Abstract
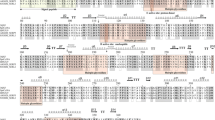
A gene library of Cellulomonas pachnodae was constructed in Escherichia coli and was screened for endoglucanase activity. Five endoglucanase-positive clones were isolated that carried identical DNA fragments. The gene, designated cel6A, encoding an endoglucanase enzyme, belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase family 6 (cellulase family B). The recombinant Cel6A had a molecular mass of 53 kDa, a pH optimum of 5.5, and a temperature optimum of 50–55 °C. The recombinant endoglucanase Cel6A bound to crystalline cellulose and beech litter. Based on amino acid sequence similarity, a clear cellulose-binding domain was not distinguished. However, the regions in the Cel6A amino acid sequence at the positions 262–319 and 448–473, which did not show similarity to any of the known family-6 glycosyl hydrolases, may be involved in substrate binding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 January 1999 / Received revision: 29 March 1999 / Accepted: 6 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cazemier, A., Verdoes, J., Op den Camp, H. et al. A β-1,4-endoglucanase-encoding gene from Cellulomonas pachnodae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52, 232–239 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051514
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051514