Abstract.
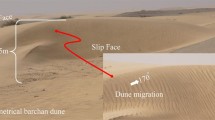
Serious hazards have taken place in urban areas and road construction in Saudi Arabia because of the presence of accumulations of drifting sand dunes. Several researches, which carried out investigative work to solve this problem, were reviewed. Three locations of dune fields along the area between Jeddah and Al-Lith were investigated. The dune forms was identified. Detailed field investigations showed that barchan dunes are dominant in the area. The sands from the studied locations were found to be similar in grain size and shape parameters. Mineralogically, the sand reflects the composition of the surrounding igneous and metamorphic rocks. Regression analyses were performed and empirical relationships between dune height, width, windward length, slip-face length, and rate of movements were developed. Relatively strong relations exist between these parameters. The most important geometric parameter controlling dune movement with wind speed and direction is determined to be the dune height. A reasonable similarity occurs between the barchan dunes in the study area and those existing in Al Nufud, Al Jafurah sand seas, and Khulays area. The studied dune fields pose some natural hazards on the roads, and the surrounding buildings and constructions in the villages along the area between Jeddah and Al-Lith, especially during wind storms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Harthi, A. Geohazard assessment of sand dunes between Jeddah and Al-Lith, western Saudi Arabia. Env Geol 42, 360–369 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-001-0501-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-001-0501-z