Abstract
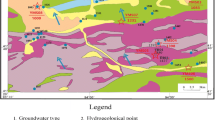
The sources of nitrate in the shallow groundwater at urban area, Hangzhou City, China were investigated using chemical and isotopic techniques. Groundwater electric conductivity was high in the study area and ranged from 369–1,544 μS/cm. Most of the groundwater was weakly alkaline and the groundwater chemistry was seriously influenced by land use in the city. There was a high frequency of groundwater (43% of total) with nitrate above World Heath Organization’s standards of 10 mg NO3/L. The different land-use areas had different nitrate concentrations (0.04–34.41 mgN/L) and δ15N NO3 values (7.8~35.5‰). Domestic wastewater was the major nitrate source of shallow groundwater in the urban area, and the point source (septic tank) still existed in residential settings. At agricultural settings manure was the major NO3 sources. High δ15N NO3 value (>20‰) and temporal variations of the δ15N NO3 value suggested that in residential areas it probably resulted from denitrification.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravena R, Evans ML, Cherry JA (1993) Stable isotopes of oxygen and nitrogen in source identification of nitrate from septic system. Ground Water 31:180–186
Aravena R, Robertson WD (1998) Use of multiple isotope tracers to evaluate denitrification in groundwater: study of nitrate from a large-flux septic system plume. Ground Water 36:975–982
Dong L (2001) GIS-based nonpoint source pollution modeling in West Lake watershed. PhD Thesis. Zhejiang University, pp 17–20
Flipse W, Bonner F (1985) Nitrogen-isotope ratios of NO3 in groundwater under fertilized fields. Ground Water 23:59–67
Fogg GE, Rolston DE, Decker DL (1998) Spatial variation in nitrogen isotope values beneath nitrate contamination sources. Ground Water 36:418–426
Gilliom RJ, Alley WM, Gurtz ME (1995) Design of the National Water-Quality Assessment Program: occurrence and distribution of water-quality conditions, US Geol Surv Circ 1112, 33 pp
Gormly JR, Spalding RF (1979) Sources and concentrations of nitrate-nitrogen in groundwater of the central Platte region, Nebraska. Ground Water 17:291–301
Heaton T (1986) Isotopic studies of nitrogen pollution in the hydrosphere and atmosphere: A review. Chem Geol 59:87–102
Helmut K (2000) Soil and groundwater contamination and remediation technology in Europe. In: Sato K (ed) Groundwater updates. Springer, Best-set Typesetter Ltd., Hong Kong, pp 3–8
HESRI (Hangzhou Environment Science Research Institute) (1984) Water pollution, sources and control plan in the Grand Canal area in Hangzhou City. pp 228–244
Hirata KM (1996) Pollution of soil and groundwater and its management (in Japanese). Law and Regulations Center Publishing House, Tokyo, pp 181–193
Hübner H (1986) Isotope effects of nitrogen in the soil and biosphere. In: Fritz P, Fontes J (eds) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry, 2. The terrestrial environmental. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 361–425
Junk G, Svec HV (1958) The absolute abundance of the nitrogen isotopes in the atmosphere and compressed gas from various sources. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 14:234–243
Komor SC, Anderson HW (1993) Nitrogen isotopes as indicators of nitrate sources in Minnesota sand-plain aquifers. Ground Water 31:269–270
Kreitler CW (1975) Determining the sources of nitrate in groundwater by nitrogen isotope studies. Report of investigations No. 83. Austin, Texas: University of Texas at Austin Bureau of Economic Geology
Kreitler CW (1979) Nitrogen-isotope ratio studies of soils and groundwater nitrate from alluvial fan aquifer in Texas. J Hydrol 42:147–170
Kreitler CW, Ragone SE, Katz BG (1978) 15 N/14 N ratios of groundwater nitrate, Long Island, New York. Ground Water 16:404–409
Madison RJ, Brunett JO (1985) Overview of the occurrence of nitrate in ground water of the United States, in National water summary 1984—Hydrologic events, selected water-quality trends, and ground-water resources: US Geol Surv Water-Suppl Pap 2275:93–105
Mariotti A, Landreau A, Simon B (1988) 15 N isotope biogeochemistry and natural denitrification process in groundwater: Application to the chalk aquifer of northern France. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:252–268
Nolan BT (1999) Nitrate behavior in groundwater of southeastern USA. J Environ Qual 28:1518–1527
Smith Rl, Howes BL, Duff JH (1991) Denitrification in nitrate contaminated groundwater: occurrence in steep vertical geochemical gradients. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:1815–1825
Spalding RF, Exner ME (1993) Occurrence of nitrate in groundwater-a review. J Environ Qual 22:392–402
Spalding RF, Exner ME, Lindau CW, Eaton DW (1982) Investigation of sources of groundwater nitrate contamination in Burbank-Wallula area of Washington, USA. J Hydrol 58:307–324
Spalding RF, Fulton JW (1988) Groundwater munition residues and nitrate near Grand Island, Nebraska, USA., J Contam Hydrol 2:139–153
Wada E, Hattori A (1976) Natural abundance of 15N in particulate matter in the North Pacific Ocean. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 40:249–251
Wells ER, Krothe NC (1989) Seasonal fluctuation of δ15N of groundwater nitrate in a mantled karst aquifer due to macropore transport of fertilizer-derived nitrate. J Hydrol 112:191–201
WHO (World Heath Organization) (1984) Guidelines for drinking water quality. Recommendation 1, WHO, Geneva
Williams AE, Lund JL, Johnson JA, Kabala ZJ (1998) Natural and anthropogenic nitrate contamination of groundwater in a rural community, California. Environ Sci Technol 32:32–39
ZGEMS (Zhejiang Geological Environment Monitoring Station) (1992) Report of groundwater using and protection in Hangzhou (in Chinese)
ZGS (Zhejiang Geology and Survey Bureau) (1986) (in Chinese) Hunan Map Press, Hunan
Zhang PK (1999) The climate of Zhejiang Province and its application (in Chinese). Weather Publish House, Beijing
Zhu GW (2001) Pollution of sediment in the Grand Canal and its ecological risk (in Chinese). Zhejiang University, PhD Thesis
ZSB (Zhejiang Statistical Bureau) (1983–2001) Zhejiang statistical yearbook (in Chinese). Chinese Statistical Publishing House, Beijing
ZSIO (Zhejiang Soil Investigation Office) (1993) Zhejiang soil species chronicles (in Chinese). Zhejiang Science and Technology Publish House, Hangzhou
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Key Basic Research Special Foundation Program (973 program, No. 2002CB410807) for their financial support. The authors wish to express their gratitude to the Laboratory of Aquatic Environmental Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Japan, for supporting the chemical analysis and collection of samples. The authors appreciate the assistance of Dr. S. Ueda, College of Bioresource Sciences, Nihon University, Japan, for his help on stable isotope analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, F. et al. Detection of nitrate sources in urban groundwater by isotopic and chemical indicators, Hangzhou City, China. Env Geol 45, 1017–1024 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-0962-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-0962-y