yadev YS (2000) Seasonal variation in groundwater quality of Agra city. Indian J Environ Health 42:59–69
Stallard RE, Edmond JM (1983) Geochemistry of Amazon River-the influence of the geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. J Geophysical Res 88:9671–9688
Subba Rao N (2001) Geochemistry of groundwater in parts of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 41:552–562
Subba Rao N (2002) Groundwater chemistry in two different hydrogeologic environments. J Appl Geochem 4:61–70
Subba Rao N (2003) Groundwater quality–focus on fluoride concentration in rural parts of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Hydrol Sci J 45:835–847
Subba Rao N (2006) Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 49:413–429
Subba Rao N, John Devadas D (2003) Fluoride incidence in groundwaters in an area of Peninsular India. Environ Geol 45:243–251
Subba Rao N, Prakasa Rao J, Nagamalleswara Rao B, Niranjan Babu P, Madhusudhana Reddy P, John Devadas D (1998) A preliminary report on fluoride content in groundwaters of Guntur area, Andhra Pradesh, India. Curr Sci 75:887–888
Subba Rao N, Srinivasa Rao G, Venkateswara Rao S, Madhusudhana Reddy P, John Devadas D (1999) Environmental control of groundwater quality in a tribal region of Andhra Pradesh, India. Indian J Geol 71:299–304
Subba Rao N, Prakasa Rao J, John Devadas D, Srinivasa Rao KV, Krishna C, Nagamalleswara Rao B (2002) Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality in a developing urban environment of a semi-arid region, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 59:159–166
Subba Rao N, Saroja Nirmal I, Suryanarayana K (2005) Groundwater quality in a coastal area–a case study from Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 48:534–550
Subba Rao N, Prakasa Rao J, Subrahmanyam A (2006) Principal component analysis in groundwater quality in a developing urban area of Andhra Pradesh. J Geol Soc India (In press)
Tipper ET, Bickle MJ, Galy A, West AJ, Pomies C, Chapman HJ (2006) The short term climatic sensitivity of carbonate and silicate weathering fluxes–insight from seasonal variations in river chemistry. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70:2737–2754
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology. Wiley, New York
White AF, Schulz MS, Lowenstern JB, Vivit DV, Bullen TB (2005) The ubiquitous nature of accessory calcite in granitoid rocks-implications for weathering, solute evolution and petrogenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 69:1455–1471
WHO (1984) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wodeyar BK, Srinivasan G (1996) Occurrence of fluoride in the groundwaters and its impact in Peddavankahalla basin, Bellary district, Karnatakaa preliminary study. Curr Sci 70:71–74
Zhang J, Huang WW, Letolle R, Jusserand C (1995) Major element chemistry of the Huanghe (Yellow River), Chinaweathering processes and chemical fluxes. J Hydrol 168:173–203
Acknowledgments
The first author, D. John Devadas, is grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi–110 016 for providing the financial assistance to carryout the present work under the Young Scientist Scheme (SR/FTP/ES-06/2003). The authors are very much thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their critical comments and valuable suggestions in improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
John Devadas, D., Subba Rao, N., Thirupathi Rao, B. et al. Hydrogeochemistry of the Sarada river basin, Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 52, 1331–1342 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0577-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0577-6