Abstract
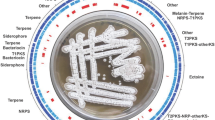
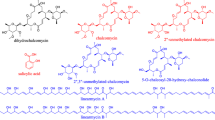
The genus Streptomyces have been highly regarded for their important source of natural products. Combined with the technology of genome sequencing and mining, we could identify the active ingredients from fermentation broth quickly. Here, we report on Streptomyces sp. strain fd1-xmd, which was isolated from a soil sample collected in Shanghai. Interestingly, the fermentation broth derived from this strain demonstrated broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, and eukaryotes. To identify the antimicrobial substances and their biosynthetic gene clusters, we sequenced the fd1-xmd strain and obtained a genome 7,929,999 bp in length. The average GC content of the chromosome was 72.5 mol%. Knockout experiments demonstrated that out of eight biosynthetic gene clusters we could identify, two are responsible for the biosynthesis of the antibiotics streptothricin (ST) and tunicamycin (TM). The ST biosynthetic gene cluster from fd1-xmd was verified via successful heterologous expression in Streptomyces coelicolor M1146. ST production had a yield of up to 0.5 g/L after the optimization of culture conditions. This study describes a novel producer of ST and TM and outlines the complete process undertaken for Streptomyces sp. strain fd1-xmd genome mining.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltz RH (2007) Antimicrobials from actinomycetes: back to the future. Microbe 2(3):125–131
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417(6885):141–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/417141a
Berdy J (2005) Bioactive microbial metabolites. J Antibiot 58(1):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2005.1
BillotKlein D, Shlaes D, Bryant D, Bell D, Legrand R, Gutmann L, van Heijenoort J (1997) Presence of UDP-N-acetylmuramyl-hexapeptides and -heptapeptides in enterococci and staphylococci after treatment with ramoplanin, tunicamycin, or vancomycin. J Bacteriol 179(15):4684–4688. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.15.4684-4688.1997
Blin K, Medema MH, Kazempour D, Fischbach MA, Breitling R, Takano E, Weber T (2013) antiSMASH 2.0—a versatile platform for genome mining of secondary metabolite producers. Nucleic Acids Res 41(W1):W204–W212. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt449
Borders DB, Sax KJ, Lancaste JE, Hausmann WK, Mitscher LA, Wetzel ER, Patterson EL (1970) Structures of Ll-Ac541 and Ll-Ab664—new streptothricin-type antibiotics. Tetrahedron 26(13):3123–3133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)92895-9
Carver T, Berriman M, Tivey A, Patel C, Bohme U, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Rajandream MA (2008) Artemis and ACT: viewing, annotating and comparing sequences stored in a relational database. Bioinformatics 24(23):2672–2676. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn529
Carver T, Thomson N, Bleasby A, Berriman M, Parkhill J (2009) DNAPlotter: circular and linear interactive genome visualization. Bioinformatics 25(1):119–120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn578
Chang CY, Lyu SY, Liu YC, Hsu NS, Wu CC, Tang CF, Lin KH, Ho JY, Wu CJ, Tsai MD, Li TL (2014) Biosynthesis of streptolidine involved two unexpected intermediates produced by a dihydroxylase and a cyclase through unusual mechanisms. Angew Chem Int Edit 53(7):1943–1948. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201307989
Chen WQ, Qu DJ, Zhai LP, Tao MF, Wang YM, Lin SJ, Price NPJ, Deng ZX (2010) Characterization of the tunicamycin gene cluster unveiling unique steps involved in its biosynthesis. Protein Cell 1(12):1093–1105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-010-0127-6
Dai RX, Zhang B, Zhao GP, Ding XM (2015) Site-specific recombination for cloning of large DNA fragments in vitro. Eng Life Sci 15(6):655–659. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201400267
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence-limits on phylogenies—an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Flett F, Mersinias V, Smith CP (1997) High efficiency intergeneric conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to methyl DNA-restricting streptomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 155(2):223–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1997.tb13882.x
Gan ML, Zheng XD, Liu YF, Guan Y, Xiao CL (2012) Three new 12-carbamoylated streptothricins from Streptomyces sp I08A 1776. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(19):6151–6154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.08.003
Gause GF, Preobrazhenskaya TP, Sveshnikova MA, Terekhova LP, Maximova TS (1983) A guide for the determination of Actinomycetes. Nauka, Moscow (in Russian)
Ghai R, Hain T, Chakraborty T (2004) GenomeViz: visualizing microbial genomes. BMC Bioinf 5(1):198. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-5-198
Gomez-Escribano JP, Bibb MJ (2011) Engineering Streptomyces coelicolor for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters. Microb Biotechnol 4(2):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7915.2010.00219.x
Goodfellow M, Fiedler HP (2010) A guide to successful bioprospecting: informed by actinobacterial systematics. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 98(2):119–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9460-2
Guo Z, Li J, Qin H, Wang M, Lv X, Li X, Chen Y (2015) Biosynthesis of the carbamoylated D-gulosamine moiety of streptothricins: involvement of a guanidino-N-glycosyltransferase and an N-acetyl-D-gulosamine deacetylase. Angew Chem Int Edit 54(17):5175–5178. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201412190
Hartl A, Guttner J, Stockel U, Hoffmann H (1986) Acute and subchronic toxicity of nourseothricin in laboratory animals. Arch Exp Vet 40(5):727–735
Haupt I, Jonak J, Rychlik I, Thrum H (1980) Action of streptothricin-F on ribosomal functions. J Antibiot 33(6):636–641. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.33.636
Hoffmann H, Hartl A, Bocker H, Kuhnel HJ, Hesse G, Flemming J (1986a) Pharmacokinetics of nourseothricin in laboratory animals. Arch Exp Vet 40(5):699–709
Hoffmann H, Kirchner E, Knappe H, Hillesheim HG, Hartl A, Hubler D, Chemnitius KH, Morgenstern E, Grupe R (1986b) Pharmacological action profile of nourseothricin. Arch Exp Vet Med 40(5):710–720
Inamori Y, Amino H, Tsuboi M, Yamaguchi S, Tsujibo H (1990) Biological activities of racemomycin-B, beta-lysine rich streptothricin antibiotic, the main component of Streptomyces-Lavendulae Op-2. Chem Pharm Bull 38(8):2296–2298. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.38.2296
Jelenska J, Tietze E, Tempe J, Brevet J (2000) Streptothricin resistance as a novel selectable marker for transgenic plant cells. Plant Cell Rep 19(3):298–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050016
Ji ZQ, Wang MA, Zhang JW, Wei SO, Wu WJ (2007) Two new members of streptothricin class antibiotics from Streptomyces qinlingensis sp nov. J Antibiot 60(12):739–744. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2007.96
Kenig M, Reading C (1979) Holomycin and an antibiotic (Mm-19290) related to tunicamycin, metabolites of Streptomyces-Clavuligerus. J Antibiot 32(6):549–554. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.32.549
Khokhlov AS, Reshetov PD (1964) Chromatography of streptothricins on carboxymethylcellulose. J Chromatogr 14(3):495–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(00)86662-5
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kim BT, Lee JY, Lee YY, Kim OY, Chu JH, Goo YM (1994) N-Methylstreptothricin-D—a new streptothricin-group antibiotic from a Streptomyces spp. J Antibiot 47(11):1333–1336. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.47.1333
Krumsiek J, Arnold R, Rattei T (2007) Gepard: a rapid and sensitive tool for creating dotplots on genome scale. Bioinformatics 23(8):1026–1028. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm039
Kusumoto S, Imaoka S, Kambayashi Y, Shiba T (1982a) Total synthesis of antibiotic streptothricin-F. Tetrahedron Lett 23(29):2961–2964. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(00)87506-1
Kusumoto S, Kambayashi Y, Imaoka S, Shima K, Shiba T (1982b) Total chemical-structure of streptothricin. J Antibiot 35(7):925–927. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.35.925
Labeda DP, Goodfellow M, Brown R, Ward AC, Lanoot B, Vanncanneyt M, Swings J, Kim SB, Liu Z, Chun J, Tamura T, Oguchi A, Kikuchi T, Kikuchi H, Nishii T, Tsuji K, Yamaguchi Y, Tase A, Takahashi M, Sakane T, Suzuki KI, Hatano K (2012) Phylogenetic study of the species within the family Streptomycetaceae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101(1):73–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9656-0
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10(3):R25. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2009-10-3-r25
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, Proc GPD (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25(16):2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li JE, Guo ZY, Huang W, Meng XX, Ai GM, Tang GL, Chen YH (2013) Mining of a streptothricin gene cluster from Streptomyces sp TP-A0356 genome via heterologous expression. Sci China Life Sci 56(7):619–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-013-4504-2
Maruyama C, Toyoda J, Kato Y, Izumikawa M, Takagi M, Shin-ya K, Katano H, Utagawa T, Hamano Y (2012) A stand-alone adenylation domain forms amide bonds in streptothricin biosynthesis. Nat Chem Biol 8(9):791–797. https://doi.org/10.1038/Nchembio.1040
Medema MH, Trefzer A, Kovalchuk A, van den Berg M, Muller U, Heijne W, Wu LA, Alam MT, Ronning CM, Nierman WC, Bovenberg RAL, Breitling R, Takano E (2010) The sequence of a 1.8-Mb bacterial linear plasmid reveals a rich evolutionary reservoir of secondary metabolic pathways. Genome Biol Evol 2:212–224. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evq013
Ohba K, Nakayama H, Furihata K, Furihata K, Shimazu A, Seto H, Otake N, Yang ZZ, Xu LS, Xu WS (1986) Albothricin, a new streptothricin antibiotic. J Antibiot 39(6):872–875. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.39.872
Olden K, Pratt RM, Jaworski C, Yamada KM (1979) Evidence for role of glycoprotein carbohydrates in membrane-transport-specific inhibition by tunicamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76(2):791–795. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.76.2.791
Romer W, Hesse G, Miosga N, Fricke H (1986) Chemical determination of the streptothricin antibiotic nourseothricin. Arch Exp. Vet Med 40(5):693–698
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method—a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Shima J, Penyige A, Ochi K (1996) Changes in patterns of ADP-ribosylated proteins during differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and its developmental mutants. J Bacteriol 178(13):3785–3790. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.178.13.3785-3790.1996
Takatsuki A, Arima K, Tamura G (1971) Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic. 1. Isolation and characterization of tunicamycin. J Antibiot 24(4):215–223. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.24.215
Takatsuki A, Kawamura K, Okina M, Kodama Y, Ito T, Tamura G (1977) Structural elucidation of tunicamycin. 2. Structure of tunicamycin. Agric Biol Chem Tokyo 41(11):2307–2309
Takemoto T, Inamori Y, Kato Y, Kubo M, Morimoto K, Morisaka K, Sakai M, Sawada Y, Taniyama H (1980) Physiological-activity of streptothricin antibiotics. Chem Pharm Bull 28(10):2884–2891. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.28.2884
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tang B, Wang Q, Yang MJ, Xie F, Zhu YQ, Zhuo Y, Wang SY, Gao H, Ding XM, Zhang LX, Zhao GP, Zheng HJ (2013) ContigScape: a Cytoscape plugin facilitating microbial genome gap closing. BMC Genomics 14(1):289. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-289
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44(14):6614–6624. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw569
Vantamelen E, Whitfield GB, Dyer JR, Carter HE, Whaley HA (1961) Constitution of the streptolin-streptothricin group of Streptomyces antibiotics. J Am Chem Soc 83(20):4295–4296. https://doi.org/10.1021/Ja01481a051
Waksman SA (1943) Production and activity of streptothricin. J Bacteriol 46(3):299–310
Waksman SA, Henrici AT (1943) The nomenclature and classification of the actinomycetes. J Bacteriol 46(4):337–341
Waksman SA, Woodruff HB (1942) Streptothricin, a new selective bacteriostatic and bactericidal agent active against gram-negative bacteria. P Soc Exp Biol Med 49(2):207–210. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-49-13515
Witte W (2000) Selective pressure by antibiotic use in livestock. Int J Antimicrob Agents 16:S19–S24
Xu HL, Inagaki Y, Seyama Y, Sugawara Y, Kokudo N, Nakata M, Wang FS, Tang W (2009) Expression of KL-6 mucin, a human MUC1 mucin, in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its potential involvement in tumor cell adhesion and invasion. Life Sci 85(9–10):395–400
Zhang L, Ou XJ, Zhao GP, Ding XM (2008) Highly efficient in vitro site-specific recombination system based on Streptomyces phage phi BT1 integrase. J Bacteriol 190(19):6392–6397. https://doi.org/10.1128/Jb.00777-08
Zhang B, Zhang L, Dai RX, Yu MY, Zhao GP, Ding XM (2013) An efficient procedure for marker-free mutagenesis of S. coelicolor by site-specific recombination for secondary metabolite overproduction. PLoS One 8(2):e55906. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055906
Zhu CX, Jiang XL, Sun DY, Ji HJ, Tian YL, Xie DL, Ni CF (2002) Zhongshengmycin, a new agro-antibiotics. Fine Specialty Chem 16:14–17 (In Chinese)
Funding
This work was financially supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFA0500600), the Basic Research Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (17JC1401800), and the Youth Talent Training Program of Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2017R19R08E01). This work was also supported by grant from the Natural Science Foundation for the Youth (31700007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 582 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Tang, B., Dai, R. et al. Identification of the streptothricin and tunicamycin biosynthetic gene clusters by genome mining in Streptomyces sp. strain fd1-xmd. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 2621–2633 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8748-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8748-4