Abstract
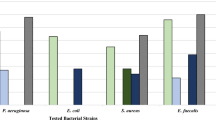
This work aimed at investigating the chemical composition, antibacterial properties, and effect mechanism of Smilax china L. polyphenols (SCLP). SCLP was extracted and purified, and then, its eighteen polyphenolic compounds were identified by LC-MS/MS analysis. SCLP exhibited antibacterial activity against five bacteria (Salmonella typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, and Escherichia coli) with minimum inhibitory concentration in a range of 195.31 to 781.25 μg/mL. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus showed a higher sensitivity to SCLP. Notably, when combined with antibiotics, the SCLP–thiamphenicol and SCLP–gatifloxacin combinations showed additional properties against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, while SCLP–streptomycin and SCLP–penicillin combinations exhibited dramatically synergistic effects. In addition, the changes in permeability and integrity of the cell membrane and cell wall were observed by measuring UV absorption, extracellular AKP concentration, FTIR spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy. It is speculated that the mechanism of action of SCLP on bacteria may be described as destruction of bacterial cell wall and cell membrane. In conclusion, SCLP was a potential natural antimicrobial substance with strong antimicrobial activity, which may reduce the use of antibiotics or combat drug-resistant bacteria through synergistic combination with antibiotics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzoreky NS, Nakahara K (2003) Antibacterial activity of extracts from some edible plants commonly consumed in Asia. Int J Food Microbiol 80(3):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1605(02)00169-1
Bhattacharya D, Ghosh D, Bhattacharya S, Sarkar S, Karmakar P, Koley H, Gachhui R (2018) Antibacterial activity of polyphenolic fraction of Kombucha against Vibrio cholerae: targeting cell membrane. Lett Appl Microbiol 66(2):145–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12829
Borchers AT, Keen CL, Gershwin ME (2004) Mushrooms, tumors, and immunity: an update. Exp Biol Med 229(5):393–406. https://doi.org/10.1177/153537020422900507
Bulet P, Dimarcq JL, Hetru C, Lagueux M, Charlet M, Hegy G, Van DA, Hoffmann JA (1993) A novel inducible antibacterial peptide of Drosophila carries an O-glycosylated substitution. J Biol Chem 268(20):14893–14897
Calo JR, Crandall PG, O'Bryan CA, Ricke SC (2015) Essential oils as antimicrobials in food systems–a review. Food Control 54:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.12.040
Chen L, Yin H, Lan Z, Ma S, Zhang C, Yang Z, Li P, Lin B (2011) Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of Smilax China L. J Ethnopharmacol 135(2):399–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.03.033
Chen TY, Kuo SH, Chen ST, Hwang DF (2016) Differential proteomics to explore the inhibitory effects of acidic, slightly acidic electrolysed water and sodium hypochlorite solution on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Chem 194:529–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.019
Daglia M (2012) Polyphenols as antimicrobial agents. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23(2):174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.08.007
Davies J, Davis BD (1968) Misreading of ribonucleic acid code words induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. The effect of drug concentration. J Biol Chem 243(12):3312–3316
Estevinho L, Pereira AP, Moreira L, Dias LG, Pereira E (2008) Antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of phenolic compounds extracts of Northeast Portugal honey. Food Chem Toxicol 46(12):3774–3779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.09.062
Fleming-Jones ME, Smith RE (2003) Volatile organic compounds in foods: a five year study. J Agric Food Chem 51(27):8120–8127. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0303159
Ghosh A, Das BK, Roy A, Mandal B, Chandra G (2008) Antibacterial activity of some medicinal plant extracts. J Nat Med 62(2):259–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-007-0216-x
Guendouze-Bouchefa N, Madani K, Chibane M, Boulekbache-Makhlouf L, Hauchard D, Kiendrebeogo M, Stévigny C, Okusa PN, Duez P (2015) Phenolic compounds, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of three Ericaceae from Algeria. Ind Crop Prod 70:459–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.03.053
Hajji M, Jarraya R, Lassoued I, Masmoudi O, Damak M, Nasri M (2010) GC/MS and LC/MS analysis, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of various solvent extracts from Mirabilis jalapa tubers. Process Biochem 45(9):1486–1493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.05.027
Helm D, Labischinski H, Schallehn G, Naumann D (1991) Classification and identification of bacteria by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Microbiology. 137(1):69–79. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-137-1-69
Lee SY, Kim JH, Park JM, Lee IC, Lee JY (2014) Antioxidant activity and inhibition activity against α-amylase and α-glucosidase of Smilax China L. Korean J Food Pres 21(2):254–263. https://doi.org/10.11002/kjfp.2014.21.2.254
Lee H, Kim J, Whang W (2017) Chemical constituents of Smilax China L. stems and their inhibitory activities against glycation, aldose reductase, α-glucosidase, and lipase. Molecules. 22(3):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030451
Liang S, Dang Q, Liu C, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhu W, Chang G, Sun H, Cha D, Fan B (2018) Characterization and antibacterial mechanism of poly (aminoethyl) modified chitin synthesized via a facile one-step pathway. Carbohydr Polym 195:275–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.109
Lv F, Liang H, Yuan Q, Li C (2011) In vitro antimicrobial effects and mechanism of action of selected plant essential oil combinations against four food-related microorganisms. Food Res Int 44(9):3057–3064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.07.030
Moellering RC, Weinberg AN (1971) Studies on antibiotic synergism against enterococci: II. Effect of various antibiotics on the uptake of 14C-labeled streptomycin by enterococci. J Clin Invest 50(12):2580–2584. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI106758
Nho KJ, Chun JM, Kim HK (2015) Anti-metastatic effect of Smilax china L. extract on MDA-MB-231 cells. Mol Med Rep 11(1):499–502. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2698
Nowacka N, Nowak R, Drozd M, Olech M, Los R, Malm A (2014) Analysis of phenolic constituents, antiradical and antimicrobial activity of edible mushrooms growing wild in Poland. LWT-Food Sci Technol 59(2):689–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.05.041
Oust A, Møretrø T, Kirschner C, Narvhus JA, Kohler A (2004) FT-IR spectroscopy for identification of closely related lactobacilli. J Microbiol Methods 59(2):149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2004.06.011
Park SC, Kim MH, Hossain MA, Shin SY, Kim Y, Stella L, Wade JD (2008) Amphipathic α-helical peptide, HP (2–20), and its analogues derived from Helicobacter pylori: pore formation mechanism in various lipid compositions. BBA-Biomembranes. 1778(1):229–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.09.020
Pereira V, Dias C, Vasconcelos MC, Rosa E, Saavedra MJ (2014) Antibacterial activity and synergistic effects between Eucalyptus globulus leaf residues (essential oils and extracts) and antibiotics against several isolates of respiratory tract infections (Pseudomonas aeruginosa). Ind Crop Prod 52:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.09.032
Shan B, Cai YZ, Brooks JD, Corke H (2008) Antibacterial properties of Polygonum cuspidatum roots and their major bioactive constituents. Food Chem 109(3):530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.064
Shen S, Zhang T, Yuan Y, Lin S, Xu J, Ye H (2015) Effects of cinnamaldehyde on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus membrane. Food Control 47:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.07.003
Shu XS, Gao ZH, Yang XL (2006) Anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities of Smilax china L. aqueous extract. J Ethnopharmacol 103(3):327–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.08.004
Slinkard K, Singleton VL (1977) Total phenol analysis: automation and comparison with manual methods. Am J Enol Vitic 28(1):49–55
Song L, Tian L, Ma Y, Xie Y, Feng H, Qin F, Mo L, Lin S, Hou L (2017) Protection of flavonoids from Smilax china L. rhizome on phenol mucilage-induced pelvic inflammation in rats by attenuating inflammation and fibrosis. J Funct Foods 28:194–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2016.11.015
Springer B, Kidan YG, Prammananan T, Ellrott K, Böttger EC, Sander P (2001) Mechanisms of streptomycin resistance: selection of mutations in the 16S rRNA gene conferring resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45(10):2877–2884. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.45.10.2877-2884.2001
Tang YL, Shi YH, Zhao W, Hao G, Le GW (2008) Insertion mode of a novel anionic antimicrobial peptide MDpep5 (Val-Glu-Ser-Trp-Val) from Chinese traditional edible larvae of housefly and its effect on surface potential of bacterial membrane. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48(4):1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2008.09.006
Tang W, Zhang H, Wang L, Qian H (2014) New cationic antimicrobial peptide screened from boiled-dried anchovies by immobilized bacterial membrane liposome chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 62(7):1564–1571. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4052286
Tatsimo SJN, Lamshöft M, Mouafo FT, Lannang AM, Sarkar P, Bag PK, Spiteller M (2015) LC-MS guided isolation of antibacterial and cytotoxic constituents from Clausena anisata. Med Chem Res 24(4):1468–1479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-1233-4
Taukoorah U, Lall N, Mahomoodally F (2016) Piper betle L. (betel quid) shows bacteriostatic, additive, and synergistic antimicrobial action when combined with conventional antibiotics. S Afr J Bot 105:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2016.01.006
Vasconcelos NG, Croda J, Simionatto S (2018) Antibacterial mechanisms of cinnamon and its constituents: a review. Microb Pathog 120:198–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.04.036
Vastano BC, Chen Y, Zhu N, Ho CT, Zhou Z, Rosen RT (2000) Isolation and identification of stilbenes in two varieties of Polygonum cuspidatum. J Agric Food Chem 48(2):253–256. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9909196
Wang N, Chen H, Xiong L, Liu X, Li X, An Q, Ye X, Wang W (2018) Phytochemical profile of ethanolic extracts of Chimonanthus salicifolius SY Hu. leaves and its antimicrobial and antibiotic-mediating activity. Ind Crop Prod 125:328–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.09.021
Wu X, Li Z, Li X, Tian Y, Fan Y, Yu C, Zhou B, Liu Y, Xiang R, Yang L (2017) Synergistic effects of antimicrobial peptide DP7 combined with antibiotics against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Drug Des Dev Ther 11:939–946. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S107195
Yang D, Zhang Q, Wang Q, Chen L, Liu Y, Cong M, Wu H, Li F, Ji C, Zhao J (2018) A defensin-like antimicrobial peptide from the manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum: investigation of the antibacterial activities and mode of action. Fish Shellfish Immunol 80:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.06.019
Zhang Y, Wu YT, Zheng W, Han XX, Jiang YH, Hu PL, Tang ZX, Shi LE (2017) The antibacterial activity and antibacterial mechanism of a polysaccharide from Cordyceps cicadae. J Funct Foods 38:273–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.09.047
Ziani BE, Heleno SA, Bachari K, Dias MI, Alves MJ, Barros L, Ferreira ICFR (2019) Phenolic compounds characterization by LC-DAD-ESI/MSn and bioactive properties of Thymus algeriensis Boiss. & Reut. and Ephedra alata Decne. Food Res Int 116:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.08.041
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81760157).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 339 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Xue, H., Li, X. et al. Chemical composition, antibacterial properties, and mechanism of Smilax china L. polyphenols. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 9013–9022 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10100-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10100-0