Abstract
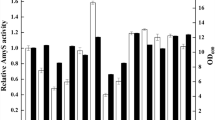
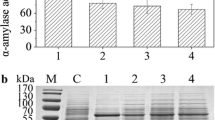
In the present work, we used systematic engineering at transport and transcription levels to significantly enhance alkaline α-amylase production in Bacillus subtilis 168M. Signal peptide YwbN’ proved to be optimal. Alkaline α-amylase production was elevated by deleting a putative peptide segment of YwbN’. Insertion of arginine (R) between residues 5 and 6 of YwbN’∆p further increased the protein yield. Enhancing positive charges at sites 4 and 10 and decreasing the hydrophobicity of the H-region of YwbN’∆p were critical for improving alkaline α-amylase production in B. subtilis 168M. PHpaII was the optimal promoter, and deleting − 27T or − 31A from PHpaII enhanced the transcription of the target gene. Using a single-pulse feeding-based fed-batch system, alkaline α-amylase activity of B. subtilis 168M P∆−27T was increased by 250.6-fold, compared with B. subtilis 168M A1.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballschmiter M, Fütterer O, Liebl W (2006) Identification and characterization of a novel intracellular alkaline α-amylase from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima MSB8. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2206–2211
Chen JQ, Zhao LQ, Fu G, Zhou WJ, Sun YX, Zhang DW (2016) A novel strategy for protein production using non-classical secretion pathway in Bacillus subtilis. Microb Cell Factories 15:69
Choi J, Lee S (2004) Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:625–635
Degering C, Eggert T, Puls M, Bongaerts J, Evers S, Maurer KH, Jaeger KE (2010) Optimization of protease secretion in Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis by screening of homologous and heterologous signal peptides. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6370–6376
Guan C, Cui W, Cheng J, Liu R, Liu Z, Zhou L, Zhou Z (2016a) Construction of a highly active secretory expression system via an engineered dual promoter and a highly efficient signal peptide in Bacillus subtilis. New Biotechnol 33:372–379
Guan C, Cui W, Cheng J, Zhou L, Liu Z, Zhou Z (2016b) Development of an efficient autoinducible expression system by promoter engineering in Bacillus subtilis. Microb Cell Factories 15:66
Harwood CR, Cranenburgh R (2008) Bacillus protein secretion: an unfolding story. Trends Microbiol 16:73–79
Helmann JD (1995) Compilation and analysis of Bacillus Subtilis σ A-dependent promoter sequences: evidence for extended contact between RNA polymerase and upstream promoter DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 23:2351–2360
Jiang Z, Niu TF, Lv XQ, Liu YF, Li JH, Lu W, Du GC, Chen J, Liu L (2019) Secretory expression fine-tuning and directed evolution of diacetylchitobiose deacetylase by Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 85:e01076–e01019
Kwon E-Y, Kim KM, Kim MK, Lee IY, Kim BS (2011) Production of nattokinase by high cell density fed-batch culture of Bacillus subtilis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34:789–793
Liu SL, Du K (2012) Enhanced expression of an endoglucanase in Bacillus subtilis by using the sucrose-inducible sacB promoter and improved properties of the recombinant enzyme. Protein Expr Purif 83:164–168
Liu L, Yang HQ, Shin HD, Chen RR, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J (2013a) How to achieve high-level expression of microbial enzymes: strategies and perspectives. Bioeng 4:212–223(b)
Liu L, Yang HQ, Shin HD, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J (2013b) Recent advances in recombinant protein expression by Corynebacterium, Brevibacterium, and Streptomyces: from transcription and translation regulation to secretion pathway selection. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9597–9608(a)
Liu L, Deng ZM, Yang HQ, Li JH, Shin HD, Chen RR, Du GC, Chen J (2014) In silico rational design and systems engineering of disulfide bridges in the catalytic domain of an alkaline alpha-amylase from Alkalimonas amylolytica to improve thermostability. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:798–807
Liu Q, Xun G, Feng Y (2018) The state-of-the-art strategies of protein engineering for enzyme stabilization. Biotechnol Adv 37:530–537
Ma YF, Yang HQ, Chen XZ, Sun B, Du GC, Zhou ZM, Song JN, Fan Y, Shen W (2015) Significantly improving the yield of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis by a novel powerful mutagenesis tool (ARTP): alkaline alpha-amylase as a case study. Protein Expr Purif 114:82–88
Ma YF, Shen W, Chen XZ, Liu L, Zhou ZM, Xu F, Yang HQ (2016) Significantly enhancing recombinant alkaline amylase production in Bacillus subtilis by integration of a novel mutagenesis-screening strategy with systems-level fermentation optimization. J Biol Eng 10:13
Nijland R, Kuipers OP (2008) Optimization of protein secretion by Bacillus subtilis. Recent Patents Biotechnol 2:79–87
Nithya K, Muthukumar C, Dhansasekaran D, Kadaikunnan S, Alharbi NS, Khaled JM, Thajuddin N (2016) Production, optimization and partial characterization of thermostable and alkaline amylase from Bacillus licheniformis KSU-6. Int J Agric Biol 18:1188–1194
Niu C, Liu C, Li Y, Zheng F, Wang J, Li Q (2018) Production of a thermostable 1, 3-1, 4-β-glucanase mutant in Bacillus subtilis WB600 at a high fermentation capacity and its potential application in the brewing industry. Int J Biol Macromol 107:28–34
Öztürk S, Calik P, Ozdamar TH (2016) Fed-batch biomolecule production by Bacillus subtilis: a state of the art review. Trends Biotechnol 34:329–345
Öztürk S, Ergün BG, Çalık P (2017) Double promoter expression systems for recombinant protein production by industrial microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:7459–7475
Phan TTP, Nguyen HD, Schumann W (2012) Development of a strong intracellular expression system for Bacillus subtilis by optimizing promoter elements. J Biotechnol 157:167–172
Phanaksri T, Luxananil P, Panyim S, Tirasophon W (2015) Synergism of regulatory elements in σB-and σA-dependent promoters enhances recombinant protein expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Biosci Bioeng 120:470–475
Ploss TN, Reilman E, Monteferrante CG, Denham EL, Piersma S, Lingner A, Vehmaanperä J, Lorenz P, van Dijl JM (2016) Homogeneity and heterogeneity in amylase production by Bacillus subtilis under different growth conditions. Microb Cell Factories 15:57
Prakash B, Vidyasagar M, Madhukumar MS, Muralikrishna G, Sreeramulua K (2009) Production, purification, and characterization of two extremely halotolerant, thermostable, and alkali-stable α-amylases from Chromohalobacter sp. TVSP 101. Process Biochem 44:210–215
Salis HM, Mirsky EA, Voigt CA (2009) Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to control protein expression. Nat Biotechnol 27:946–950
Sauer C, Ver Loren van Themaat E, LGM B, Groothuis D, Cruz R, Hamoen LW, Harwood CR, van Rij T (2018) Exploring the nonconserved sequence space of synthetic expression modules in Bacillus subtilis. ACS Synth Biol 7:1773–1784
Saxena RK, Dutt K, Agarwal L, Nayyar P (2007) A highly thermostable and alkaline amylase from a Bacillus sp. PN5. Bioresour Technol 98:260–265
Shen HB, Chou KC (2007) Signal-3L: a 3-layer approach for predicting signal peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363:297–303
Song Y, Nikoloff JM, Zhang D (2015) Improving protein production on the level of regulation of both expression and secretion pathways in Bacillus subtilis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:963–977
Song Y, Fu G, Dong H, Li J, Du Y, Zhang D (2017) High-efficiency secretion of β-mannanase in Bacillus subtilis through protein synthesis and secretion optimization. J Agric Food Chem 65:2540–2548
Spizizen J (1958) Transformation of biochemically deficient strains of Bacillus subtilis by deoxyribonucleate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 44:1072–1078
Tian RZ, Liu YL, Chen JR, Li JH, Liu L, Du GC, Chen J (2019) Synthetic N-terminal coding sequences for fine-tuning gene expression and metabolic engineering in Bacillus subtilis. Metab Eng 55:131–141
Trang Thi Phuong P, Hoang Duc N, Schumann W (2012) Development of a strong intracellular expression system for Bacillus subtilis by optimizing promoter elements. J Biotechnol 157:167–172
van Dijl J, Hecker M (2013) Bacillus subtilis: from soil bacterium to super-secreting cell factory. Microb Cell Factories 12:3
Veening JW, Igoshin OA, Eijlander RT, Nijland R, Hamoen LW, Kuipers OP (2008) Transient heterogeneity in extracellular protease production by Bacillus subtilis. Mol Syst Biol 4:184
Voskuil MI, Chambliss GH (1998) The −16 region of Bacillus subtilis and other gram-positive bacterial promoters. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3584–3590
Wu S-M, Feng C, Zhong J, Huan L-D (2011) Enhanced production of recombinant nattokinase in Bacillus subtilis by promoter optimization. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:99–106
Yang HQ, Liu L, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J (2011) Heterologous expression, biochemical characterization, and overproduction of alkaline alpha-amylase from Bacillus alcalophilus in Bacillus subtilis. Microb Cell Factories 10:77
Yang HQ, Liu L, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J (2012a) Advances of alkaline amylase production and applications. Chin J Biotechnol 28:432–439(a)
Yang HQ, Liu L, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J (2012b) Cloning, heterologous expression, and comparative characterization of a mesophilic alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus subtilis JN16 in Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 62:1219–1226(b)
Yang HQ, Liu L, Shin HD, Chen RR, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J (2013a) Integrating terminal truncation and oligopeptide fusion for a novel protein engineering strategy to improve specific activity and catalytic efficiency: alkaline alpha-amylase as a case study. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:6429–6438(a)
Yang HQ, Lu XY, Liu L, Li JH, Shin HD, Chen RR, Du GC, Chen J (2013b) Fusion of an oligopeptide to the N terminus of an alkaline alpha-amylase from Alkalimonas amylolytica simultaneously improves the enzyme’s catalytic efficiency, thermal stability, and resistance to oxidation. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3049–3058(b)
Yang M, Zhang W, Ji S, Cao P, Chen Y, Zhao X (2013c) Generation of an artificial double promoter for protein expression in Bacillus subtilis through a promoter trap system. PLoS One 8:e56321(c)
Yang HQ, Hu JY, Lu X, Wang FX, Shen W, Hu W, Wang LL, Chen XZ, Liu L (2019) Improving extracellular protein production in Escherichia coli by overexpressing D, D-carboxypeptidase to perturb peptidoglycan network synthesis and structure. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:793–806
Zanen G, Houben EN, Meima R, Tjalsma H, Jongbloed JD, Westers H, Oudega B, Luirink J, van Dijl JM, Quax WJ (2005) Signal peptide hydrophobicity is critical for early stages in protein export by Bacillus subtilis. FEBS J 272:4617–4630
Zhang YZ, Shen HB (2017) Signal-3L 2.0: a hierarchical mixture model for enhancing protein signal peptide prediction by incorporating residue-domain cross-level features. J Chem Inf Model 57:988–999
Zou M, Guo F, Li X, Zhao J, Qu Y (2014) Enhancing production of alkaline polygalacturonate lyase from Bacillus subtilis by fed-batch fermentation. PLoS One 9:e90392
Funding
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21406089), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20140152, BK20191185), and the Open Project Program of the Key Laboratory of Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biotechnology, Ministry of Education, China (KLCCB-KF201802), 111 Project (111-2-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Y. and X.C. designed the research; H.Y. and Y.M. performed the research; W.S., Y.Z., and X.C. analysed the data; H.Y., Y.M., and X.C. wrote this paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This work follows ethical standards. It contains no experiments with animals performed or human participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 710 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Ma, Y., Zhao, Y. et al. Systematic engineering of transport and transcription to boost alkaline α-amylase production in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 2973–2985 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10435-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10435-z