Abstract
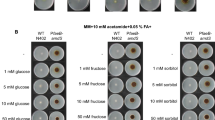
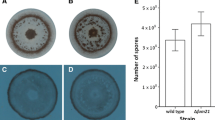
The aflR gene of Aspergillus parasiticus and A. flavus encodes a binuclear zinc-finger, DNA-binding protein, AflR, responsible for activating the transcription of all known aflatoxin biosynthetic genes including itself. Studies to determine how environmental and nutritional factors affect aflR expression and hence aflatoxin production in A. parasiticus have been difficult to perform due to the lack of aflR“knockout” mutants. Transformation of an O-methylsterigmatocystin (OMST)-accumulating strain of A. parasiticus with an aflR-niaD gene disruption vector resulted in clones harboring a recombinationally inactivated aflR gene which no longer produced OMST or aflR transcript. By transformation of this aflR disruptant strain with constructs containing mutated versions of the aflR promoter, we identified three cis-acting sites that were necessary for aflR function: an AflR-binding site, a PacC-binding site, and a G + A-rich site near the transcription start site of aflR.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 July 1999 / Received revision: 30 November / Accepted: 12 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cary, J., Ehrlich, K., Wright, M. et al. Generation of aflR disruption mutants of Aspergillus parasiticus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53, 680–684 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000319
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000319