Abstract.
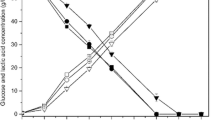
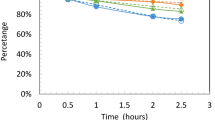
Alkaline wet oxidation (WO) (using water, 6.5 g/l sodium carbonate, and 12 bar oxygen at 195 °C) was used for pre-treating wheat straw (60 g/l), resulting in a hemicellulose-rich hydrolysate and a cellulose-rich solid fraction. The hydrolysate consisted of soluble hemicellulose (9 g/l), aliphatic carboxylic acids (6 g/l), phenols (0.27 g/l or 1.7 mM), and 2-furoic acid (0.007 g/l). The wet-oxidized wheat straw hydrolysate caused no inhibition of ethanol yield by the anaerobic thermophilic bacterium Thermoanaerobacter mathranii. Nine phenols and 2-furoic acid, identified to be present in the hydrolysate, were each tested in concentrations of 10–100× the concentration found in the hydrolysate for their effect on fermentation by T. mathranii. At 2 mM, these aromatic compounds were not inhibitory to growth or ethanol yield in T. mathranii. When the concentration of aromatics was increased to 10 mM, the fermentation was severely inhibited by the phenol aldehydes and to a lesser extent by the phenol ketones. By adding the same aromatic compounds to WO hydrolysate (10 mM), synergistic inhibitory effects of all tested compounds with hydrolysate components were shown. When the hydrolysate was concentrated three- and six-fold, growth and fermentation with T. mathranii were inhibited. At a six-fold hydrolysate concentration, the total concentration of phenolic monomers was 17 mM; hence aromatic monomers are an important co-factor in hydrolysate inhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received revision: 20 August 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klinke, .H., Thomsen, .A. & Ahring, .B. Potential inhibitors from wet oxidation of wheat straw and their effect on growth and ethanol production by Thermoanaerobacter mathranii . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57, 631–638 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100825
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100825