Abstract
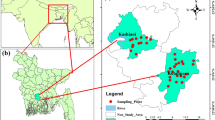
A hydrochemical study has been carried out on the fresh groundwater resources of Potharlanka, Krishna Delta, India. Groundwater samples were collected at 58 sites and analyzed in June and December 2001. The groundwater is mildly alkaline with a pH of 7.2–8.2, electrical conductivity (EC) varies from 645–4,700 μS/cm in June 2001 (pre-monsoon) and from 605–5,770 μS/cm in December 2001 (post-monsoon). More than 75% of the samples have >1000 mg/l TDS which is higher than the maximum permissible limit for potable water. Na and Cl are the dominating cations and these are directly proportional to TDS. Extremely low HCO3 /Cl and variable high Mg/Ca (molar ratios) indicated the transformation of the fresh groundwater aquifer systems to saline. Groundwater of this island is classified as Na–Cl, Na–Ca–Cl–HCO3, Na–Mg–Cl–SO4 and mixed types. A high percentage of mixed water types indicates the possibility of simultaneous fresh groundwater dilution activity along with a seawater ingression/intrusion process. Low rainfall and excessive withdrawal of groundwater has caused the increase of saline water intrusion.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste, 16th edn. Am Public Health Assoc, Washington, DC, pp 1–100
Biksham G, Subramanyam V, Griker R Van (1991) Heavy metals distribution in the Godavari river regions. Environ Geol Water Sci 17:117–126
Brown E, Skougstad MW, Fishmen MJ (1983) Method for collection and analyzing of water samples for dissolved minerals and gases. US Govt Printing Office, Washington, DC, pp 1–75
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical character of natural water, 2nd edn. USGS Water Supply Paper 2254, 263 pp
Howard KWF, Mullings E (1996) Study of groundwater flow and saline water in the Clarendou Basin, Jamaica. Groundwater 34(5):801–810
Karanath KR (1987) Quality of groundwater In: Karnath KR (ed) Groundwater assessment development and management Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, pp 217–275
Mercado A (1985) Use of hydrochemical pattern in carbonate, sand and sandstone aquifers to identify intrusion and flushing saline water. Groundwater 23(5):635–645
Saxena VK, Radhakrishna I, Krishna KVSS, Nagini V (2002a) Nitrate pollution in groundwater, Krishna delta. In: Thangarajan M, Rai SN, Singh VS(eds) Proc Int GWC. Dindigul, Oxford & IBH Publisher, New Delhi, pp 261–269
Saxena VK, Krishna KVSS, Singh VS, Jain SC (2002b) Hydrochemical study for delineation of fresh groundwater region in the Potharlanka, Krishna Delta, India. In: Rao, Reddy, Sarala, Raju (eds) Proceeding Int Conference of Hydrology and watershed management, JNTU, Hyderabad. BS Publisher, Hyderabad, pp 200–211
Subba Rao N (2002) Geochemistry of groundwater in parts of Guntur Dist., A.P., India. Environ Geol 41:552–562
USPHA G (1993) International standard for drinking water. United States Public Health Association, US Govt Printing Office, Washington, DC, pp 75–88
WHO (1984) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization, Washington, DC, pp 333–335
Acknowledgements
Thanksare extended to Dr. V.P. Dimri, Director, National Geophysical Research Institute, Hyderabad, for his kind permission to publish this paper. Mr. P.T.Varghese is also thanked for his assistance in preparing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, V.K., Singh, V.S., Mondal, N.C. et al. Use of hydrochemical parameters for the identification of fresh groundwater resources, Potharlanka Island, India. Env Geol 44, 516–521 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0807-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0807-0