Abstract
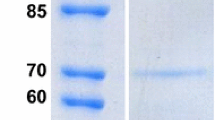
Two endo-1,4-β-glucanase genes, designated celA and celB, from a shoyu koji mold Aspergillus oryzae KBN616, were cloned and characterized. The celA gene comprised 877 bp with two introns. The CelA protein consisted of 239 amino acids and was assigned to the cellulase family H. The celB gene comprised 1248 bp with no introns. The CelB protein consisted of 416 amino acids and was assigned to the cellulase family C. Both genes were overexpressed under the promoter of the A. oryzae taka-amylase A gene for purification and enzymatic characterization of CelA and CelB. CelA had a molecular mass of 31 kDa, a pH optimum of 5.0 and temperature optimum of 55 °C, whereas CelB had a molecular mass of 53 kDa, a pH optimum of 4.0 and temperature optimum of 45 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 July 1996 / Accepted: 15 July 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitamoto, N., Go, M., Shibayama, T. et al. Molecular cloning, purification and characterization of two endo-1,4-β-glucanases from Aspergillus oryzae KBN616. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46, 538–544 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050857
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050857