Abstract
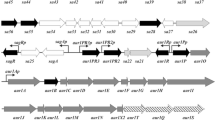
The upstream flanking region of the ftsQ and ftsZ genes of Brevibacterium flavum MJ233, which belongs to the coryneform bacteria, was amplified by the inverse polymerase chain reaction method and cloned in Escherichia coli. Complementation analysis of E. coli mutant with a defective cell-wall synthesis mechanism with the cloned fragment and its DNA sequencing indicated the presence of the murC gene, encoding UDP-N-acetylmuramate:l-alanine ligase involved in peptidoglycan synthesis, just upstream from the ftsQ gene. The B. flavum murC gene could encode a protein of 486 amino acid residues with a calculated molecular mass of 51 198 Da. A 50-kDa protein was synthesized by the B. flavummurC gene in an in vitro transcription/translation system using E. coli S30 lysate. These results indicate that the genes responsible for cell-wall synthesis and cell division are located as a cluster in B. flavum similar to the E. coli mra region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 June 1998 / Received last revision: 21 September 1998 / Accepted: 2 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wachi, M., Wijayarathna, C., Teraoka, H. et al. A murC gene from coryneform bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51, 223–228 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051385
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051385