Abstract
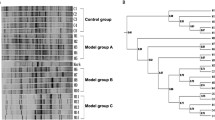
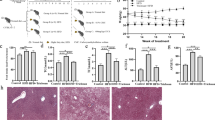
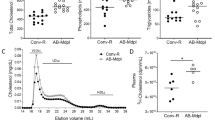
Increasing evidence suggests that maintenance of homeostasis between gut microbiota and host plays an important role in human health. Many diseases, such as those affecting the liver, have been linked to imbalances in gut microbial communities. However, it is not clear whether an imbalance in gut microbiota promotes the onset of liver injury or if the imbalance results from the pathological state. In the current study, antibiotics were used to disturb the gut microbiota of both rats fed a high-cholesterol diet and rats fed a normal diet (controls). The prevalence of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes were reduced, and Proteobacteria was greatly increased in the guts of rats after antibiotic treatment. The antibiotic-induced perturbation of gut microbiota aggravated cholesterol accumulation and liver injury in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. This may have been due to an increase in intestinal permeability and plasma lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which lead to an increase in LPS absorption and activation of TLR4 signaling, resulting in the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in liver tissues. This study suggests that imbalances in gut microbiota may be a predisposing factor for the onset of metabolic diseases and liver injuries related to cholesterol and high-cholesterol diets. Modulation of gut microbiota could be a novel target for preventing cholesterol-related metabolic disorders.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson A, Covacu R, Sunnemark D, Danilov AI, Dal Bianco A, Khademi M, Wallstrom E, Lobell A, Brundin L, Lassmann H, Harris RA (2008) Pivotal advance: HMGB1 expression in active lesions of human and experimental multiple sclerosis. J Leukoc Biol 84(5):1248–1255
Arrieta MC, Stiemsma LT, Amenyogbe N, Brown EM, Finlay B (2014) The intestinal microbiome in early life: health and disease. Front Immunol 5:427
Batista Jr ML, Neves RX, Peres SB, Yamashita AS, Shida CS, Farmer SR, Seelaender M (2012) Heterogeneous time-dependent response of adipose tissue during the development of cancer cachexia. J Endocrinol 215(3):363–373
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A, Delmee E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrieres J, Tanti JF, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC, Burcelin R (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56(7):1761–1772
Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R (2008) Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 57(6):1470–1481
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Tumbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Carvalho BM, Guadagnini D, Tsukumo DM, Schenka AA, Latuf-Filho P, Vassallo J, Dias JC, Kubota LT, Carvalheira JB, Saad MJ (2012) Modulation of gut microbiota by antibiotics improves insulin signalling in high-fat fed mice. Diabetologia 55(10):2823–2834
Cho I, Yamanishi S, Cox L, Methe BA, Zavadil J, Li K, Gao Z, Mahana D, Raju K, Teitler I, Li HL, Alekseyenko AV, Blaser MJ (2012) Antibiotics in early life alter the murine colonic microbiome and adiposity. Nature 488(7413):621–626
Claus SP, Ellero SL, Berger B, Krause L, Bruttin A, Molina J, Paris A, Want EJ, de Waziers I, Cloarec O, Richards SE, Wang Y, Dumas ME, Ross A, Rezzi S, Kochhar S, Van Bladeren P, Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK (2011) Colonization-induced host-gut microbial metabolic interaction. Mbio 2(2):e00271-10
Clemente JC, Ursell LK, Parfrey LW, Knight R (2012) The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view. Cell 148(6):1258–1270
Frank DN, Amand ALS, Feldman RA, Boedeker EC, Harpaz N, Pace NR (2007) Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(34):13780–13785
Hill MJ (1997) Intestinal flora and endogenous vitamin synthesis. Eur J Cancer Prev 6:S43–S45
Hooper LV, Gordon JI (2001) Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science 292(5519):1115–1118
Hu M, Wang Z, Rao J, Cao Y, Jiang W, Zhang F, Li X, Wang X (2010) Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase worsens liver damage regardless of lipopolysaccharide treatment in small-for-size liver transplantation. Transpl Immunol 23(1–2):6–11
Ioannou GN, Morrow OB, Connole ML, Lee SP (2009) Association between dietary nutrient composition and the incidence of cirrhosis or liver cancer in the United States population. Hepatology 50(1):175–184
Kainuma M, Fujimoto M, Sekiya N, Tsuneyama K, Cheng C, Takano Y, Terasawa K, Shimada Y (2006) Cholesterol-fed rabbit as a unique model of nonalcoholic, nonobese, non-insulin-resistant fatty liver disease with characteristic fibrosis. J Gastroenterol 41(10):971–980
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology—human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444(7122):1022–1023
Li L, Chen L, Hu L, Liu Y, Sun HY, Tang J, Hou YJ, Chang YX, Tu QQ, Feng GS, Shen F, Wu MC, Wang HY (2011) Nuclear factor high-mobility group Box1 mediating the activation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling in hepatocytes in the early stage of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatology 54(5):1620–1630
Long JP, Tong HH, Shannon PA, DeMaria TF (2003) Differential expression of cytokine genes and inducible nitric oxide synthase induced by opacity phenotype variants of Streptococcus pneumoniae during acute otitis media in the rat. Infect Immun 71(10):5531–5540
Mazmanian SK, Liu CH, Tzianabos AO, Kasper DL (2005) An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic bacteria directs maturation of the host immune system. Cell 122(1):107–118
Membrez M, Blancher F, Jaquet M, Bibiloni R, Cani PD, Burcelin RG, Corthesy I, Mace K, Chou CJ (2008) Gut microbiota modulation with norfloxacin and ampicillin enhances glucose tolerance in mice. FASEB J 22(7):2416–2426
Mencin A, Kluwe J, Schwabe RF (2009) Toll-like receptors as targets in chronic liver diseases. Gut 58(5):704–720
Millan J, Pinto X, Munoz A, Zuniga M, Rubies-Prat J, Pallardo LF, Masana L, Mangas A, Hernandez-Mijares A, Gonzalez-Santos P, Ascaso JF, Pedro-Botet J (2009) Lipoprotein ratios: physiological significance and clinical usefulness in cardiovascular prevention. Vasc Health Risk Manag 5:757–765
Miyake Y, Yamamoto K (2013) Role of gut microbiota in liver diseases. Hepatol Res 43(2):139–146
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Wilson ID (2005) Gut microorganisms, mammalian metabolism and personalized health care. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(5):431–438
Owyang C, Wu GD (2014) The gut microbiome in health and disease. Gastroenterology 146(6):1433–1436
Park JS, Gamboni-Robertson F, He QB, Svetkauskaite D, Kim JY, Strassheim D, Sohn JW, Yamada S, Maruyama I, Banerjee A, Ishizaka A, Abraham E (2006) High mobility group box 1 protein interacts with multiple toll-like receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290(3):C917–C924
Poltorak A, He XL, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282(5396):2085–2088
Qiao Y, Sun J, Ding YY, Le GW, Shi YH (2013) Alterations of the gut microbiota in high-fat diet mice is strongly linked to oxidative stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(4):1689–1697
Qin JJ, Li YR, Cai ZM, Li SH, Zhu JF, Zhang F, Liang SS, Zhang WW, Guan YL, Shen DQ, Peng YQ, Zhang DY, Jie ZY, Wu WX, Qin YW, Xue WB, Li JH, Han LC, Lu DH, Wu PX, Dai YL, Sun XJ, Li ZS, Tang AF, Zhong SL, Li XP, Chen WN, Xu R, Wang MB, Feng Q, Gong MH, Yu J, Zhang YY, Zhang M, Hansen T, Sanchez G, Raes J, Falony G, Okuda S, Almeida M, LeChatelier E, Renault P, Pons N, Batto JM, Zhang ZX, Chen H, Yang RF, Zheng WM, Li SG, Yang HM, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Nielsen R, Pedersen O, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2012) A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 490(7418):55–60
Qin N, Yang FL, Li A, Prifti E, Chen YF, Shao L, Guo J, Le Chatelier E, Yao J, Wu LJ, Zhou JW, Ni SJ, Liu L, Pons N, Batto JM, Kennedy SP, Leonard P, Yuan CH, Ding WC, Chen YT, Hu XJ, Zheng BW, Qian GR, Xu W, Ehrlich SD, Zheng SS, Li LJ (2014) Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 513(7516):59–64
Savage DC (1977) Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol 31:107–133
Scaffidi P, Misteli T, Bianchi ME (2002) Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature 418(6894):191–195
Schnabl B, Brenner DA (2014) Interactions between the intestinal microbiome and liver diseases. Gastroenterology 146(6):1513–1524
Sumiyoshi M, Sakanaka M, Kimura Y (2010) Chronic intake of a high-cholesterol diet resulted in hepatic steatosis, focal nodular hyperplasia and fibrosis in non-obese mice. Br J Nutr 103(3):378–385
van Zoelen MAD, Yang H, Florquin S, Meijers JCM, Akira S, Arnold B, Nawroth PP, Bierhaus A, Tracey KJ, van der Poll T (2009) Role of toll-like receptors 2 and 4, and the receptor for advanced glycation end products in high-mobility group box 1-induced inflammation in vivo. Shock 31(3):280–284
Vergnes L, Phan J, Strauss M, Tafuri S, Reue K (2003) Cholesterol and cholate components of an atherogenic diet induce distinct stages of hepatic inflammatory gene expression. J Biol Chem 278(44):42774–42784
Vrieze A, Out C, Fuentes S, Jonker L, Reuling I, Kootte RS, van Nood E, Holleman F, Knaapen M, Romijn JA, Soeters MR, Blaak EE, Dallinga-Thie GM, Reijnders D, Ackermans MT, Serlie MJ, Knop FK, Holst JJ, van der Ley C, Kema IP, Zoetendal EG, de Vos WM, Hoekstra JBL, Stroes ES, Groen AK, Nieuwdorp M (2014) Impact of oral vancomycin on gut microbiota, bile acid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. J Hepatol 60(4):824–831
Wang JC, Zhao Y, Chen SJ, Long J, Jia QQ, Zhai JD, Zhang Q, Chen Y, Long HB (2013) AOPPs induce MCP-1 expression by increasing ROS-mediated activation of the NF-kappaB pathway in rat mesangial cells: inhibition by sesquiterpene lactones. Cell Physiol Biochem 32(6):1867–1877
Xia XM, Wang FY, Wang ZK, Wan HJ, Xu WA, Lu H (2010) Emodin enhances alveolar epithelial barrier function in rats with experimental acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 16(24):2994–3001
Xiao J, Ching YP, Liong EC, Nanji AA, Fung ML, Tipoe GL (2013) Garlic-derived S-allylmercaptocysteine is a hepato-protective agent in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in vivo animal model. Eur J Nutr 52(1):179–191
Zhang TJ, Hang J, Wen DX, Hang YN, Sieber FE (2006) Hippocampus bcl-2 and bax expression and neuronal apoptosis after moderate hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass in rats. Anesth Analg 102(4):1018–1025
Zhang W, Wang LW, Wang LK, Li X, Zhang H, Luo LP, Song JC, Gong ZJ (2013) Betaine protects against high-fat-diet-induced liver injury by inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 and toll-like receptor 4 expression in rats. Dig Dis Sci 58(11):3198–3206
Zhu LX, Baker SS, Gill C, Liu WS, Alkhouri R, Baker RD, Gill SR (2013) Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: a connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 57(2):601–609
Acknowledgments
We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Grants
The study was granted by NS Bio Japan and NS Bio Guangzhou.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xu Hu and Tao Wang contributed to the work equally and should be regarded as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Wang, T., Liang, S. et al. Antibiotic-induced imbalances in gut microbiota aggravates cholesterol accumulation and liver injuries in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 9111–9122 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6753-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6753-4