Abstract
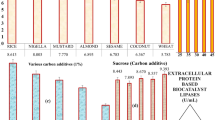
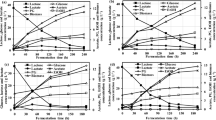
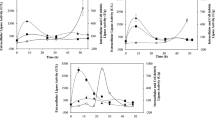
Currently, much attention is paid to technologies which can be drivers of the circular economy across different sectors, in particular, to develop technologies for utilization or reusability of biocompatible materials from industrial waste. One of such is the milk whey, which is a cheap biobased raw material, the disposal of which is a major problem for the dairy industry. Our proposed and investigated technology is based on a continuous exploitation of the whey combining microbiology and biotechnology. Primarily, whey was used as a nutrition source for the cultivation of Kluyveromyces lactis with the aim to produce the targeted biocatalyst—lipase. During cultivation, the whey was transformed into the hydrolyzed form, which was further successfully applied as a protein feeder (external linker) for immobilization of lipase by cross-linked enzyme aggregate (CLEA) method. The first time use of whey as a co-feeder for immobilization of enzymes by CLEA method has shown promising results and increased the stability of lipases for temperature and organic solvents. Hydrolysis of rapeseed oil catalyzed with immobilized derivatives was obtained with 45–96% efficiency at non-optimized conditions. Additionally, the determined kinetic parameters indicated that the rate of p-nitrophenyl palmitate hydrolysis was not changed drastically after immobilization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belem MAF, Lee BH (1998) Production of bioingredient from Kluyveromyces marxianus grown on whey—an alternative. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 38:565–598. doi:10.1080/10408699891274318
Bornscheuer UT (2008) Alteration of lipase properties by protein engineering methods. OCL 15(3):184–188. doi:10.1051/ocl.2008.0192
Bornscheuer UT (2013) Enzymes in lipid modification: from classical biocatalysis with commercial enzymes to advanced protein engineering. OCL 20(1):45–49. doi:10.1051/ocl.2012.0487
Cantone S, Ferrario V, Corici L, Ebert C, Fattor D, Spizzoa P, Gardossi L (2013) Efficient immobilization of industrial biocatalysts: criteria and constraints for the selection of organic polymeric carriers and immobilization methods. Chem Soc Rev 42:6262–6276. doi:10.1039/C3CS35464D
Celik E, Calik P (2012) Production of recombinant proteins by yeast cells. Biotechnol Adv 30:1108–1118. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.09.011
Cui JD, Jia SR (2015) Optimization protocols and improved strategies of cross-linked enzyme aggregates technology: current development and future challenges. Crit Rev Biotechnol 35(1):15–28. doi:10.3109/07388551.2013.795516
Datta S, Christena LR, Rajaram YRS (2013) Enzyme immobilization: an overview on techniques and support materials. 3. Biotech 3(1):1–9. doi:10.1007/s13205-012-0071-7
Gupta R, Gupta N, Rathi P (2004) Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification, and biochemical properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:763–781. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1568-8
Gurung N, Ray S, Bose S, Rai V (2013) A broader view: microbial enzymes and their relevance in industries, medicine and beyond. BioMed Res Int article ID 32912. Doi: 10.1155/2013/329121
Jesionowski T, Zdarta J, Krajewska B (2014) Enzyme immobilization by adsorption: a review. Adsorption 20(5–6):801–821. doi:10.1007/s10450-014-9623-y
Karimpil JJ, Melo JS, D’Souza SF (2011) Hen egg white as a feeder protein for lipase immobilization. J Mol Cat B Enz 71:113–118. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2011.04.006
Knezevic ZD, Siler-Marinkovic SS, Majovic LV (2004) Immobilized lipases as practical catalysts. APTE 35:151–164. doi:10.2298/APT0435151K
Lima VMG, Krieger N, Mitchell DA, Fontana JD (2004) Activity and stability of a crude lipase from Penicillium aurantiogriseum in aqueous media and organic solvents. Biochem Eng J 18:65–71. doi:10.1016/S1369-703X(03)00165-7
Liu W, Wang L, Jiang R (2012) Specific enzyme immobilization approaches and their application with nanomaterials. Top Catal 55:1146–1156. doi:10.1007/s11244-012-9893-0
Rumbold K, van Buijsen HJJ, Gray VM, van Groenestijn JW, Overkamp KM, Slomp RS, van der Werf MJ, Punt PJ (2010) Microbial renewable feedstock utilization. Bioengineered Bugs 1(5):359–366. doi:10.4161/bbug.1.5.12389
Sheldon RA, van Pelt S, Kanbak-Aksu S, Rasmussen J, Janssen MHA (2013) Cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) in organic synthesis. Aldrichimica Acta 46(3):81–93. doi:10.1039/C3CS60075K
Šiekštelė R, Veteikytė A, Tvaska B, Matijošytė I (2015) Yeast Kluyveromyces lactis as host for expression of the bacterial lipase: cloning and adaptation of the new lipase gene from Serratia sp. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:1309–1317. doi:10.1007/s10295-015-1655-0
Tran DN, Balkus K Jr (2011) Perspective of recent progress in immobilization of enzymes. ACS Catal 1:956–968. doi:10.1021/cs200124a
Treichel H, de Oliveira D, Mazutti MA, DiLuccio M, Oliveira JV (2010) A review of microbial lipases production. Food Bioprocess Technol 3:182–196. doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0202-2
Tukel SS, Hurrem F, Yildirim D, Alptekin O (2013) Preparation of crosslinked enzyme aggregates (CLEA) of catalase and its characterization. J Mol Cat B: Enz 97:252–257. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2013.09.007
Vakhlu J, Kour A (2006) Yeast lipases: enzyme purification, biochemical properties, and gene cloning. Electron J Biotechnol 9(1):69–85. doi:10.2225/vol9-issue1-fulltext-9
Winkler UK, Stuckmann M (1979) Glycogen, hyaluronate, and some other polysaccharides greatly enhance the formation of exolipase by Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol 138:663–670
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by project Biolubricant No. 31V-45, Agency for Science, Innovation, and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veteikytė, A., Šiekštelė, R., Tvaska, B. et al. Sequential application of waste whey as a medium component for Kluyveromyces lactis cultivation and a co-feeder for lipase immobilization by CLEA method. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 3617–3626 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8131-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8131-x