Abstract
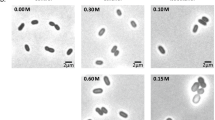
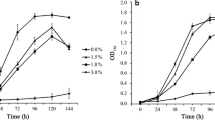
1-Butanol has been utilized widely in industry and can be produced or transformed by microbes. However, current knowledge about the mechanisms of 1-butanol tolerance in bacteria remains quite limited. Here, we applied untargeted metabolomics to study Bacillus subtilis cells under 1-butanol stress and identified 55 and 37 ions with significantly increased and decreased levels, respectively. Using accurate mass determination, tandem mass spectra, and synthetic standards, 86 % of these ions were characterized. The levels of phosphatidylethanolamine, diglucosyldiacylglycerol, and phosphatidylserine were found to be upregulated upon 1-butanol treatment, whereas those of diacylglycerol and lysyl phosphatidylglycerol were downregulated. Most lipids contained 15:0/15:0, 16:0/15:0, and 17:0/15:0 acyl chains, and all were mapped to membrane lipid biosynthetic pathways. Subsequent two-stage quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase PCR analyses of genes in the two principal membrane lipid biosynthesis pathways revealed elevated levels of ywiE transcripts in the presence of 1-butanol and reduced expression levels of cdsA, pgsA, mprF, clsA, and yfnI transcripts. Thus, the gene transcript levels showed agreement with the metabolomics data. Lastly, the cell morphology was investigated by scanning electron microscopy, which indicated that cells became almost twofold longer after 1.4 % (v/v) 1-butanol stress for 12 h. Overall, the studies uncovered changes in the composition of glycerolipids and phospholipids in B. subtilis under 1-butanol stress, emphasizing the power of untargeted metabolomics in the discovery of new biological insights.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aono R, Kobayashi H (1997) Cell surface properties of organic solvent-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(9):3637–3642
Beaven MJ, Charpentier C, Rose AH (1982) Production and tolerance of ethanol in relation to phospholipid fatty-acyl composition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCYC 431. J Gen Microbiol 128(7):1447–1455
Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini AM, Alloni G, Azevedo V, Bertero MG, Bessieres P, Bolotin A, Borchert S, Borriss R, Boursier L, Brans A, Braun M, Brignell SC, Bron S, Brouillet S, Bruschi CV, Caldwell B, Capuano V, Carter NM, Choi SK, Codani JJ, Connerton IF, Cummings NJ, Daniel RA, Denizot F, Devine KM, Dusterhoft A, Ehrlich SD, Emmerson PT, Entian KD, Errington J, Fabret C, Ferrari E, Foulger D, Fritz C, Fujita M, Fujita Y, Fuma S, Galizzi A, Galleron N, Ghim SY, Glaser P, Goffeau A, Golightly EJ, Grandi G, Guiseppi G, Guy BJ, Haga K, Haiech J, Harwood CR, Henaut A, Hilbert H, Holsappel S, Hosono S, Hullo MF, Itaya M, Jones L, Joris B, Karamata D, Kasahara Y, Klaerr-Blanchard M, Klein C, Kobayashi Y, Koetter P, Koningstein G, Krogh S, Kumano M, Kurita K, Lapidus A, Lardinois S, Lauber J, Lazarevic V, Lee SM, Levine A, Liu H, Masuda S, Mauel C, Medigue C, Medina N, Mellado RP, Mizuno M, Moestl D, Nakai S, Noback M, Noone D, O’Reilly M, Ogawa K, Ogiwara A, Oudega B, Park SH, Parro V, Pohl TM, Portetelle D, Porwollik S, Prescott AM, Presecan E, Pujic P, Purnelle B, Rapoport G, Rey M, Reynolds S, Rieger M, Rivolta C, Rocha E, Roche B, Rose M, Sadaie Y, Sato T, Scanlan E, Schleich S, Schroeter R, Scoffone F, Sekiguchi J, Sekowska A, Seror SJ, Serror P, Shin BS, Soldo B, Sorokin A, Tacconi E, Takagi T, Takahashi H, Takemaru K, Takeuchi M, Tamakoshi A, Tanaka T, Terpstra P, Tognoni A, Tosato V, Uchiyama S, Vandenbol M, Vannier F, Vassarotti A, Viari A, Wambutt R, Wedler E, Wedler H, Weitzenegger T, Winters P, Wipat A, Yamamoto H, Yamane K, Yasumoto K, Yata K, Yoshida K, Yoshikawa HF, Zumstein E, Yoshikawa H, Danchin A (1997) The complete genome sequence of the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature 390(6657):249–256
Boch J, Kempf B, Bremer E (1994) Osmoregulation in Bacillus subtilis: synthesis of the osmoprotectant glycine betaine from exogenously provided choline. J Bacteriol 176(17):5364–5371
Bohin JP, Rigomier D, Schaeffer P (1976) Ethanol sensitivity of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis: a new tool for the analysis of the sporulation process. J Bacteriol 127(2):934–940
Borden JR, Papoutsakis ET (2007) Dynamics of genomic-library enrichment and identification of solvent tolerance genes for Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(9):3061–3068. doi:10.1128/AEM.02296-06
Bustard MT, Whiting S, Cowan DA, Wright PC (2002) Biodegradation of high-concentration isopropanol by a solvent-tolerant thermophile, Bacillus pallidus. Extremophiles 6(4):319–323. doi:10.1007/s00792-001-0260-5
Clejan S, Krulwich TA, Mondrus KR, Seto-Young D (1986) Membrane lipid composition of obligately and facultatively alkalophilic strains of Bacillus spp. J Bacteriol 168(1):334–340
Connor MR, Liao JC (2009) Microbial production of advanced transportation fuels in non-natural hosts. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20(3):307–315. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2009.04.002
Durre P (2011) Fermentative production of butanol—the academic perspective. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(3):331–336. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2011.04.010
Fischer CR, Klein-Marcuschamer D, Stephanopoulos G (2008) Selection and optimization of microbial hosts for biofuels production. Metab Eng 10(6):295–304. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2008.06.009
Fortman JL, Chhabra S, Mukhopadhyay A, Chou H, Lee TS, Steen E, Keasling JD (2008) Biofuel alternatives to ethanol: pumping the microbial well. Trends in Biotechnology 26(7):375–381. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2008.03.008
Gidden J, Denson J, Liyanage R, Ivey DM, Lay JO (2009) Lipid compositions in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis during growth as determined by MALDI-TOF and TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom 283(1–3):178–184. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2009.03.005
Green EM (2011) Fermentative production of butanol—the industrial perspective. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(3):337–343. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2011.02.004
Grundling A, Schneewind O (2007) Synthesis of glycerol phosphate lipoteichoic acid in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(20):8478–8483. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701821104
Ingram LO (1976) Adaptation of membrane lipids to alcohols. J Bacteriol 125(2):670–678
Jervis AJ, Thackray PD, Houston CW, Horsburgh MJ, Moir A (2007) SigM-responsive genes of Bacillus subtilis and their promoters. J Bacteriol 189(12):4534–4538. doi:10.1128/Jb.00130-07
Kabelitz N, Santos PM, Heipieper HJ (2003) Effect of aliphatic alcohols on growth and degree of saturation of membrane lipids in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 220(2):223–227
Kataoka N, Tajima T, Kato J, Rachadech W, Vangnai AS (2011) Development of butanol-tolerant Bacillus subtilis strain GRSW2-B1 as a potential bioproduction host. AMB Express 1(1):10. doi:10.1186/2191-0855-1-10
Kilelee E, Pokorny A, Yeaman MR, Bayer AS (2010) Lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol attenuates membrane perturbation rather than surface association of the cationic antimicrobial peptide 6W-RP-1 in a model membrane system: implications for daptomycin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(10):4476–4479. doi:10.1128/AAC.00191-10
Kongpol A, Kato J, Vangnai AS (2008) Isolation and characterization of Deinococcus geothermalis T27, a slightly thermophilic and organic solvent-tolerant bacterium able to survive in the presence of high concentrations of ethyl acetate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 286(2):227–235. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01273.x
Lee AG (2004) How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1666(1–2):62–87. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.05.012
Lepage C, Fayolle F, Hermann M, Vandecasteele JP (1987) Changes in membrane lipid composition of Clostridium acetobutylicum during acetone-butanol fermentation: effects of solvents, growth temperature and pH. J Gen Microbiol 133(1):103–110
Liu S, Qureshi N (2009) How microbes tolerate ethanol and butanol. New Biotechnology 26(3–4):117–121. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2009.06.984
Lopez CS, Alice AF, Heras H, Rivas EA, Sanchez-Rivas C (2006) Role of anionic phospholipids in the adaptation of Bacillus subtilis to high salinity. Microbiology 152(Pt 3):605–616. doi:10.1099/mic.0.28345-0
Matias VR, Beveridge TJ (2008) Lipoteichoic acid is a major component of the Bacillus subtilis periplasm. J Bacteriol 190(22):7414–7418. doi:10.1128/JB.00581-08
Matsumoto M, de Bont JA, Isken S (2002) Isolation and characterization of the solvent-tolerant Bacillus cereus strain R1. J Biosci Bioeng 94(1):45–51
Matsuoka S, Hashimoto M, Kamiya Y, Miyazawa T, Ishikawa K, Hara H, Matsumoto K (2011) The Bacillus subtilis essential gene dgkB is dispensable in mutants with defective lipoteichoic acid synthesis. Genes Genet Syst 86(6):365–376
Nakano MM, Dailly YP, Zuber P, Clark DP (1997) Characterization of anaerobic fermentative growth of Bacillus subtilis: identification of fermentation end products and genes required for growth. J Bacteriol 179(21):6749–6755
Neumann G, Veeranagouda Y, Karegoudar TB, Sahin O, Mausezahl I, Kabelitz N, Kappelmeyer U, Heipieper HJ (2005) Cells of Pseudomonas putida and Enterobacter sp. adapt to toxic organic compounds by increasing their size. Extremophiles 9(2):163–168. doi:10.1007/s00792-005-0431-x
Ni Y, Sun Z (2009) Recent progress on industrial fermentative production of acetone-butanol-ethanol by Clostridium acetobutylicum in China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83(3):415–423. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2003-y
Nicolaou SA, Gaida SM, Papoutsakis ET (2010) A comparative view of metabolite and substrate stress and tolerance in microbial bioprocessing: from biofuels and chemicals, to biocatalysis and bioremediation. Metab Eng 12(4):307–331. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2010.03.004
Nielsen LE, Kadavy DR, Rajagopal S, Drijber R, Nickerson KW (2005) Survey of extreme solvent tolerance in Gram-positive cocci: membrane fatty acid changes in Staphylococcus haemolyticus grown in toluene. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(9):5171–5176. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.9.5171-5176.2005
Petersohn A, Brigulla M, Haas S, Hoheisel JD, Volker U, Hecker M (2001) Global analysis of the general stress response of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 183(19):5617–5631. doi:10.1128/JB.183.19.5617-5631.2001
Rigomier D, Bohin JP, Lubochinsky B (1980) Effects of ethanol and methanol on lipid metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol 121(1):139–149
Saghatelian A, Trauger SA, Want EJ, Hawkins EG, Siuzdak G, Cravatt BF (2004) Assignment of endogenous substrates to enzymes by global metabolite profiling. Biochemistry 43(45):14332–14339
Salzberg LI, Helmann JD (2008) Phenotypic and transcriptomic characterization of Bacillus subtilis mutants with grossly altered membrane composition. J Bacteriol 190(23):7797–7807. doi:10.1128/JB.00720-08
Schirner K, Marles-Wright J, Lewis RJ, Errington J (2009) Distinct and essential morphogenic functions for wall- and lipo-teichoic acids in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J 28(7):830–842. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.25
Smith CA, O’Maille G, Want EJ, Qin C, Trauger SA, Brandon TR, Custodio DE, Abagyan R, Siuzdak G (2005) METLIN: a metabolite mass spectral database. Ther Drug Monit 27(6):747–751
Smith CA, Want EJ, O’Maille G, Abagyan R, Siuzdak G (2006) XCMS: processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal Chem 78(3):779–787. doi:10.1021/ac051437y
Spizizen J (1958) Transformation of biochemically deficient strains of Bacillus subtilis by deoxyribonucleate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 44(10):1072–1078
Thackray PD, Moir A (2003) SigM, an extracytoplasmic function sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis, is activated in response to cell wall antibiotics, ethanol, heat, acid, and superoxide stress. J Bacteriol 185(12):3491–3498. doi:10.1128/Jb.185.12.3491-3498.2003
Torres S, Pandey A, Castro GR (2011) Organic solvent adaptation of Gram positive bacteria: applications and biotechnological potentials. Biotechnol Adv 29(4):442–452. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.04.002
Vinayavekhin N, Saghatelian A (2009) Regulation of alkyl-dihydrothiazole-carboxylates (ATCs) by iron and the pyochelin gene cluster in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Chem Biol 4(8):617–623. doi:10.1021/cb900075n
Vinayavekhin N, Saghatelian A (2010) Untargeted metabolomics. Current protocols in molecular biology/edited by Frederick M Ausubel [et al] Chapter 30:Unit 30 1 1–24. doi:10.1002/0471142727.mb3001s90
Vinayavekhin N, Saghatelian A (2011) Discovery of a protein-metabolite interaction between unsaturated fatty acids and the nuclear receptor Nur77 using a metabolomics approach. J Am Chem Soc 133(43):17168–17171. doi:10.1021/ja208199h
Weber FJ, de Bont JA (1996) Adaptation mechanisms of microorganisms to the toxic effects of organic solvents on membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1286(3):225–245
Wormann ME, Corrigan RM, Simpson PJ, Matthews SJ, Grundling A (2011) Enzymatic activities and functional interdependencies of Bacillus subtilis lipoteichoic acid synthesis enzymes. Mol Microbiol 79(3):566–583. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07472.x
Zingaro KA, Papoutsakis ET (2012) Toward a semisynthetic stress response system to engineer microbial solvent tolerance. MBio 3(5). doi:10.1128/mBio.00308-12
Acknowledgments
We thank Sitthiporn Associates Co., Ltd. for providing us with the Waters Alliance e2695 high performance LC instrument; the Food Research and Testing Laboratory, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University for access to the nitrogen concentrator; the Thai Government Stimulus Package 2 (TKK2555) for the financial support to acquire the Bruker MicrOTOF Q-II mass spectrometer; Poompat Aroonsri for his initial help with the project; and Dr. Robert Douglas John Butcher (Publication Counseling Unit, Chulalongkorn University) for his thorough checking of English usage and constructive comments in preparing this manuscript. This work was supported by the Thailand Research Fund (TRG5780194) and the Ratchadapisek Somphot Fund of Chulalongkorn University. The opinions expressed in this paper are the sole responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Thailand Research Fund or Chulalongkorn University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 3995 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinayavekhin, N., Mahipant, G., Vangnai, A.S. et al. Untargeted metabolomics analysis revealed changes in the composition of glycerolipids and phospholipids in Bacillus subtilis under 1-butanol stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 5971–5983 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6692-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6692-0