Abstract
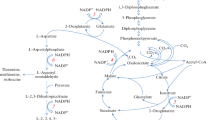
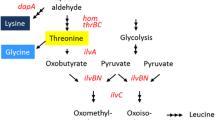
A 2.9-kb SacI fragment containing the ask-asd operon, encoding aspartokinase and aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, was cloned from an aminoethylcysteine-resistant, lysine-producing Corynebacterium lactofermentum strain. Enzymatic analysis showed that the aspartokinase (ASK) activity was completely resistant to inhibition by mixtures of lysine and threonine. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of the β submit of the ask gene showed three amino acid residue changes with ask genes encoding wild-type, feedback-sensitive enzymes. Three C. lactofermentum strains, one being aspartokinase-negative, one carrying two ask genes on the chromosome and one having a sixfold higher specific ASK activity than the parental strain, were constructed by transconjugation and electroporation, and used to analyse the role of ASK in the lysine production by C. lactofermentum. The results indicate that, in this study, feed-back-resistant ASK is necessary for high-level lysine production, but dispensable for lysine and diaminopimelate synthesis required for cell growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen G, Saint-Girons I (1987) Biosynthesis of threonine, lysine and methionine. In: Neidhardt FC (ed) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, cellular and molecular biology, vol 1. ASM, Washington, DC. pp 429–444
Cremer J, Eggeling L, Sahm H (1991) Control of lysine biosynthesis sequence in Corynebacterium glutamicum as analyzed by overexpression of the individual corresponding genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1746–1752
Follettie MT, Peoples OP, Agoropoulou C, Sinskey AJ (1993) Gene structure and expression of the Corynebacterium flavum N13 ask-asd operon. J Bacteriol 175:4096–4103
Gubler ME, Park SM, Jetten MSM, Stephanopoulos G, Sinskey AJ (1993) Effects of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase deficiency on metabolism and lysine production in Corynebacterium glultamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:857–863
Jetten MSM, Sinskey AJ (1993) Characterization of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from Corynebacterium glutamicum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 111:183–188
Jetten MSM, Gubler ME, McCormick MM, Colon GE, Follettie MT, Sinskey AJ (1993) Molecular organization and regulation of the biosynthetic pathway for aspartate-derived amino acids in Corynebacterium glutamicum. In: Blatz RH, Hegeman GD, Skatrud PL (eds) Industrial microorganisms: basic and applied molecular genetics. ASM, Washington DC, pp 97–104
Kalinowski J, Bachmann B, Thierbach G, Puhler A (1990) Aspartokinase genes lysCa and lysCβ overlap and are adjacent to the aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene asd in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mol Gen Genet 224:317–324
Kalinowski J, Cremer J, Bachmann B, Eggeling L, Sahm H, Puhler A (1991) Genetic and biochemical analysis of the aspartokinase from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mol Microbiol 5: 1197–1204
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sano K, Shiio I (1970) Microbial production of l-lysine III. Production by mutants resistant to S-(2-aminoethyl)-l-cysteine. J Gen Appl Microbiol 16:373–391
Schaefer A, Kalinowski, J, Simon R, Seep-Feldhaus A, Puehler A (1990) High-frequency conjugal plasmid transfer from gram-negative Escherichia coli to various gram-positive coryneform bacteria J Bacteriol 172:1663–1669
Schrumpf, Eggeling L, Sahm H (1992) Isolation and prominent characteristics of an l-lysine hyper-producing strain of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37:566–571
Schwarzer A, Puhler A (1990) Manipulation of Corynebacterium glutamicum by gene disruption and replacement. Biotechnology 9:84–87
Shiio I, Miyajima R (1969) Concerted inhibition and its reversal by endproducts of aspartokinase in Brevibacterium flavum. J. Biochem (Tokyo) 65:849–855
Shiio I, Yoshino H, Sugimoto S (1990) Isolation and properties of lysine producing mutants with feedback-resistant aspartokinase derived from a Brevibacterium flavum strain with citrate synthase and pyruvate kinase defects and feedback resistant phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase. Agric Biol Chem 54:3275–3282
Thierbach G, Kalinowski G, Bachmann B, Puehler A (1990) Cloning of a DNA fragment from Corynebacterium glutamicum conferring aminoethyl cysteine resistance and feedback resistance to aspartokinase. Appl Micriobiol Biotechnol 32:443–448
Tosaka O, Takinami K (1978) Pathway regulation of lysine biosynthesis in Brevibacterium lactofermentum. Agric Biol Chem 42:95–100
Tosaka O, Takinami K, Hirose Y (1978) l-Lysine production by S(2-aminoethyl)-cysteine and 1-amino-2-hydroxyvaleric acid resistant mutants of Brevibacterium lactofermentum. Agric Biol Chem 42:745–752
Zhang JJ, Hu FM, Chen NY, Paulus H (1990) Comparison of the three aspartokinase isoenzymes in Bacillus subtilis Marburg and 168. J Bacteriol 172:701–708
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jetten, M.S.M., Follettie, M.T. & Sinskey, A.J. Effect of different levels of aspartokinase of the lysine production by Corynebacterium lactofermentum . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43, 76–82 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170626
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170626