Abstract
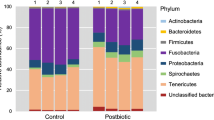
The intestinal microbiota and morphology of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) were investigated after the application of a multi-species probiotic containing Lactobacillus reuteri, Bacillus subtilis, Enterococcus faecium and Pediococcus acidilactici (AquaStar® Growout). Tilapia (55.03 ± 0.44 g) were fed either a control diet or a probiotic diet (control diet supplemented with AquaStar® Growout at 5 g kg−1). After four and eight weeks, culture-dependent analysis showed higher levels of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), enterococci and Bacillus spp. in the mucosa and digesta of fish fed AquaStar® Growout. At week four, polymerase chain reaction denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE) revealed a higher similarity within the probiotic fed replicates than replicates of the control group; after eight weeks, the compositional dissimilarity of the microbiome profiles between the groups was greater than the dissimilarities within each group (P < 0.05). High-throughput sequencing revealed that the probiotic treatment significantly reduced the number of operational taxonomic units and species richness in the digesta. Significantly higher proportions of reads belonging to Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria were detected in the control group whereas the probiotic-fed fish displayed a significantly higher abundance of reads assigned to the Firmicutes (which accounted for >99 % of reads). Bacillus, Cetobacterium and Mycobacterium were the dominant genera in the digesta of control fish whereas Bacillus, Enterococcus and Pediococcus were the largest constituents in probiotic-fed fish. The addition of AquaStar® Growout to tilapia diets led to increased populations of intraepithelial leucocytes, a higher absorptive surface area index and higher microvilli density in the intestine. These data suggest that AquaStar® Growout can modulate both the intestinal microbiota and morphology of tilapia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hisnawi A, Ringø E, Davies SJ, Waines P, Bradley G, Merrifield DL (2014) First report on the autochthonous gut microbiota of brown trout (Salmo trutta linnaeus). Aquac Res. doi:10.1111/are.12451
AOAC (1995) Association Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). (1995) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Arlington
Balcázar JL, de Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Vendrell D, Calvo AC, Márquez I, Gironés O, Muzquiz JL (2007) Changes in intestinal microbiota and humoral immune response following probiotic administration in brown trout (Salmo trutta). Brit J Nutr 97(3):522–527. doi:10.1017/S0007114507432986
Bates JM, Mittge E, Kuhlman J, Baden KN, Cheesman SE, Guillemin K (2006) Distinct signals from the microbiota promote different aspects of zebrafish gut differentiation. Dev Biol 297(2):374–386
Bourouni OC, El Bour M, Calo-Mata P, Mraouna R, Abedellatif B, Barros-Velàzquez J (2012) Phylogenetic analysis of antimicrobial lactic acid bacteria from farmed seabass Dicentrarchus labrax. Can J Microbiol 58(4):463–474. doi:10.1139/w2012-014
Boutin S, Bernatchez L, Audet C, Derôme N (2013) Network analysis highlights complex interactions between pathogen, host and commensal microbiota. PLoS One 8 (12):e84772. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084772
Cai Y, Suyanandana P, Saman P, Benno Y (1999) Classification and characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the intestines of common carp and freshwater prawns. J Gen Appl Microbiol 45(4):177–184. doi:10.2323/jgam.45.177
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010a) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26(2):266–267. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp636
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010b) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Carda-Diéguez M, Mira A, Fouz B (2013) Pyrosequencing survey of intestinal microbiota diversity in cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed functional diets. FEMS Microbiol Ecol doi:. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12236
Carnevali O, Sun Y, Merrifield DL, Zhou Z, Picchietti S (2014) Probiotic applications in temperate and warm water fish species. In: Merrifield D, Ringø E (eds) Aquaculture nutrition gut health, probiotics and prebiotics. Wiley, Chichester, pp. 253–289
Defoirdt T, Sorgeloos P, Bossier P (2011) Alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial disease in aquaculture. Curr Opin Microbiol 14(3):251–258. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2011.03.004
Desai AR, Links MG, Collins SA, Mansfield GS, Drew MD, Van Kessel AG, Hill JE (2012) Effects of plant-based diets on the distal gut microbiome of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 350:134–142. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.04.005
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):5069–5072. doi:10.1128/aem.03006-05
Dimitroglou A, Merrifield D, Moate R, Davies S, Spring P, Sweetman J, Bradley G (2009) Dietary mannan oligosaccharide supplementation modulates intestinal microbial ecology and improves gut morphology of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Anim Sci 87(10):3226–3234
Dimitroglou A, Merrifield DL, Carnevali O, Picchietti S, Avella M, Daniels C, Güroy D, Davies SJ (2011) Microbial manipulations to improve fish health and production—a mediterranean perspective. Fish Shellfish Immun 30(1):1–16. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2010.08.009
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26(19):2460–2461. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461
Falcinelli S, Picchietti S, Rodiles A, Cossignani L, Merrifield DL, Taddei AR, Maradonna F, Olivotto I, Gioacchini G, Carnevali O (2015) Lactobacillus rhamnosus lowers lipid content by changing gut microbiota and host transcription of genes involved in lipid metabolism in zebrafish. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep09336
FAO (2014) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2014. Food Agricultural Organization United Nations, Rome
Ferguson RMW, Merrifield DL, Harper GM, Rawling MD, Mustafa S, Picchietti S, Balcázar JL, Davies SJ (2010) The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici on the gut microbiota and immune status of on-growing red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Appl Microbiol 109(3):851–862. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04713.x
Fogel GB, Collins CR, Li J, Brunk CF (1999) Prokaryotic genome size and SSU rDNA copy number: estimation of microbial relative abundance from a mixed population. Microb Ecol 38(2):93–113. doi:10.1007/s002489900162
Gopalakannan A, Arul V (2011) Inhibitory activity of probiotic Enterococcus faecium MC13 against Aeromonas hydrophila confers protection against hemorrhagic septicemia in common carp Cyprinus carpio. Aquacult Int 19(5):973–985. doi:10.1007/s10499-011-9415-2
Ingerslev HC, von Gersdorff JL, Lenz Strube M, Larsen N, Dalsgaard I, Boye M, Madsen L (2014) The development of the gut microbiota in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is affected by first feeding and diet type. Aquaculture 424–425:24–34. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.12.032
Jatobá A, Fd V, Buglione-Neto C, Mouriño’ J, Silva BC, Seiftter W, Andreatta ER (2011) Diet supplemented with probiotic for Nile tilapia in polyculture system with marine shrimp. Fish Physiol Biochem 37(4):725–732. doi:10.1007/s10695-011-9472-5
Kim D-H, Austin B (2006) Innate immune responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) induced by probiotics. Fish Shellfish Immun 21(5):513–524. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2006.02.007
Lauzon HL, Perez-Sanchez T, Merrifield DL, Ringø E, Balcazar JL (2014) Probiotic applications in cold water fish species. In: Merrifield D & Ringø E (eds.) Aquaculture nutrition gut health, probiotics and prebiotics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 223-252
Liu W, Ren P, He S, Xu L, Yang Y, Gu Z, Zhou Z (2013) Comparison of adhesive gut bacteria composition, immunity, and disease resistance in juvenile hybrid tilapia fed two different Lactobacillus strains. Fish Shellfish Immun 35(1):54–62. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2013.04.010
Merrifield DL, Carnevali O (2014) Probiotic modulation of the gut microbiota of fish. In: Merrifield D, Ringø E (eds) Aquaculture nutrition gut health, probiotics and prebiotics. Wiley, Chichester, pp. 185–222
Merrifield DL, Dimitroglou A, Foey A, Davies SJ, Baker RTM, Bøgwald J, Castex M, Ringø E (2010a) The current status and future focus of probiotic and prebiotic applications for salmonids. Aquaculture 302(1-2):1–18. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.02.007
Merrifield DL, Güroy D, Güroy B, Emery MJ, Llewellyn CA, Skill S, Davies SJ (2010b) Assessment of Chlorogloeopsis as a novel microbial dietary supplement for red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 299(1–4):128–133. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.12.004
Miles A, Misra S, Irwin J (1938) The estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood. J Hyg-Cambridge 38(06):732–749
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
Nikoskelainen S, Ouwehand AC, Bylund G, Salminen S, Lilius E-M (2003) Immune enhancement in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by potential probiotic bacteria (Lactobacillus rhamnosus). Fish Shellfish Immun 15(5):443–452. doi:10.1016/S1050-4648(03)00023-8
NRC (2011) Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. The National Academies Press, Washington, p. 376
Pirarat N, Pinpimai K, Endo M, Katagiri T, Ponpornpisit A, Chansue N, Maita M (2011) Modulation of intestinal morphology and immunity in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Res Vet Sci 91(3):e92–e97. doi:10.1016/j.rvsc.2011.02.014
Ran C, Carrias A, Williams MA, Capps N, Dan BCT, Newton JC, Kloepper JW, Ooi EL, Browdy CL, Terhune JS, Liles MR (2012) Identification of Bacillus strains for biological control of catfish pathogens. PLoS One 7 (9):e45793. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045793
Rawls JF, Samuel BS, Gordon JI (2004) Gnotobiotic zebrafish reveal evolutionarily conserved responses to the gut microbiota. P Natl Acad Sci USA 101(13):4596–4601. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400706101
Ringø E, Zhou Z, He S, Olsen RE (2014) Effect of stress on intestinal microbiota of arctic charr, atlantic salmon, rainbow trout and atlantic cod: a review. Afr J Microbiol Res 8:609–618
Roeselers G, Mittge EK, Stephens WZ, Parichy DM, Cavanaugh CM, Guillemin K, Rawls JF (2011) Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. The ISME J 5(10):1595–1608
Romero J, Ringø E, Merrifield DL (2014) The gut microbiota of fish. In: Merrifield D & Ringø E (eds.) Aquaculture nutrition gut health, probiotics and prebiotics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 75-100
Round JL, Mazmanian SK (2009) The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9(5):313–323
Sahnouni F, Matallah-Boutiba A, Chemlal D, Boutiba Z (2012) Technological characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from intestinal microbiota of marine fish in the Oran Algeria coast. Afr J Microbiol Res 6(13):3125–3133
Standen BT, Rawling MD, Davies SJ, Castex M, Foey A, Gioacchini G, Carnevali O, Merrifield DL (2013) Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici modulates both localised intestinal- and peripheral-immunity in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immun 35(4):1097–1104. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2013.07.018
Sugita H, Deguchi Y, Sakata T, Ishida Y, Kadota H (1981) Measurement of total viable counts in the gastro-intestinal bacteria of freshwater fish. B Jap Soc of Sci Fish 47
Sun Y, Yang H, Ling Z, Chang J, Ye J (2009) Gut microbiota of fast and slow growing grouper Epinephelus coioides. Afr J Microbiol Res 3(11):713–720
van Kessel M, Dutilh B, Neveling K, Kwint M, Veltman J, Flik G, Jetten M, Klaren P, Op den Camp H (2011) Pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons to study the microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). AMB Expr 1(1):1–9. doi:10.1186/2191-0855-1-41
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267. doi:10.1128/aem.00062-07
Wintzingerode FV, Göbel UB, Stackebrandt E (1997) Determination of microbial diversity in environmental samples: pitfalls of PCR-based rRNA analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21(3):213–229. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.1997.tb00351.x
Wong S, Waldrop T, Summerfelt S, Davidson J, Barrows F, Kenney PB, Welch T, Wiens GD, Snekvik K, Rawls JF (2013) Aquacultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) possess a large core intestinal microbiota that is resistant to variation in diet and rearing density. Appl Environ Microb 79(16):4974–4984
Wu S-G, Tian J-Y, Gatesoupe F-J, Li W-X, Zou H, Yang B-J, Wang G-T (2013) Intestinal microbiota of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) and its origin as revealed by 454 pyrosequencing. World J Microb Biot 29(9):1585–1595. doi:10.1007/s11274-013-1322-4
Wu S, Wang G, Angert ER, Wang W, Li W, Zou H (2012) Composition, diversity, and origin of the bacterial community in grass carp intestine. PLoS One 7 (2):e30440. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030440
Zarkasi KZ, Abell GCJ, Taylor RS, Neuman C, Hatje E, Tamplin ML, Katouli M, Bowman JP (2014) Pyrosequencing-based characterization of gastrointestinal bacteria of atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) within a commercial mariculture system. J Appl Microbiol 117(1):18–27. doi:10.1111/jam.12514
Zhou Z-G, He S, Liu Y, Shi P, Huang G, Yao B (2009) The effects of dietary yeast culture or short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides on the intestinal autochthonous bacterial communities in juvenile hybrid tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus♀ × Oreochromis aureus♂. J World Aquacult Soc 40(4):450–459. doi:10.1111/j.1749-7345.2009.00272.x
Zhou Z, Yao B, Romero J, Waines P, Ringø E, Emery M, Liles MR, Merrifield DL (2014) Methododogical approaches used to assess fish gastrointestinal communities. In: Merrifield D & Ringø E (eds.) Aquaculture nutrition gut health, probiotics and prebiotics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 101-127
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out as part of a PhD studentship which was jointly funded by Plymouth University and Biomin Holding GmbH (Herzogenburg, Austria). The authors would like to thank Biomin Holding GmbH for providing the materials for this research as well as their input with regard to experimental design. Finally, the authors would like to thank Matthew Emery, Dr. Michele Kiernan and Glenn Harper for their assistance in the laboratory.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 89 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Standen, B...T., Rodiles, A., Peggs, D.L. et al. Modulation of the intestinal microbiota and morphology of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, following the application of a multi-species probiotic. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 8403–8417 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6702-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6702-2