Abstract
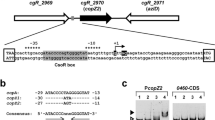
The MarR family, as multiple antibiotic resistance regulators, is associated with the resistance of organisms to unfavorable conditions. MarR family extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)–associated transcriptional regulator (EpsRAc) was closely associated with copper resistance in Acidithiobacillus caldus (A. caldus). Transcriptional analysis showed high activity of the epsR promoter (PI) in Escherichia coli and differential response to metal ions. The copper content and UV absorption spectrum of the co-purified protein did not increase, but a stoichiometry of 0.667 mol Cu(I) per EpsRAc monomer was observed in vitro in copper titration experiments, suggesting that Cu(II) acts with low affinity in binding to the EpsRAc protein. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) demonstrated that EpsRAc could bind to its own promoter in vitro, and the binding region was the palindrome sequence TGTTCATCGTGTGTGAGCACACA. EpsRAc negatively regulated its own gene expression, whereas Cu(II) mitigates this negative effect. EpsRAc did not bind to other neighboring gene promoters. Finally, we developed a working model to illustrate the regulatory mechanism of A. caldus in response to extreme copper stress.
Key points
• Identification of a MarR family EPS-associated transcriptional regulator, named EpsRAc.
• Cu(I) can bind to the EpsRAc protein with low affinity.
• EpsRAc negatively regulates the expression of epsR, and Cu(II) can alleviate this negative regulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support for the findings of this study are all contained in the manuscript and supplement materials.
References
Alekshun MN, Levy SB, Mealy TR, Seaton BA, Head JF (2001) The crystal structure of MarR, a regulator of multiple antibiotic resistance, at 2.3 A resolution. Nat Struct Biol 8:710–714. https://doi.org/10.1038/90429
Chen J, Zhang A, Xiang Z, Lu M, Li Y (2021) EpsR negatively regulates Streptococcus mutans exopolysaccharide synthesis. J Dent Res 100(9):968–976. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345211000668
Deochand DK, Grove A (2017) MarR family transcription factors: dynamic variations on a common scaffold. Crit Rev Biochem Mol 52:595–613. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2017.1344612
Feng S, Hou S, Cui Y, Tong Y, Yang H (2020) Metabolic transcriptional analysis on copper tolerance in moderate thermophilic bioleaching microorganism Acidithiobacillus caldus. J Microbiol Biotechn 47:21–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02247-6
Feng S, Yin Y, Yin Z, Zhang H, Zhu D, Tong Y, Yang H (2021) Simultaneously enhance iron/sulfur metabolism in column bioleaching of chalcocite by pyrite and sulfur oxidizers based on joint utilization of waste resource. Environ Res 194(1):110702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110702
Flemming H-C (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2415
Flemming HC, Wingender J, Szewzyk U, Steinberg P, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S (2016) Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life. Nat Rev Microbiol 14(9):563–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.94
González DM, Lara RH, Alvarado KN, Valdez-Pérez D, Navarro-Contreras HR, Cruz R, García-Meza JV (2012) Evolution of biofilms during the colonization process of pyrite by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Appl Microbiol Biot 93(2):763–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3465-2
Grove A (2013) MarR family transcription factors. Curr Biol 23(4):R142–R143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.013
Gupta A, Pande A, Sabrin A, Thapa SS, Gioe BW, Grove A (2018) MarR family transcription factors from Burkholderia species: hidden clues to control of virulence-associated genes. Microbiol Mol Biol R 83(1):e00039-e118. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00039-18
Hao Z, Lou H, Zhu R, Zhu J, Zhang D, Zhao BS, Zeng S, Xing C, Chan J, He C (2014) The multiple antibiotic resistance regulator MarR is a copper sensor in Escherichia coli. Nat Chem Biol 10(1):21–28. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1380
Hou S, Tong Y, Yang H, Feng S (2021) Molecular insights into the copper-sensitive operon repressor in Acidithiobacillus caldus. Appl Environ Microb 87(16): AEM0066021 https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00660-21
Houng Aloune S, Kawaai T, Hiroyoshi N, Ito M (2014) Study on schwertmannite production from copper heap leach solutions and its efficiency in arsenic removal from acidic sulfate solutions. Hydrometallurgy 147–148(1):30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.04.001
Jenkins J, Davenport WG, Kennedy B, Robinson T (1999) Electrolytic copper - leach, solvent extraction and electrowinning world operating data. 4th Int Conf COPPER 99-COBRE 99 4: 493–566.
Kang F, Alvarez PJ, Zhu D (2014) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances reduce Ag+ to silver nanoparticles and antagonize bactericidal activity. Environ Sci Tech Let 48(1):316–322. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403796x
Kang F, Qu X, Alvarez PJ, Zhu D (2017) Extracellular saccharide-mediated reduction of Au3+ to gold nanoparticles: New insights for heavy metals biomineralization on microbial surfaces. Environ Sci Technol 51(5):2776–2785. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05930
Kucera J, Lochman J, Bouchal P, Pakostova E, Johnson DB (2020) A model of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of hydrogen in the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Front Microbiol 11:610836. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.610836
Lara RH, García-Meza JV, Cruz R, Valdez-Pérez D, González I (2012) Influence of the sulfur species reactivity on biofilm conformation during pyrite colonization by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Appl Microbiol Biot 95(3):799–809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3715-3
Liu Y, Wang J, Hou H, Chen G, Liu H, Liu X, Shen L (2020) Effect of introduction of exogenous strain Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans A01 on structure and function of adsorbed and planktonic microbial consortia during bioleaching of low-grade copper sulfide. Front Microbiol 10:3034. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.03034
Martínez-Bussenius C, Navarro CA, Jerez CA (2017) Microbial copper resistance: importance in biohydrometallurgy. Microb Biotechnol 10(2):279–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12450
Neu TR, Lawrence JR (2009) Extracellular polymeric substances in microbial biofilms. Academic Press, San Diego
Okibe N, Gericke M, Hallberg KB, Johnson DB (2003) Enumeration and characterization of acidophilic microorganisms isolated from a pilot plant stirred-tank bioleaching operation. Appl Environ Microb 69(4):1936–1943. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.4.1936-1943.2003
Peng T, Zhou D, Liu X, Yu R, Jiang T, Gu G, Chen M, Qiu G, Zeng W (2016) Enrichment of ferric iron on mineral surface during bioleaching of chalcopyrite. T Nonferr Metal Soc 26(2):544–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64143-2
Perera IC, Grove A (2010) Molecular mechanisms of ligand-mediated attenuation of DNA binding by MarR family transcriptional regulators. J Mol Cell Biol 2(005):243–254. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjq021
Safar C, Castro C, Donati E (2020) Importance of initial interfacial steps during chalcopyrite bioleaching by a Thermoacidophilic Archaeon. Microorganisms 8(7):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071009
Shi Y, Latifi T, Cromie MJ, Groisman EA (2004) Transcriptional control of the antimicrobial peptide resistance ugtL gene by the Salmonella PhoP and SlyA regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem 279(37):38618–38625. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M406149200
Spory A, Bosserhoff A, Rhein CV, Goebel W, Ludwig A (2002) Differential regulation of multiple proteins of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium by the transcriptional regulator SlyA. J Bacteriol 184:3549–3459. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.13.3549-3559.2002
Stapleton MR, Norte VA, Read RC, Green J (2002) Interaction of the Salmonella typhimurium transcription and virulence factor SlyA with target DNA and identification of members of the SlyA regulon. J Biol Chem 277(20):17630. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110178200
Teitzel GM, Parsek MR (2003) Heavy metal resistance of biofilm and planktonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microb 69(4):2313. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.4.2313-2320.2003
Wilkinson SP, Grove A (2006) Ligand-responsive transcriptional regulation by members of the MarR family of winged helix proteins. Curr Issues Mol Biol, 8(1): 51 https://doi.org/10.21775/cimb.008.051
Zeng W, Qiu G, Zhou H, Liu X, Miao C, Chao W, Zhang C, Peng J (2010) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances extracted during the bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 96(3–4):177–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2009.11.002
Zhang Q, Chen Q, Zhuang S, Chen Z, Wen Y, Li J, Liu S (2015) A MarR family transcriptional regulator, DptR3, activates daptomycin biosynthesis and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces roseosporus. Appl Environ Microb 81(11):3753–3765. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00057-15
Zhou H, Zeng W, Yang Z, Xie Y, Qiu G (2009) Bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by a moderately thermophilic culture in a stirred tank reactor. Bioresource Technol 100(2):515–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.06.033
Zhu R, Hao Z, Lou H, Song Y, Zhao J, Chen Y, Zhu J, Chen P (2017) Structural characterization of the dna-binding mechanism underlying the copper(II)-sensing MarR transcriptional regulator. J Biol Inorg Chem 22(5):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-017-1442-7
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21878128; 21776113; 21606110; 31701582), the funding of Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Ministry of Education (KLIBKF202005), the funding of Key Laboratory of Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biotechnology, Ministry of Education (KLCCB-KF202001), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2050205), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (No. 111–2-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY and SF designed the research and analyzed the data. YY performed the experiments and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. SF, HY, and YT contributed to manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Y., Tong, Y., Yang, H. et al. EpsRAc is a copper-sensing MarR family transcriptional repressor from Acidithiobacillus caldus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 3679–3689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11971-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11971-6