Abstract.
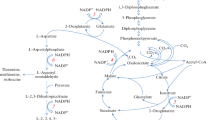
Transketolase, one of the enzymes in the nonoxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway, operates to shuttle ribose 5-phosphate and glycolytic intermediates together with transaldolase, and might be involved in the availability of ribose 5-phosphate, a precursor of nucleotide biosynthesis. The tkt and tal genes encoding transketolase and transaldolase, respectively, were cloned from the typical nucleotide- and nucleoside-producing organism Corynebacterium ammoniagenes by a PCR approach using oligonucleotide primers derived from conserved regions of each amino acid sequence from other organisms. Enzymatic and molecular analyses revealed that the two genes were clustered on the genome together with the glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (zwf). The effect of transketolase modifications on the production of inosine and 5′-xanthylic acid was investigated in industrial strains of C. ammoniagenes. Multiple copies of plasmid-borne tkt caused about tenfold increases in transketolase activity and resulted in 10–20% decreased yields of products relative to the parents. In contrast, site-specific disruption of tkt enabled both producers to accumulate 10–30% more products concurrently with a complete loss of transketolase activity and the expected phenotype of shikimate auxotrophy. These results indicate that transketolase normally shunts ribose 5-phosphate back into glycolysis in these biosynthetic processes and interception of this shunt allows cells to redirect carbon flux through the oxidative pentose pathway from the intermediate towards the purine-nucleotide pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received revision: 18 May 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamada, .N., Yasuhara, .A., Takano, .Y. et al. Effect of transketolase modifications on carbon flow to the purine-nucleotide pathway in Corynebacterium ammoniagenes . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56, 710–717 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100738
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100738