Abstract
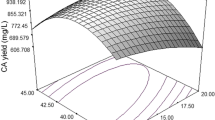
Response-surface methodology was applied to determine the effect of the fermentation process conditions, namely pH, temperature, rates of agitation and aeration, on surfactin production. The effects of the mutual interactions between these parameters were extensively studied to optimize the process conditions for the maximum production of surfactin. With a view to simultaneously reducing the number of experiments and obtaining the mutual interactions between the variables required for achieving the optimal experimental conditions, a 24 full-factorial central composite design followed by multi-stage Monte-Carlo optimization was employed for experimental design and analysis of the results. The optimum process conditions for the enhanced production of surfactin were as follows: pH = 6.755, temperature = 37.4 °C, agitation = 140 rpm and aeration = 0.75 vvm. Relative surfactin concentrations were denoted by the reciprocal of the critical micelle concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 October 1996 / Accepted: 15 November 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, R., Swaminathan, T. Application of response-surface methodology to evaluate the optimum environmental conditions for the enhanced production of surfactin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47, 358–363 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050940
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050940