Abstract
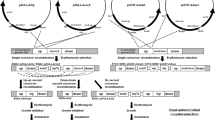
In this paper, we present a new counterselection method for deleting fragments from Lactococcus lactis chromosome. The method uses a non-replicating plasmid vector, which integrates into the chromosome and makes the cell sensitive to bacteriocins. The integration vector carries pUC ori functional in Escherichia coli but not in L. lactis, an erythromycin resistance gene for selecting single crossover integrants, and two fragments from L. lactis chromosome for homologous recombinations. In addition, the integration vector is equipped with the Listeria monocytogenes gene mptC encoding the mannose-phosphotransferase system component IIC, the receptor for class IIa bacteriocins. Expression of mptC from the integration vector renders the naturally resistant L. lactis sensitive to class IIa bacteriocins. This sensitivity is then used to select the double crossover colonies on bacteriocin agar. Only the cells which have regained the endogenous bacteriocin resistance through the loss of the mptC plasmid will survive. The colonies carrying the desired deletion can then be distinguished from the wild-type revertants by PCR. By using the class IIa bacteriocins leucocin A, leucocin C or pediocin AcH as the counterselective agents, we deleted 22- and 33-kb chromosomal fragments from the wild-type nisin producing L. lactis strain N8. In conclusion, this counterselection method presented here is a convenient, efficient and inexpensive technique to generate successive deletions in L. lactis chromosome.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beasley SS, Takala TM, Reunanen J, Apajalahti J, Saris PEJ (2004) Characterization and electrotransformation of Lactobacillus crispatus isolated from chicken crop and intestine. Poult Sci 83(1):45–48
Biswas I, Gruss A, Ehrlich SD, Maguin E (1993) High-efficiency gene inactivation and replacement system for gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 175(11):3628–3635
Drider D, Fimland G, Héchard Y, McMullen LM, Prévost H (2006) The continuing story of class IIa bacteriocins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70(2):564–582
Ennahar S, Aoude-Werner D, Sorokine O, Van Dorsselaer A, Bringel F, Hubert JC, Hasselmann C (1996) Production of pediocin AcH by Lactobacillus plantarum WHE 92 isolated from cheese. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(12):4381–4387
Gasson MJ (1983) Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol 154(1):1–9
Goh YJ, Azcárate-Peril MA, O’Flaherty S, Durmaz E, Valence F, Jardin J, Lortal S, Klaenhammer TR (2009) Development and application of a upp-based counterselective gene replacement system for the study of the S-layer protein SlpX of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(10):3093–3105
Gravesen A, Jydegaard Axelsen AM, Mendes da Silva J, Hansen TB, Knøchel S (2002) Frequency of bacteriocin resistance development and associated fitness costs in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(2):756–764
Holo H, Nes IF (1989) High-frequency transformation, by electroporation, of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris grown with glycine in osmotically stabilized media. Appl Environ Microbiol 55(12):3119–3123
Kjos M, Salehian Z, Nes IF, Diep DB (2010) An extracellular loop of the mannose phosphotransferase system component IIC is responsible for specific targeting by class IIa bacteriocins. J Bacteriol 192(22):5906–5913
Kuipers OP, Beerthuyzen MM, de Ruyter PGGA, Luesink EJ, de Vos WM (1995) Autoregulation of nisin biosynthesis in Lactococcus lactis by signal transduction. J Biol Chem 270(45):27299–27304
Lambert JM, Bongers RS, Kleerebezem M (2007) Cre-lox-based system for multiple gene deletions and selectable-marker removal in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(4):1126–1135
Li R, Takala TM, Qiao M, Xu H, Saris PEJ (2011) Nisin-selectable food-grade secretion vector for Lactococcus lactis. Biotechnol Lett 33(4):797–803
Linares DM, Alvarez-Sieiro P, del Rio B, Ladero V, Redruello B, Martin MC, Fernandez M, Alvarez MA (2015) Implementation of the agmatine-controlled expression system for inducible gene expression in Lactococcus lactis. Microb Cell Factories 14:208
Martinussen J, Hammer K (1994) Cloning and characterization of upp, a gene encoding uracil phosphoribosyltransferase from Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol 176(21):6457–6463
Mu D, Montalban-Lopez M, Masuda Y, Kuipers OP (2013) Zirex: a novel zinc-regulated expression system for Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(14):4503–4508
Oh J-H, van Pijkeren J-P (2014) CRISPR-Cas9-assisted recombineering in Lactobacillus reuteri. Nucleic Acids Res 42(17):e131
Ramnath M, Arous S, Gravesen A, Hastings JW, Hechard Y (2004) Expression of mptC of Listeria monocytogenes induces sensitivity to class IIa bacteriocins in Lactococcus lactis. Microbiology 150(Pt 8):2663–2668
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. 3era. Ed. 1: 1.32–1.34. Cold Spring Harbour Lab. Press, New York
Siezen RJ, Bayjanov JR, Felis GE, van der Sijde MR, Starrenburg M, Molenaar D, Wels M, van Hijum SAFT, van Hylckama Vlieg JE (2011) Genome-scale diversity and niche adaptation analysis of Lactococcus lactis by comparative genome hybridization using multi-strain arrays. Microb Biotechnol 4(3):383–402
Smith WM, Pham TH, Lei L, Dou J, Soomro AH, Beatson SA, Dykes GA, Turner MS (2012) Heat resistance and salt hypersensitivity in Lactococcus lactis due to spontaneous mutation of llmg_1816 (gdpP) induced by high-temperature growth. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(21):7753–7759
Solem C, Defoor E, Ruhdal Jensen P, Martinussen J (2008) Plasmid pCS1966, a new selection/counterselection tool for lactic acid bacterium strain construction based on the oroP gene, encoding an orotate transporter from Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(15):4772–4775
Song L, Cui H, Tang L, Qiao X, Liu M, Jiang Y, Cui W, Li Y (2014) Construction of upp deletion mutant strains of Lactobacillus casei and Lactococcus lactis based on counterselective system using temperature-sensitive plasmid. J Microbiol Methods 102:37–44
van Pijkeren JP, Britton RA (2014) Precision genome engineering in lactic acid bacteria. Microb Cell Factories 13(Suppl 1):S10
Wan X, Li R, Saris PEJ, Takala TM (2013) Genetic characterisation and heterologous expression of leucocin C, a class IIa bacteriocin from Leuconostoc carnosum 4010. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(8):3509–3518
Wan X, Saris PEJ, Takala TM (2015) Genetic characterization and expression of leucocin B, a class IId bacteriocin from Leuconostoc carnosum 4010. Res Microbiol 166(6):494–503
Zabarovsky ER, Winberg G (1990) High efficiency electroporation of ligated DNA into bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 18(19):5912
Zhu D, Liu F, Xu H, Bai Y, Zhang X, Saris PEJ, Qiao M (2015a) Isolation of strong constitutive promoters from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis N8. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362(16):fnv107
Zhu D, Zhao K, Xu H, Zhang X, Bai Y, Saris PEJ, Qiao M (2015b) Construction of thyA deficient Lactococcus lactis using the Cre-loxP recombination system. Ann Microbiol 65(3):1659–1665
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Academy of Finland (project no. 268922).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
(PDF 306 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, X., Usvalampi, A.M., Saris, P.E.J. et al. A counterselection method for Lactococcus lactis genome editing based on class IIa bacteriocin sensitivity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 9661–9669 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7828-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7828-6