Abstract
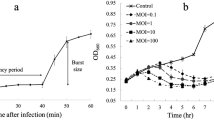
Vibrio alginolyticus is a Gram-negative bacterium commonly associated with mackerel poisoning. A bacteriophage that specifically targets and lyses this bacterium could be employed as a biocontrol agent for treating the bacterial infection or improving the shelf-life of mackerel products. However, only a few well-characterized V. alginolyticus phages have been reported in the literature. In this study, a novel lytic phage, named ΦImVa-1, specifically infecting V. alginolyticus strain ATCC 17749, was isolated from Indian mackerel. The phage has a short latent period of 15 min and a burst size of approximately 66 particles per infected bacterium. ΦImVa-1 remained stable for 2 h at a wide temperature (27–75 °C) and within a pH range of 5 to 10. Transmission electron microscopy revealed that ΦImVa-1 has an icosahedral head of approximately 60 nm in diameter with a short tail, resembling those in the Schitoviridae family. High throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis elucidated that ΦImVa-1 has a linear dsDNA genome of 77,479 base pairs (bp), with a G + C content of ~ 38.72% and 110 predicted gene coding regions (106 open reading frames and four tRNAs). The genome contains an extremely large virion-associated RNA polymerase gene and two smaller non-virion-associated RNA polymerase genes, which are hallmarks of schitoviruses. No antibiotic genes were found in the ΦImVa-1 genome. This is the first paper describing the biological properties, morphology, and the complete genome of a V. alginolyticus-infecting schitovirus. When raw mackerel fish flesh slices were treated with ΦImVa-1, the pathogen loads reduced significantly, demonstrating the potential of the phage as a biocontrol agent for V. alginolyticus strain ATCC 17749 in the food.
Graphical Abstract

Key points
• A novel schitovirus infecting Vibrio alginolyticus ATCC 17749 was isolated from Indian mackerel.
• The complete genome of the phage was determined, analyzed, and compared with other phages.
• The phage is heat stable making it a potential biocontrol agent in extreme environments.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are included in this article and its supplementary materials. The nucleotide sequence of the phage genome was deposited to NCBI GenBank and is accessible through the entry record accession no: ON042477.
References
Abdelsattar AS, Dawooud A, Rezk N, Makky S, Safwat A, Richards PJ, El-Shibiny A (2021) How to train your phage: the recent efforts in phage training. Biologics 1:70–88. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOLOGICS1020005
Adams M (1959) Bacteriophages. Wiley Interscience, New York
Alcock BP, Raphenya AR, Lau TT, Tsang KK, Bouchard M, Edalatmand A, Huynh W, Nguyen AL, Cheng AA, Liu S, Min SY (2020) CARD 2020: antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D517–D525. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz935
Apweiler R, Attwood TK, Bairoch A, Bateman A, Birney E, Biswas M, Bucher P, Cerutti L, Corpet F, Croning MDR, Durbin R, Falquet L, Fleischmann W, Gouzy J, Hermjakob H, Hulo N, Jonassen I, Kahn D, Kanapin A, Zdobnov EM (2001) The InterPro database, an integrated documentation resource for protein families, domains and functional sites. Nucleic Acids Res 29:37–40. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.1.37
Arias CR, Garay E, Aznar R (1995) Nested PCR method for rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio vulnificus in fish, sediments, and water. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3476–3478. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.9.3476-3478.1995
Ausiannikava D, Allers T (2017) Diversity of DNA replication in the archaea. Genes 8:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020056
Austin B, Pride AC, Rhodie GA (2003) Association of a bacteriophage with virulence in Vibrio harveyi. J Fish Dis 26:55–58. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2761.2003.00413.x
Bailly-Bechet M, Vergassola M, Rocha E (2007) Causes for the intriguing presence of tRNAs in phages. Genome Res 17:1486–1495. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.6649807
Balcázar JL, Gallo-Bueno A, Planas M, Pintado J (2010) Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio splendidus from captive-bred seahorses with disease symptoms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 97:207–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9398-4
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Barbarossa V, Kučišec-Tepeš N, Aldova E, Matek D, Stipoljev F (2002) Ilizarov technique in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis caused by Vibrio alginolyticus. Croat Med J 43:346–349
Bochman ML, Schwacha A (2009) The Mcm complex: unwinding the mechanism of a replicative helicase. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 73:652–683. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.00019-09
Bochow S, Elliman J, Owens L (2012) Bacteriophage adenine methyltransferase: a life cycle regulator? Modelled using Vibrio harveyi myovirus like. J Appl Microbiol 113:1001–1013. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05358.x
Boon M, De Zitter E, De Smet J, Wagemans J, Voet M, Pennemann FL, Schalck T, Kuznedelov K, Severinov K, Van Meervelt L, De Maeyer M (2020) “Drc”, a structurally novel ssDNA-binding transcription regulator of N4-related bacterial viruses. Nucleic Acids Res 48:445–459. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1048
Brettin T, Davis JJ, Disz T, Edwards RA, Gerdes S, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Overbeek R, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Shukla M, Thomason JA, Stevens R, Vonstein V, Wattam AR, Xia F (2015) RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci Rep 5:8365. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08365
Burian J, Tu N, Kl’učár L, Guller L, Lloyd-Jones G, Stuchlík S, Fejdi P, Siekel P, Turňa J (1998) In vivo and in vitro cloning and phenotype characterization of tellurite resistance determinant conferred by plasmid pTE53 of a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Folia Microbiol 43:589–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816374
Bushnell B, Rood J, Singer E (2017) BBMerge – accurate paired shotgun read merging via overlap. PLoS ONE 12:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185056
Carter RH, Demidenko AA, Hattingh-Willis S, Rothman-Denes LB (2003) Phage N4 RNA polymerase II recruitment to DNA by a single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Genes Dev 17:2334–2345. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1121403
Chang Y, Lee JH, Shin H, Heu S, Ryu S (2013) Characterization and complete genome sequence analysis of Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage SA12. Virus Genes 47:389–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-013-0938-7
Cho NY, Choi M, Rothman-Denes LB (1995) The bacteriophage N4-coded single-stranded DNA-binding protein (N4SSB) is the transcriptional activator of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase at N4 late promoters. J Mol Biol 246:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.0098
Collette BB, Reeb C, Block BA (2001) Systematics of the tunas and mackerels (Scombridae). Fish Physiol 19:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1546-5098(01)19002-3
Comeau AM, Chan AM, Suttle CA (2006) Genetic richness of vibriophages isolated in a coastal environment. Environl Microbiol 8:1164–1176. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01006.x
Darzentas N (2010) Circoletto: visualizing sequence similarity with Circos. Bioinforma 26:2620–2621. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq484
Donovan TJ, van Netten P (1995) Culture media for the isolation and enumeration of pathogenic Vibrio species in foods and environmental samples. Int J Food Microbiol 26:77–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1605(95)00015-c
Edgar RC (2021) MUSCLE v5 enables improved estimates of phylogenetic tree confidence by ensemble bootstrapping. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.20.449169
Enikeeva FN, Severinov KV, Gelfand MS (2010) Restriction–modification systems and bacteriophage invasion: who wins? J Theor Biol 266:550–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.07.006
Falco SC, Zehring W, Rothman-Denes LB (1980) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from bacteriophage N4 virions. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem 255:4339–4347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)85670-3
Feingold MH, Kumar ML (2004) Otitis media associated with Vibrio alginolyticus in a child with pressure-equalizing tubes. Pediatr Infect Dis J 23:475–476. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.INF.0000126592.19378.30
Garneau JR, Depardieu F, Fortier LC, Bikard D, Monot M (2017) PhageTerm: a tool for fast and accurate determination of phage termini and packaging mechanism using next-generation sequencing data. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07910-5
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3784–3788. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg563
Gesteland RF, Salser W, Bolle A (1967) In vitro synthesis of T4 lysozyme by suppression of amber mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 58:2036–2042. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.58.5.2036
Goulas AE, Kontominas MG (2005) Effect of salting and smoking-method on the keeping quality of chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus): biochemical and sensory attributes. Food Chem 93:511–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.09.040
Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinforma 29:1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
Hall T, Biosciences I, Carlsbad C (2011) BioEdit: an important software for molecular biology. GERF Bull Biosci 2:60–61
Hardy R, Smith JGM (1976) The storage of mackerel (Scomber scombrus). Development of histamine and rancidity. J Science Food and Agri 27:595–599. https://doi.org/10.1002/JSFA.2740270702
Herschleb J, Ananiev G, Schwartz DC (2007) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nat Protoc 2:677–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.94
Hugh R, Sakazaki R (1975) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology Subcommittee on the taxonomy of vibrios: minutes of the closed meeting, 3 September 1974. Int J Syst Bacteriol 25:389–391. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-25-4-389
Iyer LM, Koonin EV, Leipe DD, Aravind L (2005) Origin and evolution of the archaeo-eukaryotic primase superfamily and related palm-domain proteins: structural insights and new members. Nucleic Acids Res 33:3875–3896. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki702
Ji SP (1989) The first isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus from samples which caused food poisoning. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine] 23:71–73. https://europepmc.org/article/med/2737046
Jia B, Raphenya AR, Alcock B, Waglechner N, Guo P, Tsang KK, Lago BA, Dave BM, Pereira S, Sharma AN, Doshi S (2017) CARD 2017: expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D566–D573. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1004
Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL (2008) NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W5–W9. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn201
Jung GH, Leavitt MC, Hsieh JC, Ito J (1987) Bacteriophage PRD1 DNA polymerase: evolution of DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8287–8291. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.84.23.8287
Katharios P, Kalatzis PG, Kokkari C, Sarropoulou E, Middelboe M (2017) Isolation and characterization of a N4-like lytic bacteriophage infecting Vibrio splendidus, a pathogen of fish and bivalves. PLoS One 12:e0190083. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190083
Kawaguchi A, Nagata K (2007) De novo replication of the influenza virus RNA genome is regulated by DNA replicative helicase, MCM. EMBO J 26:4566–4575. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601881
Kedzierska S (2006) Structure, function and mechanisms of action of ATPases from the AAA superfamily of proteins. Postepy Biochemii 52:330–338. https://europepmc.org/article/med/17201069
Kokkari C, Sarropoulou E, Bastias R, Mandalakis M, Katharios P (2018) Isolation and characterization of a novel bacteriophage infecting Vibrio alginolyticus. Arch Microbio 200:707–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1480-8
Kovall R, Matthews BW (1997) Toroidal structure of λ-exonuclease. Sci 277:1824–1827. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5333.1824
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Kutter E, Sulakvelidze A (2004) Bacteriophages: biology and applications. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203491751
Laslett D, Canback B (2004) ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh152
Lehman IR (2003) Discovery of DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem 278:34733–34738. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.X300002200
Leipe D, Koonin EV, Aravind L (2003) Evolution and classification of P-loop kinases and related proteins. J Mol Biol 333:781–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2003.08.040
Li XC, Xiang ZY, Xu XM, Yan WH, Ma JM (2009) Endophthalmitis caused by Vibrio alginolyticus. J Clin Microbiol 47:3379–3381. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00722-09
Li J, Tian F, Hu Y, Lin W, Liu Y, Zhao F, Ren H, Pan Q, Shi T, Tong Y (2021) Characterization and genomic analysis of BUCT549, a novel bacteriophage infecting Vibrio alginolyticus with flagella as receptor. Front Microbiol 12:668319. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.668319
Li F, Tian F, Li J, Li L, Qiao H, Dong Y, Ma F, Zhu S, Tong Y (2021) Isolation and characterization of a podovirus infecting the opportunist pathogen Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Virus Res 302:198481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198481
Liu XF, Cao Y, Zhang HL, Chen YJ, Hu CJ (2015) Complete genome sequence of Vibrio alginolyticus ATCC 17749T. Am Soc Microbiol 3:1500–1514. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01500-14
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1996) TRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.5.0955
Luo P, Yun L, Li Y, Tian Y, Liu Q, Huang W, Hu C (2018) Complete genomic sequence of the Vibrio alginolyticus bacteriophage Vp670 and characterization of the lysis-related genes, cwlQ and holA. BMC Genomics 19:741. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5131-x
Macmaster R, Sedelnikova S, Baker PJ, Bolt EL, Lloyd RG, Rafferty JB (2006) RusA Holliday junction resolvase: DNA complex structure - insights into selectivity and specificity. Nucleic Acids Res 34:5577–5584. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl447
Maffei E, Shaidullina A, Burkolter M, Heyer Y, Estermann F, Druelle V, Sauer P, Willi L, Michaelis S, Hilbi H, Thaler DS, Harms A (2021) Systematic exploration of Escherichia coli phage–host interactions with the BASEL phage collection. PLoS Biol 19:e3001424. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PBIO.3001424
Merabishvili M, Vervaet C, Pirnay JP, De Vos D, Verbeken G, Mast J, Chanishvili N, Vaneechoutte M (2013) Stability of Staphylococcus aureus phage ISP after freeze-drying (lyophilization). PLoS One 8:e68797. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068797
Miyamoto Y, Nakamuma K, Takizawa K (1961) Pathogenic halophiles. Proposals of a new genus “Oceanomonas” and of the amended species names. Jpn J Microbiol 5:477–486. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.1961.tb00225.x
Model P, Webster RE, Zinder ND (1969) The UGA codon in vitro: chain termination and suppression. J Mol Biol 43:177–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(69)90087-4
Molitoris E, Joseph SW, Krichevsky MI, Sindhuhardja W, Colwell RR (1985) Characterization and distribution of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated in Indonesia. Appl Environ Microbiol 50:1388–1394. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.50.6.1388-1394.1985
Opal SM, Saxon JR (1986) Intracranial infection by Vibrio alginolyticus following injury in salt water. J Clin Microbio 23:373–374. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.23.2.373-374.1986
Panicker G, Myers ML, Bej AK (2004) Rapid detection of Vibrio vulnificus in shellfish and gulf of Mexico water by real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:498–507. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.1.498-507.2004
Prevelige PE, Cortines JR (2018) Phage assembly and the special role of the portal protein. Curr Opin Virol 31:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COVIRO.2018.09.004
Roberts RJ, Vincze T, Posfai J, Macelis D (2015) REBASE—a database for DNA restriction and modification: enzymes, genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D298–D299. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1046
Rothman-Denes LB, Schito GC (1974) Novel transcribing activities in N4-infected Escherichia coli. Virol 60:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/0042-6822(74)90366-3
Sakazaki R (1968) Proposal of Vibrio alginolyticus for the biotype 2 of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Jpn J Med Sci Biol 21:359–362. https://doi.org/10.7883/YOKEN1952.21.359
Shao Y, Wang IN (2008) Bacteriophage adsorption rate and optimal lysis time. Genet 180:471–482. https://doi.org/10.1534/GENETICS.108.090100
Simidu U, Noguchi T, Hwang DF, Shida Y, Hashimoto K (1987) Marine bacteria which produce tetrodotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1714–1715. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.53.7.1714-1715.1987
Smolikova LM, Lomov IM, Khomenko TV, Murnachev GP, Kudriakova TA, Fetsailova OP, Sanamiants EM, Makedonova LD, Kachkina GV, Golenishcheva EN (2001) Studies on halophilic vibrios causing a food poisoning outbreak in the city of Vladivostok. Zhurnal Mikrobiologii, Epidemiologii i Immunobiologii 6:3-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11881491/
Söding J, Biegert A, Lupas AN (2005) The HHpred interactive server for protein homology detection and structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W244–W248. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki408
Sofy AR, El-Dougdoug NK, Refaey EE, Dawoud RA, Hmed AA (2021) Characterization and full genome sequence of novel KPP-5 lytic phage against Klebsiella pneumoniae responsible for recalcitrant infection. Biomed 9:342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040342
Sonnhammer ELL, Eddy SR, Durbin R (1997) Pfam: a comprehensive database of protein domain families based on seed alignments. Proteins 28(3):405–420. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(199707)28:3%3c405::AID-PROT10%3e3.0.CO;2-L
Stothard P (2000) The sequence manipulation suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. Biotech 28:1102–11024. https://doi.org/10.2144/00286ir01
Stummeyer K, Dickmanns A, Mühlenhoff M, Gerardy-Schahn R, Ficner R (2005) Crystal structure of the polysialic acid-degrading endosialidase of bacteriophage K1F. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb874
Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA (2011) Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinforma 27:1009–1010. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039
Summer EJ, Berry J, Tran TAT, Niu L, Struck DK, Young R (2007) Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts. J Mol Biol 373:1098–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.045
Tan D, Gram L, Middelboe M (2014) Vibriophages and their interactions with the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:3128–3140. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03544-13
Taylor R, McDonald M, Russ G, Carson M, Lukaczynski E (1981) Vibrio alginolyticus peritonitis associated with ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Bri Med J (Clin Res Ed) 283:275. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.283.6286.275
Tcherepanov V, Ehlers A, Upton C (2006) Genome annotation transfer utility (GATU): rapid annotation of viral genomes using a closely related reference genome. BMC Genomics 7:150. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-7-150
Thompson FL, Iida T, Swings J (2004) Biodiversity of vibrios. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:403–431. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.68.3.403-431.2004
Tridge (2020) 2020 Industry report: mackerel. Market Intelligence Team. https://cdn.tridge.com/market_report_report/b9/df/33/b9df33b49173bd0adce086ca6fa89c9e66cf2890/210122_Mackerel_Report.pdf. Accessed 20 June 2022
Trimble JJ, Murthy SC, Bakker A, Grassmann R, Desrosiers RC (1988) A gene for dihydrofolate reductase in a herpesvirus. Sci 239:1145–1147. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.2830673
Walker PJ, Siddell SG, Lefkowitz EJ, Mushegian AR, Adriaenssens EM, Alfenas-Zerbini P, Davison AJ, Dempsey DM, Dutilh BE, García ML, Harrach B, Harrison RL, Hendrickson RC, Junglen S, Knowles NJ, Krupovic M, Kuhn JH, Lambert AJ, Łobocka M, Nibert ML, Oksanen HM, Orton RJ, Robertson DL, Rubino L, Sabanadzovic S, Simmonds P, Smith DB, Suzuki N, Van Dooerslaer K, Vandamme AM, Varsani A, Zerbini FM (2021) Changes to virus taxonomy and to the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2021). Arch Virol 166:2633–2648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-021-05156-1
Wen C, Ai C, Lu S, Yang Q, Liao H, Zhou S (2022) Isolation and characterization of the lytic Pseudoxanthomonas kaohsiungensi phage PW916. Viruses 14:1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081709
Willis SH, Kazmierczak KM, Carter RH, Rothman-Denes LB (2002) N4 RNA polymerase II, a heterodimeric RNA polymerase with homology to the single-subunit family of RNA polymerases. J Bacteriol 184:4952–4961. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.18.4952-4961.2002
Wittmann J, Turner D, Millard AD, Mahadevan P, Kropinski AM, Adriaenssens EM (2020) From orphan phage to a proposed new family-the diversity of N4-Like viruses. Antibiot (Basel) 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIBIOTICS9100663
Wong CL, Sieo CC, Tan WS, Abdullah N, Hair-Bejo M, Abu J, Ho YW (2014) Evaluation of a lytic bacteriophage, Φ st1, for biocontrol of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in chickens. Int J Food Microbiol 172:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.11.034
Xie ZY, Hu CQ, Chen C, Zhang LP, Ren CH (2005) Investigation of seven Vibrio virulence genes among Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains from the coastal mariculture systems in Guangdong, China. Lett Applied Microbiol 41:202–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01688.x
Yang TC, Ortiz D, Yang Q, De Angelis RW, Sanyal SJ, Catalano CE (2017) Physical and functional characterization of a viral genome maturation complex. Biophy J 112:1551–1560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2017.02.041
Yazdi M, Bouzari M, Ghaemi EA (2018) Isolation and characterization of a lytic bacteriophage (vB_PmiS-TH) and its application in combination with ampicillin against planktonic and biofilm forms of Proteus mirabilis isolated from urinary tract infection. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 28:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487137
Zadik PM, Chapman PA, Siddons CA (1993) Use of tellurite for the selection of verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli O157. J Med Microbiol 39:155–158. https://doi.org/10.1099/00222615-39-2-155
Zhang KY, Gao YZ, Du MZ, Liu S, Dong C, Guo FB (2019) Vgas: a viral genome annotation system. Front Microbiol 10:184. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00184
Zhang Y, Ding Y, Li W, Zhu W, Wang J, Wang X (2021) Application of a novel lytic Podoviridae phage Pu20 for biological control of drug-resistant Salmonella in liquid eggs. Pathog 10:34. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010034
Zivanovic Y, Confalonieri F, Ponchon L, Lurz R, Chami M, Flayhan A, Renouard M, Huet A, Decottignies P, Davidson AR, Breyton C, Boulanger P (2014) Insights into bacteriophage T5 structure from analysis of its morphogenesis genes and protein components. J Virol 88:1162–1174. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02262-13
Funding
This study was supported by UPM grant (No: UPM/800–3/3/1/GPB/2019/9682500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST designed and conducted the experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. AMK conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed data, supervised the project, provided resources, reviewed and edited the manuscript. LCC and CLW analyzed data and reviewed the manuscript. JST designed and conducted the experiments. MYIS, HYL, KLH, and ARM provided resources, supervised the project, and reviewed the manuscript. WST conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed data, supervised the project, provided resources, acquired funding, reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tajuddin, S., Khan, A.M., Chong, L.C. et al. Genomic analysis and biological characterization of a novel Schitoviridae phage infecting Vibrio alginolyticus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 749–768 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12312-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12312-3