Abstract
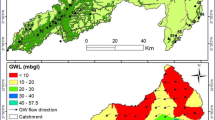
The Ordos Basin of China encompasses Shaanxi, Gansu, and Shanxi provinces, Ningxia and Inner Mongolia autonomous regions. It lacks significant surface water resources. Among the water-bearing formations, the Luohe formation, with an area of 1.32×105 km2, is the most prospective aquifer. Groundwater quality data collected at 211 boreholes drilled into the Luhe formation indicate a complex distribution of groundwater chemistry. The hydrochemical properties were used to study the recharge, runoff, and discharge conditions of the groundwater in Ordos Basin and to evaluate sustainable groundwater resources. In the northern part of the basin, the hydrochemistry types and the total dissolved solids (TDS) show a clear lateral transition from SEE to NWW, indicating that the groundwater gets recharge in the northwest region and discharges in the southeast region. In the southern part of the basin, maximum TDS occurs at the center of the Malian River valley, from which the TDS decreases radially. Therefore, the groundwater in the southern basin gets recharge from the southeast and southwest regions, and the Malian River valley is the discharge zone. As a result of this research, the areas with portable groundwater were delineated. They include most of the southeast region of the Sishili Ridge, east of the Ziwu Mountain, and the southwest corner of the basin. The TDS of the groundwater in these regions is less than 1 g/l, and the hydrochemistry type is either HCO3 or HCO3·SO4.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang P, Wei Z, Liao Z, et al (1987) Special hydrogeology. Geology Publishers, Beijing
Hou G, Zhang M et al (2004) Groundwater resources and their sustainable utilization in the Ordos Basin. Shaanxi Science and Technology Publisher, Xi’an, pp 149–165
Li Y, Feng J, Wang W (2004) The groundwater system analysis of Cretaceous system of Ordos basin. Northwestern Geol 37(2):90–95
The Fourth Hydrogeology Team of Geology Bureau of Heibei province (1978) Hydrogeology Manual. Geology Publishers, Beijing
Wang D, Zhang R, Shi Y (1995) The basis of hydrogeology. Geology Publishers, Beijing
Wang W, Liu Z, Li Y (2004) The characteristics of the groundwater resources of the Cretaceous system and its correct exploitation and utilization methods in Ordos Basin. Groundwater resources and their sustainable utilization in the Ordos Basin. Shaanxi Science and Technology Publisher, Xi’an, pp 459–463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wan, W., Wu, Y. et al. Application of hydrochemical signatures to delineating portable groundwater resources in Ordos Basin, China. Environ Geol 49, 430–436 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-0100-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-0100-5