Abstract
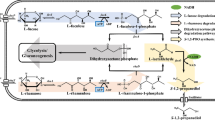
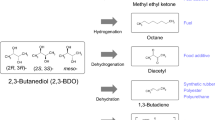
This short review covers metabolic pathways, genetics and metabolic engineering of 1,2-propanediol formation in microbes. 1,2-Propanediol production by bacteria and yeasts has been known for many years and two general pathways are recognized. One involves the metabolism of deoxyhexoses, where lactaldehyde is formed during the glycolytic reactions and is then reduced to 1,2-propanediol. The second pathway derives from the formation of methylglyoxal from dihydroxyacetonephosphate and its subsequent reduction to 1,2-propanediol. The enzymes involved in the reduction of methylglyoxal can generate isomers of lactaldehyde or acetol, which can be further reduced by specific reductases, giving chiral 1,2-propanediol as the product. The stereospecificity of the enzymes catalyzing the two reduction steps is important in deriving a complete pathway. Through genetic engineering, appropriate combinations of enzymes have been brought together in Escherichia coli and yeast to generate 1,2-propanediol from glucose. The optimization of these strains may yield microbial processes for the production of this widely used chemical.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 May 2000 / Received revision: 24 July 2000 / Accepted: 25 July 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bennett, G., San, KY. Microbial formation, biotechnological production and applications of 1,2-propanediol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55, 1–9 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000476
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000476