Abstract
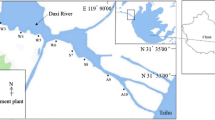
The winter and summer microbial community structure in sediment samples obtained from the estuaries of the wastewater-polluted River Ou (DO and XO), River Feiyun (DF and XF), and River Ao (DA and XA) in the south of Zhejiang Province in China was determined using 454 pyrosequencing. Sediment samples (DD and XD) were also correspondingly collected near the shore far from the estuaries for comparison. For the above sediments, 294,870 effective sequences were obtained to do the bacterial diversity and abundance determination. In total, 1924, 1517, 2071, 1956, 1995, 1800, 2261, and 2097 operational taxonomic units were obtained at 3 % distance cutoff in the DO, XO, DF, XF, DA, XA, DD, and XD sediments, respectively. Bacterial phylotype richness in DD was higher than the other sediments, and XO had the least richness. The most dominant class in the DA, DD, DF, DO, and XA sediments is Gammaproteobacteria. Deltaproteobacteria is the most dominant one in XD, XO, and XF. Circa 14.4 % sequences in XD were found to be affiliated with the Flavobacteriales order. Characterization of the estuarine sediment bacterial communities indicated that chemical pollution has the potential to decrease the natural variability that exists among estuary ecosystems. However, chemical pollutants did not cause clear bio-homogenization in these estuaries.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E, Lipman D (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Buckley DH, Schmidt TM (2001) Environmental factors influencing the distribution of rRNA from Verrucomicrobia in soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:105–112
Chen LG, Fan JF, Guan DM, Zhao HD, Ming HX, Wu LJ, Chen JY (2010) Analysis of temporal and spatial distribution of nitrobacteria in sediment of Liaohe estuary. Mar Environ Sci 29(2):174–178
Claesson M, óSullivan O, Wang Q, Nikkila J, Marchesi J, Smidt H, De Vos W, Ross R, óToole P (2009) Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenetic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS One 4:e6669
Connell JH (1978) Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science 199:1302–1310
Dai JH, Sun MY (2007) Organic matter sources and their use by bacteria in the sediments of the Altamaha estuary during high and low discharge periods. Org Geochem 38:1–15
Dai X, Zhou H, Chen YQ, Cai CH, Zhou YP, Zhou SN, Qu LH (2002) A preliminary study on the diversity of bacterial 16S rDNA in the sediments in Nansha sea area of the South China Sea. Prog Nat Sci 12(5):479–484
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072
Drury B, Rosi-Marshall E, Kelly JJ (2013) Wastewater treatment effluent reduces the abundance and diversity of benthic bacterial communities in urban and suburban rivers. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(6):1897–1905
Du P, Liu JJ, Shen LD, Hu BL, Zeng JN, Chen QZ, Shou L, Liao YB (2012) Diversity of microorganisms in sediments of the Jiaojiang estuary as estimated by Biolog and PCR-DGGE. Acta Sci Circumst 32(6):1436–1444
Ferrer M, Guazzaroni ME, Richter M, García-Salamanca A, Yarza P, Suárez-Suárez A, Solano J, Alcaide M, van Dillewijn P, Molina-Henares MA, López-Cortés N, Al-Ramahi Y, Guerrero C, Acosta A, de Eugenio LI, Martínez V, Marques S, Rojo F, Santero E, Genilloud O, Pérez-Pérez J, Rosselló-Móra R, Ramos JL (2011) Taxonomic and functional metagenomic profiling of the microbial community in the anoxic sediment of a sub-saline shallow lake (Laguna de Carrizo, Central Spain). Microb Ecol 62:824–837
Glenn TC (2011) Field guide to next generation DNA sequencers. Mol Ecol Resour 15:759–769
Goñi-Urriza M, Capdepuy M, Raymond N, Quentin C, Caumette P (1999) Impact of an urban effluent on the bacterial community structure in the Arga River, Spain, with special reference to culturable Gram-negative rods. Can J Microbiol 45:826–832
Gray JP, Herwig RP (1996) Phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial communities in marine sediments. Appl Environ Micmbiol 62(11):4049–4059
Guo CL, Ke L, Dang Z, Tam NF (2011) Temporal changes in Sphingomonas and Mycobacterium populations in mangrove sediments contaminated with different concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Mar Pollut Bull 62:133–139
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren E (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21:494–504
Haritash AK, Kaushik CP (2009) Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. J Hazard Mater 169:1–15
Hartmann M, Widmer F (2006) Community structure analyses are more sensitive to differences in soil bacterial communities than anonymous diversity indices. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7804–7812
Henriques IS, Alves A, Tacao M, Almeida A, Cunha A, Correia A (2006) Seasonal and spatial variability of free-living bacterial community composition along an estuarine gradient (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 68:139–148
Hugenholtz P, Goebel BM, Pace NR (1998) Impact of cultureindependent studies on the emerging phylogenetic view of bacterial diversity. J Bacteriol 180:4765–4774
Huo YY, Xu XW, Wang CS, Yang JY, Wu M (2008) Bacterial diversity of the sediment from Cangnan Large Fishing Bay. Acta Ecol Sin 28(10):5166–5172
Huse SM, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2010) Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ Microbiol 12:1889–1898
Huson D, Auch A, Qi J, Schuster S (2007) MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res 17:377–386
Langston WJ, Pope ND, Jonas PJC, Nikitic C, Field MDR, Dowell B, Shillabeer N, Swarbrick RH, Brown AR (2010) Contaminants in fine sediments and their consequences for biota of the Severn Estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 61:68–82
Llobet-Brossa E, Russello-Mora R, Amann R (1998) Microbial community composition of Wadden Sea sediments as revealed by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Mierobiol 64(7):2691–2696
Lu XM, Lu PZ (2014) Characterization of bacterial communities in sediments receiving various wastewater effluents with high-throughput sequencing analysis. Microb Ecol 67(3):612–623
Ma F, Cai R, Li A, Cui D, Wang JH, Pang CL, Qiu T, Yang JX (2012) Application of microbial culture-independent technology in environment contamination control. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology 44(8):31–38
McLellan S, Huse S, Mueller SS, Andreishcheva E, Sogin M (2010) Diversity and population structure of sewage derived microorganisms in wastewater treatment plant influent. Environ Microbiol 12:378–392
Mucha AP, Vasconcelos MTSD, Bordalo AA (2003) Macrobenthic community in the Douro Estuary: relations with trace metals and natural sediment characteristics. Environ Pollut 121:169–180
Osborn A, Moore E, Timmis K (2000) An evaluation of terminal1 restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis for the study of microbial community structure and dynamics. Environ Microbiol 2:39–50
Pang CM, Liu WT (2006) Biological filtration limits carbon availability and affects downstream biofilm formation and community structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5702–5712
Qian P, Wang Y, Lee O, Lau S, Yang J, Lafi F, Al-Suwailem A, Wong T (2010) Vertical stratification of microbial communities in the Red Sea revealed by 16S rDNA pyrosequencing. ISME J 5:507–518
Roeselers G, Mittge EK, Stephens WZ, Parichy DM, Cavanaugh CM, Guillemin K, Rawls JF (2011) Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J 5:1595–1608
Shoji D, Thottathil KK, Balachandran KV, Jayalakshmi GVM, Gupta SN (2008) Tidal switch on metabolic activity: salinity induced responses on bacterioplankton metabolic capabilities in a tropical estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 78(4):665–673
Singh SK, Verma P, Ramaiah N, Chandrashekar AA, Shouche YS (2010) Phylogenetic diversity of archaeal 16S rRNA and ammonia monooxygenase genes from tropical estuarine sediments on the central west coast of India. Res Microbiol 161(3):177–186
Song ZG, Xu QZ, Lu XA, Jiao BH, Ai F (2006) A primary study on population biodiversity of marine microorganisms from East China Sea. Microbiology 33(1):63–67
Bureau STS (2008a) The Specification For Marine Surveying (GB 12763—2008). Standards Press of China, Beijing
Bureau STS (2008b) The Specification For Marine Monitoring (GB 17378—2008). Standards Press of China, Beijing
Statistics Bureau of Zhejiang Province (2007) The development state and problems in ocean economy of Zhejiang Province. Conditions and Strength of China 5:63–64
Tang X, Gao G, Qin B, Zhu L, Chao J, Wang J, Yang G (2009) Characterization of bacterial communities associated with organic aggregates in a large, shallow, eutrophic freshwater lake (Lake Taihu, China). Microb Ecol 58:307–322
Tian Y, Liu HJ, Zheng TL, Kwon KK, Kim SJ, Yan CL (2008) PAHs contamination and bacterial communities in mangrove surface sediments of the Jiulong River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 57(6–12):707–715
Urakawa H, Kita-Tsukamoto K, Ohwada K (1999) Microbial diversity in marine sediments from Sagami Bay and Tokyo Bay, Japan, as determined by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Microbiology 145:3305–3315
Urich T, Lanzén A, Qi J, Huson D, Schleper C, Schuster S (2008) Simultaneous assessment of soil microbial community structure and function through analysis of the meta-transcriptome. PLoS One 3:e2527
Vezzulli L, Pruzzo C, Fabiano M (2004) Response of the bacterial community to in situ bioremediation of organic-rich sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 49(9/10):740–751
Vilchez R, Pozo C, Gómez MA, Rodelas B, González-López J (2007) Dominance of sphingomonads in a copper-exposed biofilm community for groundwater treatment. Microbiology 153:325–337
Wakelin SA, Colloff MJ, Kookana RS (2008) Effect of wastewater treatment plant effluent on microbial function and community structure in the sediment of a freshwater stream with variable seasonal flow. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2659–2668
Wang SJ, Hu JC, Xue DL, Ma CX, Xie QH, Liu QY (2001) Study on marine microbial resources in the Yellow Sea, Bohai, and Liaoning coastal areas in China. Journal of Jinzhou Teachers College (Natural Sciences Edition) 22(1):1–5
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang Y, Sheng HF, He Y, Wu JY, Jiang YX, Tam NFY, Zhou HW (2012) Comparison of the levels of bacterial diversity in freshwater, intertidal wetland, and marine sediments by using millions of illumina tags. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(23):8264–8271
Whitman WB, Coleman DC, Wiebe WJ (1998) Prokaryotes: the unseen majority. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:6578–6583
Yang YF, Wang Q, Chen JF, Pang SX (2006) Research advance in estuarine zooplankton ecology. Acta Ecol Sin 26(2):576–585
Ye L, Zhang T (2013) Bacterial communities in different sections of a municipal wastewater treatment plant revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2681–2690
Zhang S, Zhang CS, Tian XP, Wand FZ (2010) The study of diversities of marine microbes in China. Biodiversity Conservation 25(6):651–658
Zhang W, Ki J, Qian P (2008) Microbial diversity in polluted harbor sediments I: bacterial community assessment based on four clone libraries of 16S rDNA. Estu Coast Shelf Sci 76(3):668–681
Zhao YQ, Zeng JN, Gao AG, Chen QZ, Liao YB, Shou L (2009) Community pattern and diversity of macrozoobenthos in an intertidal flat, Jiaojiang estuary. Biodivers Sci 17(3):303–309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by Open Project Program of the Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, SCSIO, CAS (No. LMB141001); MEL Visiting Fellowship of State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science, Xiamen University (No. MELRS 1507); the Science and Technology Program of Wenzhou, China (No. S20140004); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41401586).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 748 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, XM., Chen, C., Zheng, TL. et al. Temporal–spatial variation of bacterial diversity in estuary sediments in the south of Zhejiang Province, China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 2817–2828 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7103-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7103-2