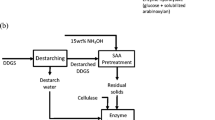
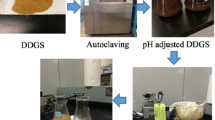
Abstract
Distillers’ dried grain with solubles (DDGS) is a byproduct of bioethanol fermentation, which uses the dry milling technology for starch-rich grains such as corn, wheat, and barley. The current interest in bioethanol is increasing due to the need for renewable liquid fuels specifically in the transportation sector. Since DDGS is rich in crude protein, fat, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, it is currently used as aquaculture, livestock, and poultry feeds. In recent years, DDGS has been used as feedstock in the production of value-added products via microbial fermentation. Numerous studies reported the production organic acids, methane, biohydrogen, and hydrolytic enzymes using DDGS. While DDGS contains remarkable amounts of macronutrients, pre-treatment of DDGS is required for release of the fermentable sugars. The pre-treatment methods such as chemical, physical, and biological origin are either solely used or combined to obtain maximal yields for different applications. Therefore, this review summarizes some of the most prominent pre-treatment processes generating high fermentable sugar yields for the productions of value-added products in the last 5 years. A special focus has been given to the effect of the variability of DDGS on the final product. Integration of hydrolytic enzyme production with the traditional bioethanol production facilities has been discussed for further improvement of bioethanol, methane, and biohydrogen using DDGS as fermentation feedstock.
Key points • Distillers’ dried grain with solubles (DDGS) has high nutritional value, but the nutritional profile is variable. • DDGS can be used for microbial fermentation feedstock to produce value-added products. • A review of the microbial products using DDGS is given for the last 5 years. • DDGS has the potential to replace expensive feedstocks of value-added products. |



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri H, Karimi K (2018) Pre-treatment and hydrolysis of lignocellulosic wastes for butanol production: challenges and perspectives. Bioresour Technol 270:702–721
Ashraf H, Iqbal J, Qadeer MA (2003) Production of alpha amylase by Bacillus licheniformis using an economical medium. Bioresour Technol 87:57–61
Balan V, Rogers CA, Chundawat SPS, da Costa SL, Slininger PJ, Gupta R, Dale BE (2009) Conversion of extracted oil cake fibers into bioethanol including DDGS, canola, sunflower, sesame, soy, and peanut for integrated biodiesel processing. J Am Oil Chem Soc 86:157–165
Bals B, Dale B, Balan V (2006) Enzymatic hydrolysis of distiller’s dry grain and solubles (DDGS) using ammonia fiber expansion pre-treatment. Energy Fuel 20:2732–2736
Behnke KC (2007) Feed manufacturing considerations for using DDGS in poultry and livestock diets. In: Proceedings of the 5th mid-Atlantic Nutrition Conference. University of Maryland, pp 77–81
Belyea RL, Rausch KD, Tumbleson ME (2004) Composition of corn and distillers dried grains with solubles from dry grind ethanol processing. Bioresour Technol 94:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.01.001
Bonnardeaux J (2007) Potential uses for distillers grains. Department of Agriculture and Food. Government of Western Australia. https://www.scribd.com/document/42277950/Potential-Uses-Grains-042007. Accessed 19 May 2020
Bothast RJ, Schlicher MA (2005) Biotechnological processes for conversion of corn into ethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:19–25
Böttger C, Südekum K-H (2017) European distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS): chemical composition and in vitro evaluation of feeding value for ruminants. Anim Feed Sci Technol 224:66–77
Brijwani K, Vadlani PV (2010) Lipase-mediated hydrolysis of corn DDGS oil: kinetics of linoleic acid production. Biochem Eng J 52:289–295
Brock S, Kuenz A, Prüße U (2019) Impact of hydrolysis methods on the utilization of agricultural residues as nutrient source for D-lactic acid production by Sporolactobacillus inulinus. Fermentation 5:12
Bušić A, Marđetko N, Kundas S, Morzak G, Belskaya H, Ivančić Šantek M, Komes D, Novak S, Šantek B (2018) Bioethanol production from renewable raw materials and its separation and purification: a review. Food Technol Biotechnol 56:289–311
Cassidy DP, Hirl PJ, Belia E (2008) Methane production from ethanol co-products in anaerobic SBRs. Water Sci Technol 58:789–793
Cekmecelioglu D, Demirci A (2019) A statistical optimization study on dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) as a potential feedstock for fermentation applications. Waste Biomass Valorization 10:3243–3249
Cekmecelioglu D, Demirci A (2020) Production of cellulase and xylanase enzymes using distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) by Trichoderma reesei at shake-flask scale and the validation in the benchtop scale bioreactor. Waste and Biomass Valorization In Press:1–10
Chatzifragkou A, Kosik O, Prabhakumari PC, Lovegrove A, Fraziera RA, Shewry PR, Charalampopoulosa D (2015) Biorefinery strategies for upgrading distillers’ dried grains with solubles (DDGS). Process Biochem 50:2194–2207
Chen H, Liu S (2015) A kinetic study of DDGS hemicellulose acid hydrolysis and NMR characterization of DDGS hydrolysate. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177:162–174
Cheng C-L, Lo Y-C, Lee K-S, Lee DJ, Lin CY, Chang JS (2011) Biohydrogen production from lignocellulosic feedstock. Bioresour Technol 102:8514–8523
Chevanan N, Muthukumarappan K, Rosentrater KA, Julson JL (2007) Effect of die dimensions on extrusion processing parameters and properties of DDGS-based aquaculture feeds. Cereal Chem 84:389–398
Chevanan N, Rosentrater KA, Muthukumarappan K (2010) Effects of processing conditions on single screw extrusion of feed ingredients containing DDGS. Food Bioprocess Technol 3:111–120
Chrenková M, Čerešňáková Z, Formelová Z, Poláčiková M, Mlyneková Z, Fľak P (2012) Chemical and nutritional characteristics of different types of DDGS for ruminants. J Anim Feed Sci 425:435
Cordonnier M (2019) Corn-based ethanol now 4.6% of Brazil’s ethanol production. http://www.soybeansandcorn.com/news/May9_19-Corn-Based-Ethanol-now-4_6-of-Brazils-Ethanol-Production. Accessed 19 May 2020
Cromwell GL, Herkelman KL, Stahly TS (1993) Physical, chemical, and nutritional characteristics of distillers dried grains with solubles for chicks and pigs. J Anim Sci 71:679–686
de Magalhães RPM (2013) Dried distillers grains with solubles (DDGS): a potential protein source in feeds for aquaculture
Department of Energy (DOE) (2019) Ethanol fuel basics. In: US. Dep. Energy. https://afdc.energy.gov/fuels/ethanol_fuel_basics.html
Drewnoski ME, Richter EL, Hansen SL (2012) Dietary sulfur concentration affects rumen hydrogen sulfide concentrations in feedlot steers during transition and finishing. J Anim Sci 90:4478–4486
Ezeji T, Blaschek HP (2008) Fermentation of dried distillers’ grains and solubles (DDGS) hydrolysates to solvents and value-added products by solventogenic clostridia. Bioresour Technol 99:5232–5242
Grains.com (2019) DDGS: production and exports. https://grains.org/buying-selling/ddgs/
Grewell D, Burns RT, Moody LB, Wu-Haan W (2008) Characterization of ultrasonic treatment of ethanol co-products for enhanced biogas production. In: 2008 Providence, Rhode Island, June 29–July 2, 2008. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, p 1
Gu J, Xin Z, Meng X, Sun S, Qiao Q, Deng H (2015) Studies on biodiesel production from DDGS-extracted corn oil at the catalysis of Novozym 435/super absorbent polymer. Fuel 146:33–40
Gyenge L, Crognale S, Lányi S, Ábrahám B, Ráduly B (2014) Anaerobic digestion of corn-DDGS: effect of pH-control, agitation and batch repetition. UPB Sci Bull Ser B Chem Mater Sci 76:163–172
Hicks KB, Montanti J, Nghiem NP (2014) Use of barley grain and straw for biofuels and other industrial uses. In: Barley. Elsevier, pp 269–291
Hoskins B, Lyons M (2009) Improving bioethanol yield: the use of solid-state fermentation products grown on DDGS. J Inst Brew 115:64–70
Houweling-Tan GBN, Sperber BLHM, van der Wal H, Bakker RRC, Lopez Contreras AM (2016) Barley distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) as feedstock for production of acetone, butanol and ethanol. BAOJ Microbiol 2:3–8
Hynes SH, Kjarsgaard DM, Thomas KC, Ingledew WM (1997) Use of virginiamycin to control the growth of lactic acid bacteria during alcohol fermentation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 18:284–291
Iram A, Cekmecelioglu D, Demirci A (2019) Optimization of dilute sulfuric acid, aqueous ammonia, and steam explosion as the pre-treatments steps for distillers’ dried grains with solubles as a potential fermentation feedstock. Bioresour Technol 282:475–481
Iram A, Cekmecelioglu D, Demirci A (2020) Screening of bacterial and fungal strains for cellulase and xylanase production using distillers’ dried grains with solubles (DDGS) as the main feedstock. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00588-x
Izadifar Z (2011) Efficient extraction of phenolic compounds from wheat distiller’s dried grain; ultrasonic pre-treatment and dielectric studies
Izadifar Z (2013) Ultrasound pre-treatment of wheat dried distiller’s grain (DDG) for extraction of phenolic compounds. Ultrason Sonochem 20:1359–1369
Jessen H (2013) Corn oil makes the grade. Ethanol Prod Mag
Kannadhason S, Rosentrater KA, Muthukumarappan K, Brown ML (2010) Twin screw extrusion of DDGS-based aquaculture feeds 1. J World Aquac Soc 41:1–15
Kannadhason S, Muthukumarappan K, Rosentrater KA (2011) Effect of starch sources and protein content on extruded aquaculture feed containing DDGS. Food Bioprocess Technol 4:282–294
Lardy G (2007) Feeding coproducts of the ethanol industry to beef cattle
Leathers TD, Gupta SC (1994) Production of pullulan from fuel ethanol byproducts by Aureobasidium sp. strain NRRl Y-12,974. Biotechnol Lett 16:1163–1166
Lei H, Ren S, Wang L, Bu Q, Julson J, Holladay J, Ruand R (2011) Microwave pyrolysis of distillers dried grain with solubles (DDGS) for biofuel production. Bioresour Technol 102:6208–6213
Levin DB, Jo JH, Maness P-C (2012) Biohydrogen production from cellulosic biomass. In: Integrated forest biorefineries. pp 256–275
Li X, Chen S, Yu Y, Wang S, Xu Z, Huang H, Jin M (2019) Ethanol production from mixtures of distiller’s dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and corn. Ind Crop Prod 129:59–66
Lin Y, Zhang W, Li C, Sakakibara K, Tanaka S, Konga H (2012) Factors affecting ethanol fermentation using Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742. Biomass Bioenergy 47:395–401
Liu K (2009) Fractionation of distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) by sieving and winnowing. Bioresour Technol 100:6559–6569
Liu K (2011) Chemical composition of distillers grains, a review. J Agric Food Chem 59:1508–1526
Liu Y, Xu JX, Zhang Y, He M, Liang C, Yuan Z, Xie J (2016) Improved ethanol production based on high solids fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation with alkali-pretreated sugarcane bagasse. BioResources 11:2548–2556
Liu H, Yue X, Jin Y, Wang M, Deng L, Wang F, Tan T (2017) Preparation of hydrolytic liquid from dried distiller’s grains with solubles and fumaric acid fermentation by Rhizopus arrhizus RH 7–13. J Environ Manag 201:172–176
Liu H, Zhang S, Yu N, Dou L, Deng L, Wang F, Tan T (2018) Direct utilization of non-pretreated hydrolytic liquid of dried distiller’s grains with solubles for bio-ethanol by Rhizopus arrhizus RH 7-13-9. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 186:590–596
Lopes DD, Rosa CA, Hector RE, Dien BS, Mertens JA, Ayub MAZ (2017) Influence of genetic background of engineered xylose-fermenting industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains for ethanol production from lignocellulosic hydrolysates. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44:1575–1588
Lumpkins BS, Batal AB (2005) The bioavailability of lysine and phosphorus in distillers dried grains with solubles. Poult Sci 84:581–586
Morrow LA, Felix TL, Fluharty FL, Daniels KM, Loerch SC (2013) Effects of sulfur and acidity on performance and digestibility in feedlot lambs fed dried distillers grains with solubles. J Anim Sci 91:2211–2218
Mosier NS, Ileleji KE (2015) How fuel ethanol is made from corn. In: Bioenergy. Elsevier, pp 379–384
Mousdale DM (2010) Introduction to biofuels. CRC Press
Murthy GS, Townsend DE, Meerdink GL, Bargren GL, Tumbleson ME, Singh V (2005) Effect of Aflatoxin B1 on dry-grind ethanol process. Cereal Chem 82:302–304
Mustafa AF, McKinnon JJ, Christensen DA (2000) Chemical characterization and in situ nutrient degradability of wet distillers’ grains derived from barley-based ethanol production. Anim Feed Sci Technol 83:301–311
Najafpour G, Younesi H, Ismail KSK (2004) Ethanol fermentation in an immobilized cell reactor using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 92:251–260
National Hog Farmer (2009) Low-Solubles Distillers Dried Grains Diets Improve Hog Carcass Fat Firmness. https://www.nationalhogfarmer.com/nutrition/1215-dds-improve-firmness
Nelson KA, Motavalli PP, Smoot RL (2009) Utility of dried distillers grain as a fertilizer source for corn. J Agric Sci 1:3
Nghiem NP, Montanti J, Kim TH (2016) Pre-treatment of dried distiller grains with solubles by soaking in aqueous ammonia and subsequent enzymatic/dilute acid hydrolysis to produce fermentable sugars. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179:237–250
Noureddini H, Byun J (2010) Dilute-acid pre-treatment of distillers’ grains and corn fiber. Bioresour Technol 101:1060–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.094
Nuez Ortín WG, Yu P (2009) Nutrient variation and availability of wheat DDGS, corn DDGS and blend DDGS from bioethanol plants. J Sci Food Agric 89:1754–1761
Otto E, Escovar-Kousen J (2005) Ethanol production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF)
Øverland M, Krogdahl Å, Shurson G, Skrede A, Denstadli V (2013) Evaluation of distiller’s dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and high protein distiller’s dried grains (HPDDG) in diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 416:201–208
Parsons CM, Martinez C, Singh V, Radhakrishman S, Noll S (2006) Nutritional value of conventional and modified DDGS for poultry. In: Multi-state Poult. Nutr. Feeding Conf. [CD-ROM]
Renewable Fuel Association (RFA) (2019) Annual World Fuel Ethanol Production. https://ethanolrfa.org/statistics/annual-ethanol-production/. Accessed 26 Dec 2019
Reuters (2019) China set to triple its ethanol production capacity: government researcher. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-ethanol/china-set-to-triple-its-ethanol-production-capacity-government-researcher-idUSKBN1OA0FH
RFA (2019) 2019 Ethanol Industry Outlook. https://ethanolrfa.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/RFA2019Outlook.pdf. Accessed 26 Dec 2019
Romero E, Bautista J, Garcia-Martinez AM, Cremades O, Parrado J (2007) Bioconversion of corn distiller’s dried grains with solubles (CDDGS) to extracellular proteases and peptones. Process Biochem 42:1492–1497
Rosentrater KA, Verbeek CJR (2017) Water adsorption characteristics of extruded blends of corn gluten meal and distillers dried grains with solubles. Food Bioprod Process 101:110–117
Rosentrater KA, Muthukumarappan K, Kannadhason S (2009) Effects of ingredients and extrusion parameters on aquafeeds containing DDGS and potato starch. J Aquac Feed Sci Nutr 1:22–38
Sargsyan H, Gabrielyan L, Trchounian A (2016) The distillers grains with solubles as a perspective substrate for obtaining biomass and producing bio-hydrogen by Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biomass Bioenergy 90:90–94
Seo J, Park TS, Kim JN, Ha JK, Seo S (2014) Production of endoglucanase, beta-glucosidase and xylanase by Bacillus licheniformis grown on minimal nutrient medium containing agriculture residues. Asian-Australasian J Anim Sci 27:946–950
Shurson J, Noll S (2005) Feed and alternative uses for DDGS. University of Minnesota
Singh V, Rausch KD, Yang P, Shapouri H, Belyea RL, Tumbleson ME (2001) Modified dry grind ethanol process. Dep Agric Eng Univ Illinois Champaign-Urbana, UILU
Song R, Chen C, Wang L, Johnston LJ, Kerr BJ, Weber TE, Shurson GC (2013) High sulfur content in corn dried distillers grains with solubles protects against oxidized lipids by increasing sulfur-containing antioxidants in nursery pigs. J Anim Sci 91:2715–2728
Spiehs MJ, Whitney MH, Shurson GC (2002) Nutrient database for distiller’s dried grains with solubles produced from new ethanol plants in Minnesota and South Dakota. J Anim Sci 80:2639–2645
Srinivasan R, Dien BS, Rausch KD, Tumbleson ME, Singh V (2007) Fiber separated from distillers dried grains with solubles as a feedstock for ethanol production. Cereal Chem 84:563–566
Szymanowska D, Grajek W (2009) Fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and ethanol fermentation of native corn starch. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment 8:5–16
Thaler B (2002) Use of distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) in swine diets. South Dakota State University
Tunpaiboon N (2019) Ethanol Industry. https://www.krungsri.com/bank/getmedia/0c42d6fd-18d7-41c1-9369-96dded234800/IO_Ethanol_190710_EN_EX.aspx. Accessed 31 Dec 2019
Ulrich JF, Anderson SC (2001) Extraction of corn oil from flaked corn grain
USDA (2019) GAIN report: India. https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/report/downloadreportbyfilename?filename=Biofuels Annual_New Delhi_India_8-9-2019.Pdf. Accessed 27 Dec 2019
Vertès AA, Qureshi N, Blaschek HP, Yukawa H (2020) Green energy to sustainability. Wiley Online Library, Hoboken
Voegele E (2019a) Canadian ethanol industry operating at full capacity. In: Ethanol Prod. Mag. http://ethanolproducer.com/articles/13646/report-canadian-ethanol-industry-operating-at-full-capacity. Accessed 27 Dec 2019
Voegele E (2019b) EU ethanol consumption to increase in 2019. In: Ethanol Prod. Mag. http://ethanolproducer.com/articles/16422/report-eu-ethanol-consumption-to-increase-in-2019. Accessed 27 Dec 2019
Wang H, Wang T, Johnson LA, Pometto AL III (2008) Effect of the corn breaking method on oil distribution between stillage phases of dry-grind corn ethanol production. J Agric Food Chem 56:9975–9980
Wang B, Ezeji T, Shi Z, Feng H, Blaschek HP (2009) Pre-treatment and conversion of distiller’s dried grains with solubles for acetone–butanol–ethanol (ABE) production. Trans ASABE 52:885–892
Wang X, Wang Y, Wang B, Blaschek H, Feng H, Li Z (2013) Biobutanol production from fiber-enhanced DDGS pretreated with electrolyzed water. Renew Energy 52:16–22
Weiss WP, Erickson DO, Erickson GM, Fisher GR (1989) Barley distillers grains as a protein supplement for dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 72:980–987
Welker TL, Lim C, Barrows FT, Liu K (2014) Use of distiller’s dried grains with solubles (DDGS) in rainbow trout feeds. Anim Feed Sci Technol 195:47–57
Wu YV (1986) Fractionation and characterization of protein-rich material from barley after alcohol distillation. Cereal Chem 63:142–145
Wu-Haan W, Burns RT, Moody LB, Hearn CJ, Grewell D (2010) Effect of ultrasonic pre-treatment on methane production potential from corn ethanol coproducts. Trans ASABE 53:883–890
Ximenes EA, Dien BS, Ladisch MR, Mosier N, Cotta MA, Li XL (2007) Enzyme production by industrially relevant fungi cultured on coproduct from corn dry grind ethanol plants. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 137:171–183
Zaini NABM, Chatzifragkou A, Charalampopoulos D (2019a) Microbial production of d-lactic acid from dried distiller’s grains with solubles. Eng Life Sci 19:21–30
Zaini NAM, Chatzifragkou A, Tverezovskiy V, Charalampopoulos D (2019b) Purification and polymerisation of microbial D-lactic acid from DDGS hydrolysates fermentation. Biochem Eng J 107265
Funding
This study was funded in part by Fulbright Student Program and USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture Federal Appropriations under Project PEN04594 and accession number 1007291.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.D. and D.C. conceived the idea. A.I. drafted the manuscript of the mini-review paper. A.D. and D.C. critically evaluated and made significant improvements. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Declarations of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iram, A., Cekmecelioglu, D. & Demirci, A. Distillers’ dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and its potential as fermentation feedstock. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 6115–6128 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10682-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10682-0