Abstract
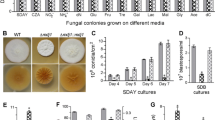
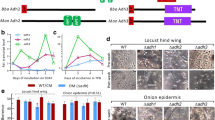
The filamentous fungus, Isaria fumosorosea, is a promising insect biological control agent. Chitinases have been implicated in targeting insect cuticle structures, with biotechnological potential in insect and fungal control. The I. fumosorosea chitinase gene, Ifchit1, was isolated and determined to encode a polypeptide of 423 amino acids (46 kDa, pI = 6.53), present as a single copy in the I. fumosorosea genome. A split marker transformation system was developed and used to construct an Ifchit1 gene knockout. The ΔIfchit1 strain displayed minor alterations in mycelial growth on diverse media at 26 °C compared to the wild type and complemented (ΔIfchit1::Ifchit1) strains; however, colony morphology was affected, and the mutant strain had a temperature sensitive phenotype (32 °C). Although sporulation was delayed for the mutant, overall conidial production was almost twice than that of wild type. Biochemical assays indicated decreased chitinase activity during growth in Czapek-Dox liquid media for the ΔIfchit1 strain. Insect bioassays using diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella, larvae revealed decreased infectivity, i.e., increased LC 50 (threefold to fourfold) and a significantly delayed time to death, LT 50 from 3 to 6 days, for the ΔIfchit1 strain compared to the wild type and complemented strains. These data indicate an important role for the Ifchit1 chitinase as a virulence factor in I. fumosorosea.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Huang Z, Ren SX (2010a) Production of cuticle degrading enzymes by Isaria fumosorosea and their evaluation as a biocontrol agent against diamondback moth. J Pest Sci 83(4):361–370 doi: 10.1007/s10340-010-0305-6
Ali S, Huang Z, Ren SX (2010b) The role of diamondback moth cuticle surface compounds in pre-penetration growth of the entomopathogen Isaria fumosoroseus. J Basic Microbiol 50(5):411–419 doi: 10.1002/Jobm.201000014
Ali S, Wu JH, Huang Z, Ren SX (2010c) Production and regulation of extracellular chitinase from the entomopathogenic fungus Isaria fumosorosea. Biocontrol Sci Technol 20(7):723–738 doi: 10.1080/09583151003714091
Ali S, Huang Z, Zou SX, Bashir MH, Wang ZQ, Ren SX (2012) The effect of insecticides on growth, germination and cuticle-degrading enzyme production by Isaria fumosorosea. Biocontrol Sci Tech 22(9):1047–58. doi:10.1080/09583157.2012.708394
Altre JA, Vandenberg JD, Cantone FA (1999) Pathogenicity of Paecilomyces fumosoroseus isolates to diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella: correlation with spore size, germination speed, and attachment to cuticle. J Invertebr Pathol 73(3):332–338 doi: 10.1006/Jipa.1999.4844
Avery PB, Wekesa VW, Hunter WB, Hall DG, McKenzie CL, Osborne LS, Powell CA, Rogers ME (2011) Effects of the fungus Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) on reduced feeding and mortality of the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). Biocontrol Sci Technol 21(9):1065–1078 doi: 10.1080/09583157.2011.596927
Barreto CC, Alves LC, Aragao FJL, Rech E, Schrank A, Vainstein MH (1997) High frequency gene transfer by microprojectile bombardment of intact conidia from the entomopathogenic fungus Paecilomyces fumosoroseus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 156(1):95–9
Baratto UM, da Silva MV, Santi L, Passaglia L, Schrank IS, Vainstein MH, Schrank A (2003) Expression and characterization of the 42 kDa chitinase of the biocontrol fungus Metarhizium anisopliae in Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol 49(11):723–726 doi: 10.1139/W03-085
Baratto CM, Dutra V, Boldo JT, Leiria LB, Vainstein MH, Schrank A (2006) Isolation, characterization, and transcriptional analysis of the chitinase chi2 gene (DQ011663) from the biocontrol fungus Metarhizium anisopliae var. anisopliae. Curr Microbiol 53(3):217–221 doi: 10.1007/s00284-006-0078-6
Bogo MR, Rota CA, Pinto H, Ocampos M, Correa CT, Vainstein MH, Schrank A (1998) A chitinase encoding gene (chit1 gene) from the entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae: isolation and characterization of genomic and full-length cDNA. Curr Microbiol 37(4):221–225 doi: 10.1007/s002849900368
Boldo JT, do Amaral KB, Junges A, Pinto PM, Staats CC, Vainstein MH, Schrank A (2010) Evidence of alternative splicing of the chi2 chitinase gene from Metarhizium anisopliae. Gene 462(1–2):1–7 doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2010.04.005
Boller T, Gehri A, Mauch F, Vögeli U (1983) Chitinase in bean leaves: induction by ethylene, purification, properties, and possible function. Planta 157(1):22–31 doi: 10.1007/Bf00394536
Cantone FA, Vandenberg JD (1998) Intraspecific diversity in Paecilomyces fumosoroseus. Mycol Res 102:209–215 doi: 10.1017/S0953756297004590
Cantone FA, Vandenberg JD (1999a) Genetic transformation and mutagenesis of the entomopathogenic fungus Paecilomyces fumosoroseus. J Invertebr Pathol 74(3):281–288 doi: 10.1006/jipa.1999.4885
Cantone FA, Vandenberg JD (1999b) Use of the green fluorescent protein for investigations of Paecilomyces fumosoroseus in insect hosts. J Invertebr Pathol 74(2):193–197 doi: 10.1006/jipa.1999.4864
Charnley AK (2003) Fungal pathogens of insects: cuticle degrading enzymes and toxins. Adv Bot Res, Vol 40 40:241–321 doi: 10.1016/S0065-2296(05)40006-3
da Silva MV, Santi L, Staats CC, da Costa AM, Colodel EM, Driemeier D, Vainstein MH, Schrank A (2005) Cuticle-induced endo/exoacting chitinase CHIT30 from Metarhizium anisopliae is encoded by an ortholog of the chi3 gene. Res Microbiol 156(3):382–392 doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2004.10.013
Fan YH, Fang WG, Guo SJ, Pei XQ, Zhang YJ, Xiao YH, Li DM, Jin K, Bidochka MJ, Pei Y (2007) Increased insect virulence in Beauveria bassiana strains overexpressing an engineered chitinase. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(1):295–302. doi:10.1128/Aem.01974-06
Fan YH, Pei XQ, Guo SJ, Zhang YJ, Luo ZB, Liao XG, Pei Y (2010) Increased virulence using engineered protease-chitin binding domain hybrid expressed in the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Microb Pathog 49(6):376–380 doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2010.06.013
Fan Y, Zhang S, Kruer N, Keyhani NO (2011) High-throughput insertion mutagenesis and functional screening in the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. J Invertebr Pathol 106:274–9
Fan Y, Borovsky D, Hawkings C, Ortiz-Urquiza A, Keyhani NO (2012) Exploiting host molecules to augment mycoinsecticide virulence. Nat Biotechnol 30(1):35–7. doi:10.1038/nbt.2080
Fang WG, Zhang YJ, Yang XY, Zheng XL, Duan H, Li Y, Pei Y (2004) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Beauveria bassiana using an herbicide resistance gene as a selection marker. J Invertebr Pathol 85(1):18–24
Fang WG, Leng B, Xiao YH, Jin K, Ma JC, Fan YH, Feng J, Yang XY, Zhang YJ, Pei Y (2005) Cloning of Beauveria bassiana chitinase gene Bbchit1 and its application to improve fungal strain virulence. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(1):363–70
Fang WG, Feng J, Fan YH, Zhang YJ, Bidochka MJ, Leger RJS, Pei Y (2009) Expressing a fusion protein with protease and chitinase activities increases the virulence of the insect pathogen Beauveria bassiana. J Invertebr Pathol 102(2):155–159 doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2009.07.013
Freimoser FM, Screen S, Bagga S, Hu G, St Leger RJ (2003) Expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis of two subspecies of Metarhizium anisopliae reveals a plethora of secreted proteins with potential activity in insect hosts. Microbiology 149(Pt 1):239–47
Gan Z, Yang J, Tao N, Liang L, Mi Q, Li J , Zhang KQ (2007) Cloning of the gene Lecanicillium psalliotae chitinase Lpchi1 and identification of its potential role in the biocontrol of root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1309–1317. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-1111-9
Gao QA, Jin K, Ying SH, Zhang YJ, Xiao GH, Shang YF, Duan ZB, Hu XA, Xie XQ, Zhou G, Peng GX, Luo ZB, Huang W, Wang B, Fang WG, Wang SB, Zhong Y, Ma LJ, St Leger RJ, Zhao GP, Pei Y, Feng MG, Xia YX, Wang CS (2011) Genome sequencing and comparative transcriptomics of the model entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and M. acridum. PLoS Genet 7(1) doi: 10.1371/Journal.Pgen.1001264
Gurr SJ, Unkles SE, Kinghorn JR (1987) The structure and organization of nuclear genes of filamentous fungi. In: Kinghorn JL(ed) Gene structure in lower eukaryotes. IRL, Oxford, pp 93–139
Hao YF, Shaukat A, Shen MB, Ren SX, Huang Z (2015) Construction of Isaria fumosorosea blastospore transforming system by Agrobacterium mediated transformation with benomyl resistance gene. Pak J Zool 47(4):943–51
Huang Z, Ali S, Ren SX, Wu JH (2010) Effect of Isaria fumosoroseus on mortality and fecundity of Bemisia tabaci and Plutella xylostella. Insect Sci 17(2):140–8. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7917.2009.01299.x
Hunter WB, Avery PB, Pick D, Powell CA (2011) Broad spectrum potential of Isaria fumosorosea against insect pests of citrus. Fla Entomol 94(4):1051–4
Inglis PW, Tigano MS, Valadares-Inglis MC (1999) Transformation of the entomopathogenic fungi, Paecilomyces fumosoroseus and Paecilomyces lilacinus (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) to benomyl resistance. Genet Mol Biol 22(1):119–123 doi: 10.1590/S1415-47571999000100023
Kang SC, Park S, Lee DG (1998) Isolation and characterization of a chitinase cDNA from the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 165(2):267–271 doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1998.tb13156.x
Keyhani NO, Roseman S (1996) The chitin catabolic cascade in the marine bacterium Vibrio furnissii—molecular cloning, isolation, and characterization of a periplasmic chitodextrinase. J Biol Chem 271(52):33414–24
Keyhani NO, Wang LX, Lee YC, Roseman S (1996) The chitin catabolic cascade in the marine bacterium Vibrio furnissii. Characterization of an N,N′-diacetyl-chitobiose transport system. J Biol Chem 271(52):33409–13
Keyhani NO, Roseman S (1999) Physiological aspects of chitin catabolism in marine bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1473(1):108–22
Keyhani NO, Li XB, Roseman S (2000a) Chitin catabolism in the marine bacterium Vibrio furnissii. Identification and molecular cloning of a chitoporin. J Biol Chem 275(42):33068–76
Keyhani NO, Wang LX, Lee YC, Roseman S (2000b) The chitin disaccharide, N, N′-diacetylchitobiose, is catabolized by Escherichia coli and is transported/phosphorylated by the phosphoenolpyruvate: glycose phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem 275(42):33084–90
Kumar MNVR (2000) A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React Funct Polym 46(1):1–27
Lima IGP, Duarte RTD, Furlaneto L, Baroni CH, Fungaro MHP, Furlaneto MC (2006) Transformation of the entomopathogenic fungus Paecilomyces fumosoroseus with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Lett Appl Microbiol 42(6):631–636 doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.01861.x
Limon MC, Pintor-Toro JA, Benitez T (1999) Increased antifungal activity of Trichoderma harzianum transformants that overexpress a 33-kDa chitinase. Phytopathology 89(3):254–261 doi: 10.1094/Phyto.1999.89.3.254
Liu YG, Chen Y (2007) High-efficiency thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR for amplification of unknown flanking sequences. BioTechniques 43(5):649–656 doi: 10.2144/000112601
Lorito M, Harman GE, Hayes CK, Broadway RM, Tronsmo A, Woo SL, Dipietro A (1993) Chitinolytic enzymes produced by Trichoderma harzianum—antifungal activity of purified endochitinase and chitobiosidase. Phytopathology 83(3):302–307 doi: 10.1094/Phyto-83-302
Luangsa-Ard JJ, Hywel-Jones NL, Manoch L, Samson RA (2005) On the relationships of Paecilomyces sect. Isarioidea species. Mycol Res 109:581–9. doi:10.1017/S0953756205002741
Ortiz-Urquiza A, Keyhani NO (2013) Action on the surface: entomopathogenic fungi versus the insect cuticle. Insects 4:357–74
Pedrini N, Ortiz-Urquiza A, Huarte-Bonnet C, Zhang S, Keyhani NO (2013) Targeting of insect epicuticular lipids by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana: hydrocarbon oxidation within the context of a host-pathogen interaction. Front Microbiol 4:24. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2013.00024
Pick DA, Avery PB, Hunter WB, Powell CA, Arthurs SP (2012) Effect of Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) and Lysiphlebus testaceipes, (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) on the brown citrus aphid: preliminary assessment of a compatibility study. Fla Entomol 95(3):764–6
Screen SE, Hu G, St Leger RJ (2001) Transformants of Metarhizium anisopliae sf. anisopliae overexpressing chitinase from Metarhizium anisopliae sf. acridum show early induction of native chitinase but are not altered in pathogenicity to Manduca sexta. J Invertebr Pathol 78(4):260–6. doi:10.1006/jipa.2001.5067
Staats CC, Kmetzsch L, Lubeck I, Junges A, Vainstein MH, Schrank A (2013) Metarhizium anisopliae chitinase CHIT30 is involved in heat-shock stress and contributes to virulence against Dysdercus peruvianus. Fungal Biol-UK 117(2):137–144 doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2012.12.006
St Leger RJ, Joshi L, Bidochka MJ, Rizzo NW, Roberts DW (1996) Characterization and ultrastructural localization of chitinases from Metarhizium anisopliae, M. flavoviride, and Beauveria bassiana during fungal invasion of host (Manduca sexta) cuticle. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(3):907–12
Tiffin P (2004) Comparative evolutionary histories of chitinase genes in the genus Zea and family Poaceae. Genetics 167(3):1331–40
Vandenberg JD, Jackson MA, Lacey LA (1998) Relative efficacy of blastospores and aerial conidia of Paecilomyces fumosoroseus against the Russian wheat aphid. J Invertebr Pathol 72(2):181–183 doi: 10.1006/jipa.1998.4772
Vega FE, Goettel MS, Blackwell M, Chandler D, Jackson MA, Keller S, Koike M, Maniania NK, Monzon A, Ownley BH, Pell JK, Rangel DEN, Roy HE (2009) Fungal entomopathogens: new insights on their ecology. Fungal Ecol 2(4):149–59
Wang Y, DiGuistini S, Wang TCT, Bohlmann J, Breuil C (2010) Agrobacterium-meditated gene disruption using split-marker in Grosmannia clavigera, a mountain pine beetle associated pathogen. Curr Genet 56(3):297–307. doi:10.1007/s00294-010-0294-2
Wheeller Q, Blackwell M (eds) (1984) Fungus-insect interactions: perspectives in ecology and evolution. Columbia University Press, New York
Xiao G, Ying SH, Zheng P, Wang ZL, Zhang S, Xie XQ, Shang Y, St Leger RJ, Zhao GP, Wang C, Feng MG (2012) Genomic perspectives on the evolution of fungal entomopathogenicity in Beauveria bassiana. Sci Rep 2:483. doi:10.1038/srep00483
Ying SH, Feng MG, Keyhani NO (2013) A carbon responsive G-protein coupled receptor modulates broad developmental and genetic networks in the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. Environ Microbiol 15(11):2902–21. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12169
Zhang S, Fan Y, Xia YX, Keyhani NO (2010) Sulfonylurea resistance as a new selectable marker for the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1151–1156 doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2636-x
Zhang S, Xia YX, Kim B., Keyhani NO (2011) Two hydrophobins are involved in fungal spore coat rodlet layer assembly and each play distinct roles in surface interactions, development and pathogenesis in the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. Mol Microbiol 80(3): 811–826 doi: 10.1111/j.136-2958.2011.07613.x
Zhao KJ, Chye ML (1999) Methyl jasmonate induces expression of a novel Brassica juncea chitinase with two chitin-binding domains. Plant Mol Biol 40:1009–18
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the “863” Program of China (2011AA10A204-5), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170391), and the National Science Foundation grant IOS-1121392 to NOK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Yongfen Hao, Joint first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Hao, Y., Gao, T. et al. The Ifchit1 chitinase gene acts as a critical virulence factor in the insect pathogenic fungus Isaria fumosorosea . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 5491–5503 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7308-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7308-z