Abstract
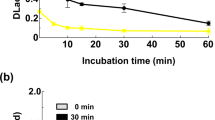
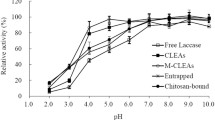
The storage stability of laccase (EC 1.10.3.2) from the white-rot basidomycete Trametes versicolor in potassium-citrate buffer was enhanced by various phenolic compounds as well as by lignin sulfonate. The highest storage stability was obtained with phenolics, e.g. phloroglucin and 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid; these represent substrates of laccase which are oxidized slowly because of their relatively high redox potential and which did not precipitate from the solution within the tested period of time. Sterilization enhanced the stability of laccase but additional stabilization by phenolics was observed both under sterile and non-sterile conditions. We thus concluded that stabilization occurred not only through prevention of microbial degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 April 2000 / Received revision: 16 June 2000 / Accepted: 18 June 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mai, C., Schormann, W., Milstein, O. et al. Enhanced stability of laccase in the presence of phenolic compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54, 510–514 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000452
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000452